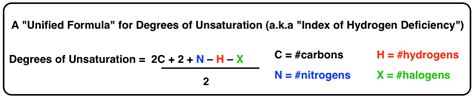
The degrees of unsaturation formula, also known as the index of hydrogen deficiency, is a fundamental concept in organic chemistry that helps chemists determine the number of rings and double bonds present in a molecule. This concept is crucial in understanding the structure and properties of organic compounds. In this article, we will delve into the details of the degrees of unsaturation formula, its significance, and how it is applied in organic chemistry.
Key Points
- The degrees of unsaturation formula is used to calculate the number of rings and double bonds in a molecule.
- The formula is given by: Degrees of Unsaturation = (2C + 2 + N - H - X)/2, where C, H, N, and X represent the number of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and halogen atoms, respectively.
- The formula is essential in understanding the structure and properties of organic compounds.
- It is used in conjunction with other analytical techniques, such as NMR and IR spectroscopy, to determine the structure of unknown compounds.
- The degrees of unsaturation formula has applications in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and biotechnology.
Understanding the Degrees of Unsaturation Formula

The degrees of unsaturation formula is based on the idea that a saturated hydrocarbon has a specific number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. For example, in a saturated alkane, each carbon atom is bonded to three hydrogen atoms, except for the terminal carbon atoms, which are bonded to one hydrogen atom. By comparing the actual number of hydrogen atoms in a molecule to the expected number, chemists can determine the number of rings and double bonds present.
Derivation of the Formula
The degrees of unsaturation formula can be derived by considering the number of valence electrons in a molecule. In a saturated hydrocarbon, each carbon atom is bonded to three hydrogen atoms, and each hydrogen atom is bonded to one carbon atom. This means that each carbon atom has three single bonds, and each hydrogen atom has one single bond. By counting the number of single bonds, we can determine the expected number of hydrogen atoms in a saturated molecule.
The formula is given by: Degrees of Unsaturation = (2C + 2 + N - H - X)/2, where C, H, N, and X represent the number of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and halogen atoms, respectively. This formula takes into account the number of valence electrons in each atom and the number of single bonds in a saturated molecule.
| Atom | Number of Valence Electrons | Number of Single Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 4 | 3 |
| Hydrogen (H) | 1 | 1 |
| Nitrogen (N) | 5 | 3 |
| Halogens (X) | 7 | 1 |

Applications of the Degrees of Unsaturation Formula
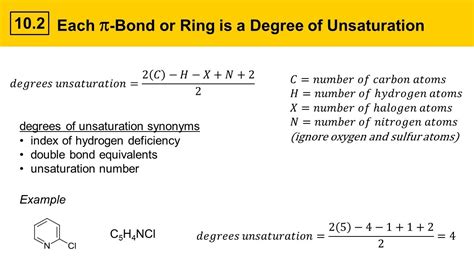
The degrees of unsaturation formula has numerous applications in organic chemistry, including the determination of molecular structure, the identification of functional groups, and the prediction of chemical properties. By using this formula in conjunction with other analytical techniques, such as NMR and IR spectroscopy, chemists can determine the structure of unknown compounds and predict their chemical properties.
Limitations and Potential Sources of Error
While the degrees of unsaturation formula is a powerful tool, it is not without limitations. One potential source of error is the assumption that the molecule is a hydrocarbon, which may not always be the case. Additionally, the formula does not take into account the presence of other functional groups, such as alcohols, amines, or carbonyls, which can affect the number of hydrogen atoms in a molecule.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
The degrees of unsaturation formula has been widely used in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and biotechnology. For example, in the development of new pharmaceuticals, chemists use this formula to determine the structure of unknown compounds and predict their chemical properties. In materials science, the formula is used to design new materials with specific properties, such as conductivity or optical activity.
In conclusion, the degrees of unsaturation formula is a fundamental concept in organic chemistry that helps chemists determine the number of rings and double bonds in a molecule. By understanding the structure of a molecule, chemists can predict its chemical properties and behavior, which is essential in the development of new pharmaceuticals, materials, and technologies.
What is the degrees of unsaturation formula used for?
+The degrees of unsaturation formula is used to calculate the number of rings and double bonds in a molecule, which is essential in understanding the structure and properties of organic compounds.
How is the degrees of unsaturation formula derived?
+The degrees of unsaturation formula is derived by considering the number of valence electrons in a molecule and the number of single bonds in a saturated molecule.
What are the limitations of the degrees of unsaturation formula?
+The degrees of unsaturation formula assumes that the molecule is a hydrocarbon and does not take into account the presence of other functional groups, which can affect the number of hydrogen atoms in a molecule.