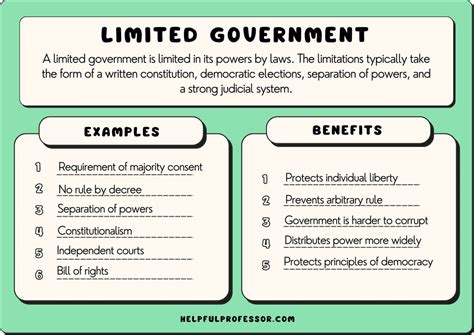
The concept of limited government has been a cornerstone of political philosophy and democratic governance for centuries. At its core, limited government refers to a system where the power of the government is restricted by a constitution, laws, or other mechanisms to prevent abuse of authority and protect individual rights and freedoms. This fundamental principle is designed to ensure that the government remains accountable to the people and does not overstep its boundaries, thereby preserving the liberty and autonomy of citizens.
Historically, the idea of limited government emerged as a response to the excesses of absolute monarchies and totalitarian regimes, where rulers wielded unchecked power over their subjects. The notion of limiting government power gained traction during the Enlightenment, with thinkers such as John Locke, Montesquieu, and James Madison advocating for the separation of powers, checks and balances, and the protection of individual rights. These ideas were later enshrined in documents such as the United States Constitution and the Bill of Rights, which have served as models for democratic governance around the world.
Key Points
- The concept of limited government is rooted in the idea of restricting government power to prevent abuse of authority and protect individual rights and freedoms.
- The principle of limited government is designed to ensure accountability and prevent the concentration of power in the hands of a few individuals or groups.
- The separation of powers, checks and balances, and the protection of individual rights are key mechanisms for limiting government power.
- Historical examples of limited government include the United States, the United Kingdom, and other democracies that have implemented constitutional safeguards and institutional checks on power.
- Challenges to limited government include the tendency towards centralized power, the erosion of individual rights, and the influence of special interest groups.
Principles of Limited Government
The principles of limited government are based on the idea that power should be distributed among different branches of government, and that individual rights and freedoms should be protected from government overreach. Some of the key principles of limited government include:
Separation of Powers
The separation of powers refers to the division of power among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government. This division is designed to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful and to ensure that each branch has checks and balances on the others. For example, in the United States, the legislative branch (Congress) has the power to make laws, while the executive branch (the President) has the power to enforce laws, and the judicial branch (the Supreme Court) has the power to interpret laws.
Checks and Balances
Checks and balances refer to the mechanisms that prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful. For example, Congress has the power to impeach the President, while the President has the power to veto laws passed by Congress. The Supreme Court, in turn, has the power to declare laws passed by Congress or actions taken by the President as unconstitutional.
Protection of Individual Rights
The protection of individual rights is a fundamental principle of limited government. This includes the right to free speech, the right to assemble, the right to bear arms, and other rights that are essential to individual liberty and autonomy. These rights are protected by constitutional safeguards, such as the Bill of Rights in the United States, and are designed to prevent government overreach and abuse of power.
| Principle | Example |
|---|---|
| Separation of Powers | Legislative, Executive, and Judicial branches in the United States |
| Checks and Balances | Congressional impeachment of the President, Presidential veto power |
| Protection of Individual Rights | First Amendment protections for free speech and assembly |

Benefits of Limited Government

The benefits of limited government are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages include:
Promoting Individual Liberty and Autonomy
Limited government promotes individual liberty and autonomy by protecting individual rights and freedoms from government overreach. This allows citizens to pursue their own goals and interests without undue interference from the state.
Encouraging Economic Growth and Prosperity
Limited government can also encourage economic growth and prosperity by reducing the burden of government regulation and taxation. This allows businesses and individuals to innovate and invest, creating jobs and wealth.
Preventing Government Abuse of Power
Limited government prevents government abuse of power by providing checks and balances on the exercise of authority. This helps to prevent the concentration of power in the hands of a few individuals or groups, and ensures that government remains accountable to the people.
Challenges to Limited Government
Despite its many benefits, limited government faces a number of challenges in practice. Some of the most significant challenges include:
Centralization of Power
The centralization of power is a major challenge to limited government, as it can lead to the concentration of authority in the hands of a few individuals or groups. This can erode individual rights and freedoms, and undermine the system of checks and balances.
Erosion of Individual Rights
The erosion of individual rights is another challenge to limited government, as it can undermine the protections that are in place to prevent government overreach. This can occur through the influence of special interest groups, or through the gradual expansion of government power over time.
Influence of Special Interest Groups
The influence of special interest groups is a significant challenge to limited government, as it can lead to the advancement of narrow interests at the expense of the general public. This can undermine the system of checks and balances, and lead to the concentration of power in the hands of a few individuals or groups.
What is the main purpose of limited government?
+The main purpose of limited government is to restrict government power and prevent abuse of authority, while protecting individual rights and freedoms.
How does the separation of powers contribute to limited government?
+The separation of powers contributes to limited government by dividing power among different branches of government, preventing any one branch from becoming too powerful.
What are some challenges to limited government?
+Challenges to limited government include the centralization of power, the erosion of individual rights, and the influence of special interest groups.



