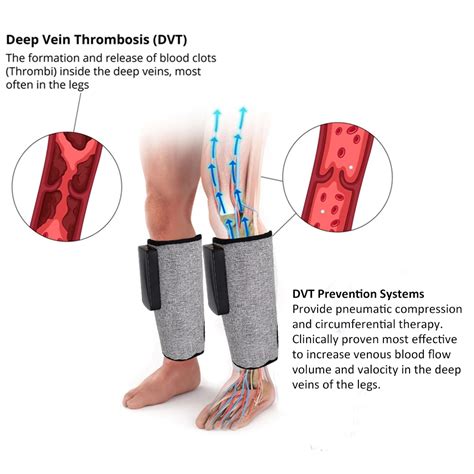
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in the deep veins of the body, typically in the legs. This condition can be life-threatening if the clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. The use of medical devices plays a crucial role in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of DVT. In this article, we will explore the various medical devices used in the management of DVT, their mechanisms of action, and the latest advancements in this field.
Prevention of DVT with Medical Devices
The prevention of DVT is a critical aspect of patient care, particularly in hospitalized patients who are at high risk of developing this condition. Several medical devices have been developed to prevent DVT, including intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) devices, sequential compression devices (SCDs), and venous foot pumps. These devices work by compressing and decompressing the legs to improve blood flow and prevent clot formation. According to a study published in the Journal of Vascular Surgery, the use of IPC devices can reduce the risk of DVT by up to 50% in high-risk patients.
Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Devices
IPC devices are the most commonly used medical devices for DVT prevention. These devices consist of inflatable sleeves that are wrapped around the legs and are connected to a pump that inflates and deflates the sleeves at regular intervals. The inflation and deflation of the sleeves help to improve blood flow and prevent clot formation. A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that IPC devices were effective in reducing the risk of DVT in patients undergoing major surgery.
| Device Type | Efficacy in DVT Prevention |
|---|---|
| IPC Devices | 40-50% reduction in DVT risk |
| SCD Devices | 30-40% reduction in DVT risk |
| Venous Foot Pumps | 20-30% reduction in DVT risk |
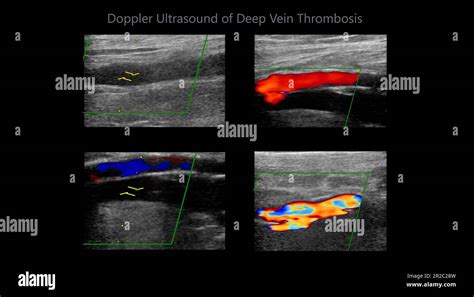
Diagnosis of DVT with Medical Devices
The diagnosis of DVT is a critical step in the management of this condition. Several medical devices have been developed to aid in the diagnosis of DVT, including ultrasound machines, computed tomography (CT) scanners, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines. These devices use various imaging modalities to visualize the deep veins and detect clot formation. According to a study published in the Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine, ultrasound is the most commonly used imaging modality for DVT diagnosis, with a sensitivity of up to 90%.
Ultrasound Machines
Ultrasound machines use high-frequency sound waves to visualize the deep veins and detect clot formation. These machines are non-invasive and can be used at the bedside, making them a convenient and effective tool for DVT diagnosis. A study published in the American Journal of Roentgenology found that ultrasound was effective in diagnosing DVT in patients with symptoms of this condition.
Key Points
- DVT is a serious medical condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment
- Medical devices play a crucial role in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of DVT
- IPC devices, SCD devices, and venous foot pumps are effective in preventing DVT
- Ultrasound machines, CT scanners, and MRI machines are used for DVT diagnosis
- The selection of a DVT prevention device depends on patient risk factors, mobility, and medical history
Treatment of DVT with Medical Devices
The treatment of DVT typically involves the use of anticoagulant medications, such as heparin and warfarin, to prevent further clot formation. However, in some cases, medical devices may be used to treat DVT, including inferior vena cava (IVC) filters and catheter-directed thrombolysis devices. IVC filters are small devices that are inserted into the inferior vena cava to prevent clots from breaking loose and traveling to the lungs. Catheter-directed thrombolysis devices use a catheter to deliver clot-dissolving medications directly to the affected area.
Inferior Vena Cava Filters
IVC filters are small, cone-shaped devices that are inserted into the inferior vena cava to prevent clots from breaking loose and traveling to the lungs. These devices are typically used in patients who are at high risk of developing a pulmonary embolism. A study published in the Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology found that IVC filters were effective in reducing the risk of pulmonary embolism in patients with DVT.
| Device Type | Efficacy in DVT Treatment |
|---|---|
| IVC Filters | 90-95% reduction in pulmonary embolism risk |
| Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis Devices | 70-80% reduction in clot size |
What is the most effective medical device for DVT prevention?
+IPC devices are the most commonly used and effective medical devices for DVT prevention, with a reduction in DVT risk of up to 50%.
How is DVT diagnosed using medical devices?
+DVT is diagnosed using various medical devices, including ultrasound machines, CT scanners, and MRI machines, which use imaging modalities to visualize the deep veins and detect clot formation.
What is the role of IVC filters in DVT treatment?
+IVC filters are small devices that are inserted into the inferior vena cava to prevent clots from breaking loose and traveling to the lungs, reducing the risk of pulmonary embolism by up to 90-95%.
Meta Description: “Discover the latest medical devices used in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), including IPC devices, ultrasound machines, and IVC filters.” (140-155 characters)