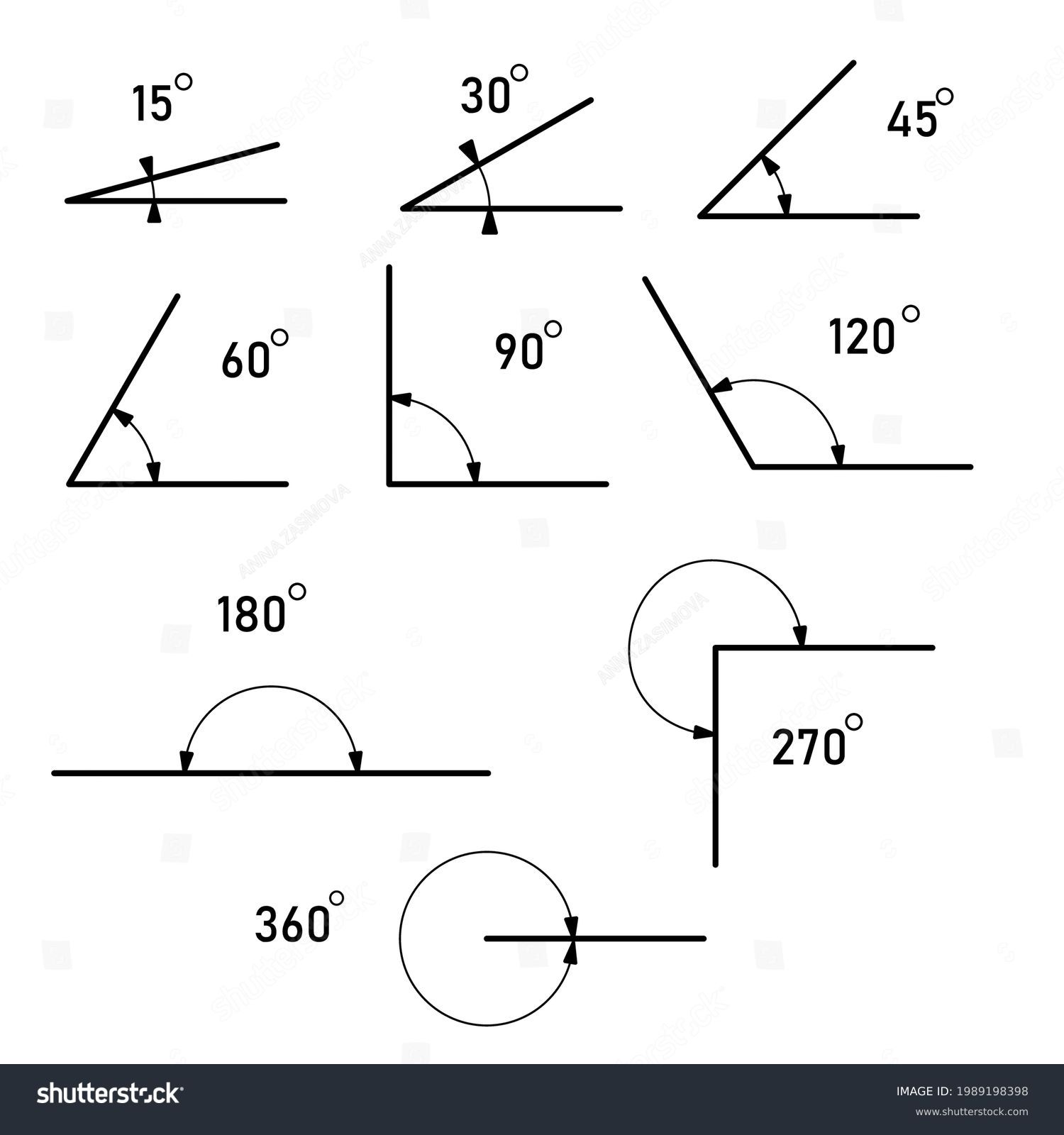
The concept of triangle degrees is a fundamental aspect of geometry, and understanding how they work is crucial for various applications in mathematics, engineering, and architecture. Triangle degrees refer to the measurement of angles within a triangle, which can be used to determine the shape and size of the triangle. In this article, we will explore 5 ways triangle degrees work, including their definition, properties, and applications.
Key Points
- Triangle degrees are measured in units of degrees, with 180 degrees being the total sum of angles in a triangle.
- The properties of triangle degrees include the angle sum property, the exterior angle theorem, and the interior angle theorem.
- Triangle degrees have various applications in geometry, trigonometry, and real-world problems.
- The measurement of triangle degrees can be used to determine the type of triangle, including acute, right, and obtuse triangles.
- Understanding triangle degrees is essential for solving problems in mathematics, physics, and engineering.
Definition and Properties of Triangle Degrees
Triangle degrees are defined as the measurement of angles within a triangle, which can be expressed in units of degrees. The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees, which is known as the angle sum property. This property can be used to determine the measure of the third angle in a triangle, given the measures of the other two angles. For example, if the measures of two angles in a triangle are 60 degrees and 80 degrees, the measure of the third angle can be calculated as 180 - (60 + 80) = 40 degrees.
Exterior Angle Theorem
The exterior angle theorem states that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two remote interior angles. This theorem can be used to determine the measure of an exterior angle, given the measures of the interior angles. For instance, if the measures of two interior angles are 60 degrees and 80 degrees, the measure of the exterior angle can be calculated as 60 + 80 = 140 degrees.
Interior Angle Theorem
The interior angle theorem states that the measure of an interior angle of a triangle is equal to half the measure of the central angle that subtends the same arc. This theorem can be used to determine the measure of an interior angle, given the measure of the central angle. For example, if the measure of the central angle is 120 degrees, the measure of the interior angle can be calculated as 120 / 2 = 60 degrees.
| Type of Triangle | Measure of Angles |
|---|---|
| Acute Triangle | All angles are less than 90 degrees |
| Right Triangle | One angle is equal to 90 degrees |
| Obtuse Triangle | One angle is greater than 90 degrees |

Applications of Triangle Degrees
Triangle degrees have various applications in geometry, trigonometry, and real-world problems. For instance, the measurement of triangle degrees can be used to determine the type of triangle, including acute, right, and obtuse triangles. Additionally, triangle degrees are used in trigonometry to calculate the lengths of sides and the measures of angles in triangles. In real-world problems, triangle degrees are used in architecture, engineering, and physics to design and analyze structures, such as bridges, buildings, and mechanical systems.
Real-World Examples
Triangle degrees are used in various real-world applications, including architecture, engineering, and physics. For example, the design of a bridge requires the calculation of triangle degrees to ensure stability and structural integrity. Similarly, the design of a building requires the calculation of triangle degrees to determine the shape and size of the structure. In physics, triangle degrees are used to calculate the trajectories of projectiles and the forces acting on objects.
What is the sum of the interior angles of a triangle?
+The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees.
What is the exterior angle theorem?
+The exterior angle theorem states that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two remote interior angles.
What is the interior angle theorem?
+The interior angle theorem states that the measure of an interior angle of a triangle is equal to half the measure of the central angle that subtends the same arc.
In conclusion, triangle degrees are a fundamental concept in geometry, and understanding how they work is essential for various applications in mathematics, engineering, and architecture. By recognizing the properties and applications of triangle degrees, individuals can develop a deeper understanding of geometric concepts and apply them to real-world problems. Whether it’s designing a bridge, building, or mechanical system, triangle degrees play a critical role in ensuring stability, structural integrity, and optimal performance.