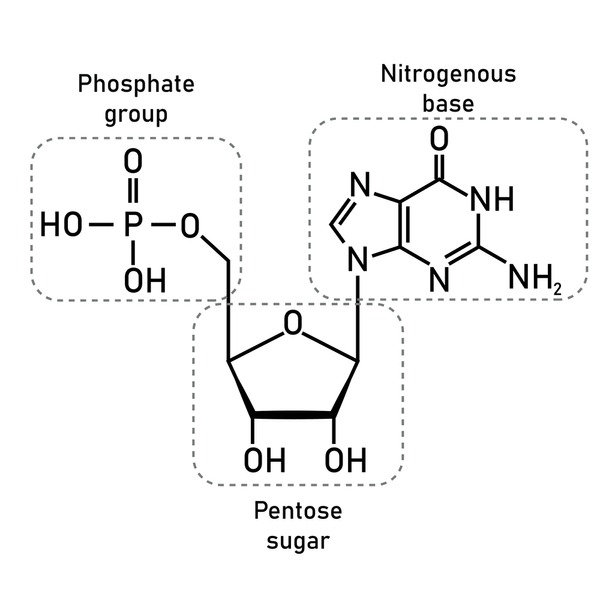
Deoxyribose sugar is a crucial component of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the molecule that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and function of all living organisms. This five-carbon sugar, also known as 2-deoxyribose, plays a pivotal role in the structure and stability of DNA. The unique chemical properties of deoxyribose sugar allow it to form a stable backbone for DNA, enabling the molecule to store and transmit genetic information with remarkable fidelity.
Chemical Structure of Deoxyribose Sugar

The chemical structure of deoxyribose sugar consists of a five-carbon ring with a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to four of the carbon atoms. The fifth carbon atom has two hydrogen atoms bonded to it, which distinguishes deoxyribose from its counterpart, ribose sugar, found in ribonucleic acid (RNA). This subtle difference in chemical structure has significant implications for the stability and function of DNA versus RNA. Deoxyribose sugar is also characterized by its planar, ring-shaped conformation, which allows it to form a stable and compact helical structure with the phosphate groups and nitrogenous bases that comprise DNA.
Role of Deoxyribose Sugar in DNA Structure
The deoxyribose sugar molecules in DNA are linked together through phosphate groups to form a backbone, known as the phosphodiester backbone. This backbone provides the structural framework for DNA, allowing it to maintain its double helix configuration and protecting the nitrogenous bases that encode genetic information. The deoxyribose sugar molecules also play a crucial role in the recognition and binding of DNA to proteins and other molecules, which is essential for processes such as gene expression, DNA replication, and repair.
| Chemical Property | Deoxyribose Sugar |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C5H10O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 110.11 g/mol |
| Chemical Structure | Five-carbon ring with hydroxyl groups |

Biological Significance of Deoxyribose Sugar
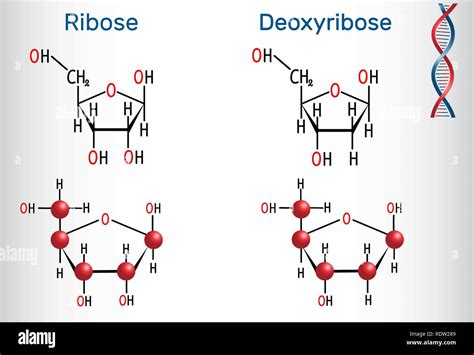
The biological significance of deoxyribose sugar cannot be overstated. As a fundamental component of DNA, it plays a critical role in the storage and transmission of genetic information. The stability and fidelity of DNA are essential for the proper functioning of all living organisms, from bacteria to humans. Deoxyribose sugar also has implications for our understanding of evolutionary processes, as changes to the DNA molecule over time can lead to the emergence of new species and the adaptation of organisms to their environments.
Deoxyribose Sugar and DNA Stability
The stability of DNA is closely tied to the chemical properties of deoxyribose sugar. The lack of a hydroxyl group on the 2’ carbon atom of deoxyribose sugar makes DNA more resistant to hydrolysis, a chemical reaction that can lead to the degradation of DNA. This stability is essential for the long-term storage of genetic information and the proper functioning of DNA. Additionally, the planar ring structure of deoxyribose sugar allows it to form a compact helical structure with the phosphate groups and nitrogenous bases, which helps to protect the DNA molecule from damage and degradation.
Key Points
- Deoxyribose sugar is a crucial component of DNA, providing the structural framework for the molecule.
- The unique chemical properties of deoxyribose sugar allow it to form a stable and compact helical structure with the phosphate groups and nitrogenous bases in DNA.
- Deoxyribose sugar plays a critical role in the recognition and binding of DNA to proteins and other molecules, which is essential for processes such as gene expression, DNA replication, and repair.
- The stability of DNA is closely tied to the chemical properties of deoxyribose sugar, including its resistance to hydrolysis and its planar ring structure.
- Deoxyribose sugar has significant implications for our understanding of evolutionary processes and the emergence of new species.
In conclusion, deoxyribose sugar is a vital component of DNA, providing the structural framework for the molecule and playing a critical role in the recognition and binding of DNA to proteins and other molecules. The unique chemical properties of deoxyribose sugar allow it to form a stable and compact helical structure with the phosphate groups and nitrogenous bases in DNA, which is essential for the proper functioning of DNA and the transmission of genetic information.
What is the molecular formula of deoxyribose sugar?
+The molecular formula of deoxyribose sugar is C5H10O4.
What is the role of deoxyribose sugar in DNA structure?
+Deoxyribose sugar molecules are linked together through phosphate groups to form a backbone, known as the phosphodiester backbone, which provides the structural framework for DNA.
Why is deoxyribose sugar more stable than ribose sugar?
+Deoxyribose sugar is more stable than ribose sugar due to the lack of a hydroxyl group on the 2’ carbon atom, which makes it more resistant to hydrolysis and other chemical reactions that can lead to degradation.