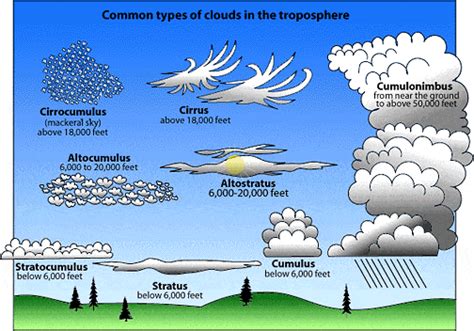
The cumulus cloud, a staple of fair weather, has been a subject of fascination for many due to its unique characteristics and behaviors. One of the most interesting aspects of cumulus clouds is their naming conventions, which provide insight into their nature and the history of cloud classification. Here are 5 cumulus name facts that highlight the intricacies and evolution of cloud nomenclature.
Key Points
- Cumulus clouds are named based on their shape and appearance, reflecting their puffy, white nature.
- The term "cumulus" comes from the Latin word for heap or pile, describing the cloud's cumiform appearance.
- Cumulus clouds can be further classified into subtypes, such as cumulus humilis and cumulus congestus, based on their size and vertical development.
- The naming of cumulus clouds has evolved over time, with early classifications focusing on basic forms and modern classifications incorporating more detailed characteristics.
- The International Cloud Atlas, published by the World Meteorological Organization, serves as the authoritative guide for cloud classification and naming, including cumulus clouds.
Origins of Cumulus Cloud Names
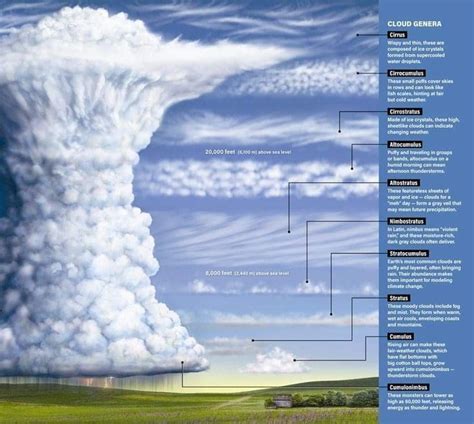
The naming of cumulus clouds originates from the work of Luke Howard, an English chemist and amateur meteorologist, who in 1802 proposed a system of cloud classification that included cumulus, stratus, and cirrus clouds. The term “cumulus” itself is derived from the Latin word “cumulus,” meaning heap or pile, which aptly describes the cloud’s appearance as a series of puffy, white heaps in the sky. This foundational work by Howard laid the basis for modern cloud classification systems, including the detailed naming conventions used today for cumulus clouds.
Classification and Subtypes
Cumulus clouds are not just limited to a single type; they can be classified into several subtypes based on their size, shape, and vertical development. Two of the main subtypes are cumulus humilis and cumulus congestus. Cumulus humilis, also known as fair-weather cumulus, is characterized by its small to moderate size and generally flat bases with rounded towers. On the other hand, cumulus congestus, often referred to as towering cumulus, is larger and can develop into towering vertical clouds that may eventually become thunderstorms. These classifications are crucial for understanding the potential development and impact of cumulus clouds on weather patterns.
| Cumulus Subtype | Description |
|---|---|
| Cumulus Humilis | Small, fair-weather clouds with flat bases and rounded tops. |
| Cumulus Congestus | Larger, towering clouds that can develop into thunderstorms. |
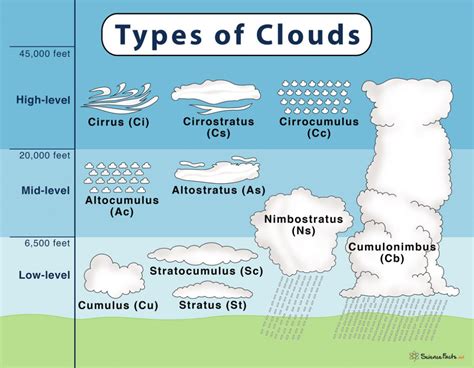
Evolution of Cloud Nomenclature

The naming and classification of cumulus clouds have evolved significantly since Luke Howard’s initial proposal. Early cloud classifications were based on basic forms and appearances, but as our understanding of meteorology and the physics of clouds has deepened, so too has the complexity and detail of cloud classification systems. The International Cloud Atlas, first published in 1896 and regularly updated by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), is the authoritative guide for cloud classification and naming, including detailed descriptions and images of cumulus clouds and their various subtypes. This evolution reflects our growing knowledge of clouds and their role in the Earth’s climate system.
Importance of Standardized Nomenclature
A standardized system of cloud classification and naming is crucial for effective communication among meteorologists, researchers, and other stakeholders. It ensures that when discussing cumulus clouds or any other cloud type, everyone refers to the same characteristics and features, facilitating the exchange of information and the advancement of knowledge in the field of meteorology. Furthermore, standardized nomenclature is essential for education and training, providing a clear and consistent framework for learning about clouds and their importance in the Earth’s atmosphere.
What is the origin of the term "cumulus" in cloud classification?
+The term "cumulus" comes from the Latin word for heap or pile, describing the cloud's cumiform appearance as a series of puffy, white heaps in the sky.
How are cumulus clouds classified, and what are their main subtypes?
+Cumulus clouds are classified based on their size, shape, and vertical development. The main subtypes include cumulus humilis (fair-weather cumulus) and cumulus congestus (towering cumulus), each with distinct characteristics and potential weather implications.
Why is standardized nomenclature important in cloud classification?
+Standardized nomenclature ensures that cloud classifications are consistent and universally understood, facilitating communication, research, and education in the field of meteorology.
In conclusion, the naming conventions of cumulus clouds reflect a deep understanding of their nature and behaviors, from their puffy, white appearance to their potential for development into more complex weather systems. Through the work of pioneers like Luke Howard and the ongoing updates to the International Cloud Atlas, our ability to classify and communicate about cumulus clouds has evolved, contributing to advancements in meteorology and our broader understanding of the Earth’s atmosphere.