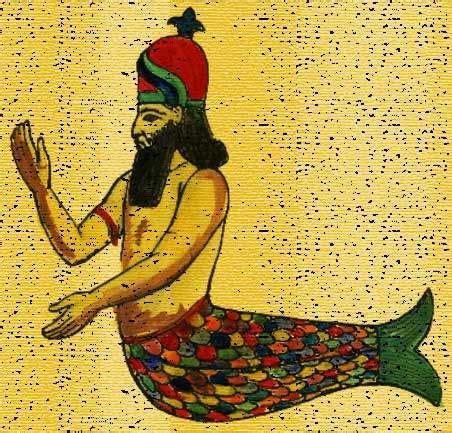
The Bible makes mention of Dagon, a deity worshipped by the ancient Philistines, in several passages. Dagon is first introduced in the book of Judges, where it is written that the Philistines, after capturing the Ark of the Covenant from the Israelites, brought it to the temple of Dagon in Ashdod and placed it beside the statue of their god (1 Samuel 5:1-2). The next morning, the Philistines found the statue of Dagon fallen on its face before the Ark, and they set it back up. However, the following morning, they found the statue of Dagon not only fallen again but also with its head and hands broken off, lying on the threshold (1 Samuel 5:3-4). This event is often seen as a demonstration of the power of the God of Israel over the pagan deities of the surrounding nations.
Another reference to Dagon can be found in 1 Chronicles 10:10, where it is mentioned that the Philistines put Saul's armor in the temple of Dagon, after they had killed him in battle. This act was a way for the Philistines to symbolize their victory over the king of Israel and to dedicate their spoils to their god.
The Significance of Dagon in Biblical Context
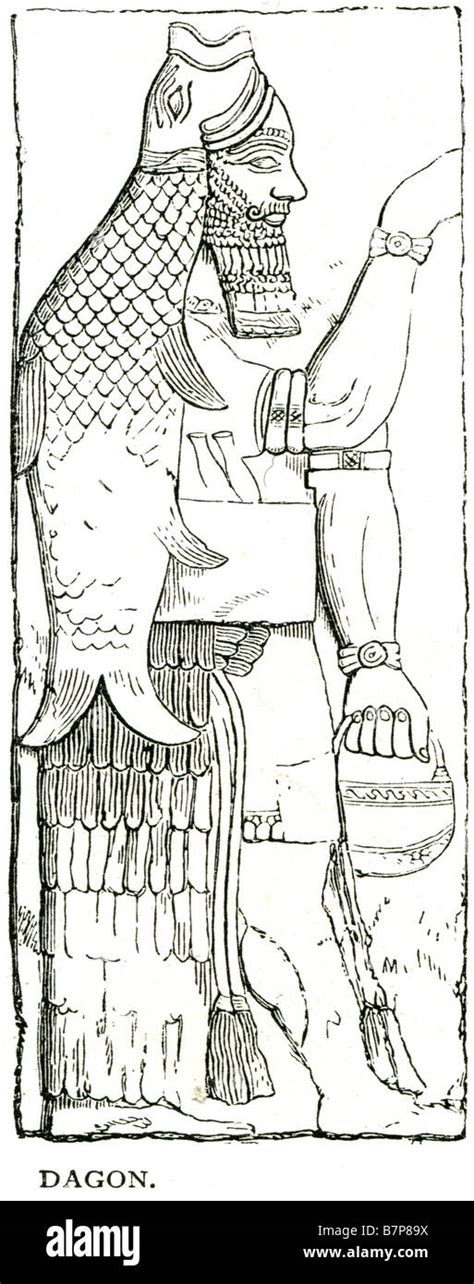
Dagon is considered to be an important deity in the ancient Near Eastern pantheon, especially among the Philistines and other maritime peoples of the region. The worship of Dagon is believed to have originated in Mesopotamia, where he was revered as a god of fertility and agriculture. However, among the Philistines, Dagon’s role may have been more closely associated with the sea and fishing, given their maritime culture and economy.
The biblical accounts of Dagon serve to illustrate the conflict between the monotheistic worship of the God of Israel and the polytheistic practices of the surrounding nations. The stories of the Ark of the Covenant in the temple of Dagon and the subsequent humiliation of the Philistine deity underscore the theme of the superiority of the God of Israel over all other gods, a central message throughout the Hebrew Bible.
Historical and Archaeological Insights into Dagon Worship
Archaeological findings have provided insights into the worship practices and beliefs surrounding Dagon. Excavations in the region of Philistia have uncovered temples and artifacts that attest to the significance of Dagon in Philistine religion. The discovery of inscriptions and pottery with symbols associated with Dagon further supports the biblical accounts of his importance among the Philistines.
| Archaeological Find | Location | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Inscriptions mentioning Dagon | Ashdod, Gaza | Confirm the worship of Dagon among the Philistines |
| Dagon temples | Ashdod, Ekron | Indicate the religious significance of Dagon in Philistine cities |
| Philistine pottery with Dagon symbols | Various Philistine sites | Suggest the widespread nature of Dagon worship |

Key Points
- Dagon was a significant deity in the Philistine pantheon, possibly associated with fertility, agriculture, and the sea.
- The biblical accounts of Dagon, particularly in 1 Samuel, demonstrate the power of the God of Israel over pagan deities.
- Archaeological findings, including inscriptions and temple remains, confirm the importance of Dagon in Philistine religion and culture.
- The worship of Dagon reflects the broader context of religious diversity and conflict in the ancient Near East.
- The stories about Dagon in the Bible serve to emphasize the monotheistic message of the Hebrew scriptures.
The study of Dagon and his role in the biblical narrative offers a fascinating glimpse into the religious and cultural dynamics of the ancient world. Through the combination of biblical accounts, historical research, and archaeological discoveries, a nuanced understanding of Dagon's significance can be developed, shedding light on the complex interactions between different religious traditions in the region.
Comparative Analysis with Other Ancient Deities

A comparative analysis of Dagon with other ancient deities of the Near East, such as Baal and Marduk, reveals similarities in their roles as gods of fertility and their association with natural phenomena. However, the specific characteristics and worship practices of Dagon, as inferred from biblical and archaeological sources, suggest a distinct place within the pantheon of ancient Near Eastern deities.
The worship of Dagon also reflects the broader trends of religious syncretism and the exchange of cultural practices that were common in the ancient world. The adoption and adaptation of deities and religious rituals across different cultures highlight the dynamic nature of ancient religious beliefs and practices.
Implications for Understanding Biblical Religion
The study of Dagon and his place in the biblical narrative has significant implications for our understanding of biblical religion and its context within the ancient Near East. It underscores the importance of considering the historical and cultural background of the biblical texts, as well as the interactions between different religious groups in the region.
Furthermore, the biblical accounts of Dagon serve as a reminder of the polemical nature of much of the Hebrew Bible, where the superiority of the God of Israel is often demonstrated through the humiliation of other gods. This theme is central to the biblical narrative and informs much of its theology and worldview.
What was the significance of Dagon in Philistine religion?
+Dagon was a significant deity in the Philistine pantheon, associated with fertility, agriculture, and possibly the sea, reflecting the importance of these aspects in Philistine culture and economy.
How does the biblical account of Dagon relate to the broader biblical theme of monotheism?
+The stories about Dagon in the Bible serve to demonstrate the power and superiority of the God of Israel over pagan deities, reinforcing the monotheistic message of the Hebrew scriptures.
What do archaeological findings reveal about the worship of Dagon?
+Archaeological findings, including inscriptions and temple remains, confirm the importance of Dagon in Philistine religion and culture, providing tangible evidence of his worship and the practices associated with it.



