Dental hygienists play a crucial role in the dental healthcare system, providing essential services such as teeth cleaning, patient education, and preventive care. To become a dental hygienist, one must complete the necessary educational requirements and obtain the required licensure. In this article, we will explore the dental hygienist school requirements, including the types of programs available, admission requirements, and curriculum.
Key Points
- The minimum educational requirement for dental hygienists is an associate's degree in dental hygiene.
- Dental hygienist programs are accredited by the Commission on Dental Accreditation (CODA).
- Admission requirements typically include a high school diploma or equivalent, prerequisite courses, and entrance exams.
- The curriculum for dental hygienist programs includes both classroom and clinical instruction in subjects such as anatomy, pharmacology, and radiography.
- Graduates of dental hygienist programs must pass the National Board Dental Hygiene Examination (NBDHE) to become licensed.
Types of Dental Hygienist Programs
There are several types of dental hygienist programs available, including associate’s degree, bachelor’s degree, and master’s degree programs. The most common type of program is the associate’s degree program, which typically takes two years to complete. These programs are designed to provide students with the necessary education and training to become licensed dental hygienists.
Bachelor's degree programs in dental hygiene are also available and typically take four years to complete. These programs provide students with a more comprehensive education in dental hygiene, including coursework in subjects such as business management and education. Master's degree programs in dental hygiene are designed for individuals who want to pursue advanced education and training in the field, and typically take two years to complete.
Admission Requirements
The admission requirements for dental hygienist programs vary depending on the institution and type of program. However, most programs require applicants to have a high school diploma or equivalent, as well as complete prerequisite courses such as biology, chemistry, and mathematics. Some programs may also require entrance exams, such as the Test of Essential Academic Skills (TEAS) or the Health Occupations Basic Entrance Test (HOBET).
In addition to academic requirements, many dental hygienist programs also require applicants to have observation hours or volunteer experience in a dental setting. This experience can help applicants gain a better understanding of the role of a dental hygienist and demonstrate their commitment to the field.
| Program Type | Length of Program | Admission Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Associate's Degree | 2 years | High school diploma, prerequisite courses, entrance exams |
| Bachelor's Degree | 4 years | High school diploma, prerequisite courses, entrance exams, observation hours |
| Master's Degree | 2 years | Bachelor's degree, prerequisite courses, entrance exams, observation hours |
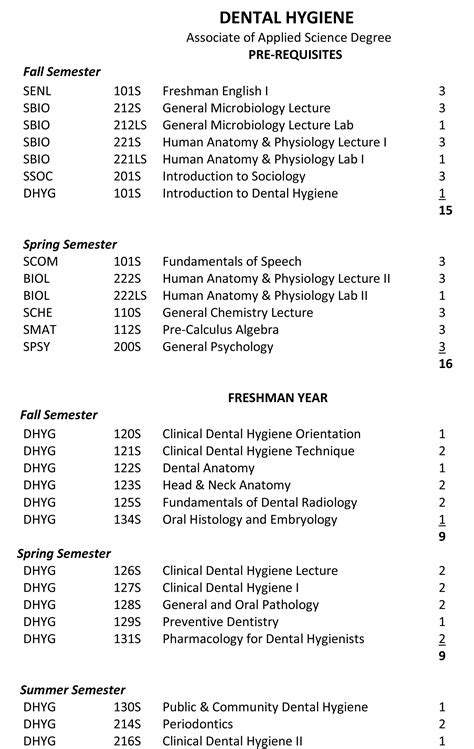
Curriculum

The curriculum for dental hygienist programs includes both classroom and clinical instruction in subjects such as anatomy, pharmacology, and radiography. Students learn about the principles of dental hygiene, including patient assessment, treatment planning, and implementation of preventive and therapeutic services. They also learn about the importance of communication and interpersonal skills in patient care.
Clinical instruction is an essential component of dental hygienist programs, providing students with hands-on experience in patient care. Students work under the supervision of licensed dental hygienists and dentists to develop their clinical skills and gain confidence in their abilities.
Clinical Experience
Clinical experience is a critical component of dental hygienist programs, providing students with the opportunity to apply their knowledge and skills in a real-world setting. Students work with patients of all ages, providing services such as teeth cleaning, fluoride treatments, and sealants. They also learn about the importance of patient education and health promotion, providing patients with information and resources to maintain good oral health.
The clinical experience component of dental hygienist programs is typically provided in a dental clinic or private practice setting. Students work under the supervision of licensed dental hygienists and dentists, who provide guidance and feedback on their clinical skills.
What is the average salary for a dental hygienist?
+The average salary for a dental hygienist varies depending on location, experience, and type of employer. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for dental hygienists was $81,360 in May 2020.
What is the job outlook for dental hygienists?
+The job outlook for dental hygienists is excellent, with employment opportunities expected to grow 6% from 2020 to 2030, faster than the average for all occupations. This growth is due to an increasing focus on preventive dental care and the expanding role of dental hygienists in the healthcare system.
What are the requirements for licensure as a dental hygienist?
+Requirements for licensure as a dental hygienist vary by state, but typically include graduating from an accredited dental hygienist program, passing the National Board Dental Hygiene Examination (NBDHE), and completing a state-specific clinical exam.
In conclusion, becoming a dental hygienist requires completing the necessary educational requirements and obtaining the required licensure. Dental hygienist programs provide students with the knowledge and skills necessary to succeed in this rewarding career, including classroom and clinical instruction in subjects such as anatomy, pharmacology, and radiography. By researching the specific admission requirements for each program and understanding the curriculum and clinical experience components, individuals can make informed decisions about their education and career path.