The derivative of arcsinx, denoted as $\frac{d}{dx} \arcsin x$, is a fundamental concept in calculus, particularly in the study of inverse trigonometric functions. The derivative of arcsinx is $\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}$. However, arriving at this result can be approached from various perspectives, reflecting the rich and multifaceted nature of calculus. This article will explore five different ways to derive the derivative of arcsinx, each method offering insights into the underlying mathematical principles and the versatility of calculus techniques.
Introduction to Arcsinx and Its Derivative
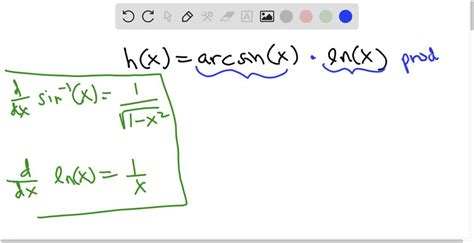
Arcsinx, or the inverse sine function, is defined as the angle whose sine is x. This function is crucial in trigonometry and calculus, especially when solving equations involving trigonometric functions. The derivative of arcsinx represents the rate of change of the angle with respect to the sine of that angle. Understanding how to derive this function is essential for various applications in physics, engineering, and mathematics.
Key Points
- The derivative of arcsinx is $\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}$.
- Derivation methods include geometric interpretation, implicit differentiation, using the definition of a derivative, trigonometric identities, and the use of the chain rule.
- Each method offers a unique perspective on calculus and the properties of inverse trigonometric functions.
- Understanding these derivations is essential for advanced calculus and applications in physics and engineering.
- The derivative of arcsinx has practical implications in optimization problems and modeling periodic phenomena.
Method 1: Geometric Interpretation

A geometric approach to finding the derivative of arcsinx involves considering the properties of right-angled triangles and the definition of the sine function. By analyzing how changes in x affect the angle and thus the arcsine, one can derive the formula. This method relies on understanding the geometric interpretation of trigonometric functions and their inverses.
Geometric Derivation Steps
1. Consider a right triangle with an angle \theta such that \sin(\theta) = x. The opposite side to \theta is x, and the hypotenuse is 1, based on the unit circle definition.
2. The adjacent side can be found using the Pythagorean theorem, \sqrt{1-x^2}. Thus, the tangent of \theta is \frac{x}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}.
3. The derivative of \theta with respect to x, which is \frac{d\theta}{dx}, can be related to the tangent of \theta. By considering the change in \theta for a small change in x, and using the fact that the derivative of \arcsin(x) is the reciprocal of the derivative of \sin(\theta), we can derive the formula \frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}.
Method 2: Implicit Differentiation
Implicit differentiation is a technique used to differentiate functions that are not given explicitly. For arcsinx, we start with the equation \sin(\arcsin x) = x and differentiate both sides implicitly with respect to x.
Implicit Differentiation Steps
1. Differentiate \sin(\arcsin x) = x implicitly to get \cos(\arcsin x) \cdot \frac{d}{dx}(\arcsin x) = 1.
2. Since \cos(\theta) = \sqrt{1 - \sin^2(\theta)} for \theta = \arcsin x, we have \cos(\arcsin x) = \sqrt{1 - x^2}.
3. Substitute \cos(\arcsin x) into the differentiated equation to solve for \frac{d}{dx}(\arcsin x), yielding \frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}.
Method 3: Using the Definition of a Derivative
The definition of a derivative, f'(x) = \lim_{h \to 0} \frac{f(x+h) - f(x)}{h}, can be applied to find the derivative of arcsinx. This method involves substituting f(x) = \arcsin x into the definition and simplifying the resulting expression.
Derivation Using the Definition
1. Substitute f(x) = \arcsin x into the derivative formula to get \lim_{h \to 0} \frac{\arcsin(x+h) - \arcsin x}{h}.
2. Utilize the addition formula for sine and the definition of arcsin to simplify the expression inside the limit.
3. After algebraic manipulations and applying the limit, the derivative \frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}} is obtained.
Method 4: Trigonometric Identities

Trigonometric identities can provide an alternative route to deriving the derivative of arcsinx. By relating arcsinx to other trigonometric functions and using known derivatives, one can arrive at the derivative of arcsinx.
Derivation Using Trigonometric Identities
1. Express arcsinx in terms of other trigonometric functions, such as \arctan\left(\frac{x}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}\right).
2. Use the derivative of arctan and the chain rule to differentiate the expression.
3. Simplify the resulting derivative to obtain \frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}.
Method 5: The Chain Rule
The chain rule, a fundamental rule in differentiation, can be applied to derive the derivative of arcsinx by considering the composition of functions involved in the inverse sine function.
Derivation Using the Chain Rule
1. Express \arcsin x as the composition of functions, e.g., \arcsin = \sin^{-1}.
2. Apply the chain rule to differentiate this composition, recognizing that the derivative of the outer function (inverse sine) with respect to its argument, times the derivative of the inner function (identity function, which is 1), gives the derivative of the composite function.
3. The derivative of the inverse sine function with respect to its argument is \frac{1}{\cos(\arcsin x)} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}, which directly yields the derivative of arcsinx.
| Method | Description | Derivative of Arcsinx |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric Interpretation | Uses geometric properties of triangles | $\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}$ |
| Implicit Differentiation | Differentiates implicitly using trigonometric identities | $\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}$ |
| Definition of a Derivative | Applies the limit definition of a derivative | $\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}$ |
| Trigonometric Identities | Relates arcsinx to other trigonometric functions | $\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}$ |
| Chain Rule | Considers the composition of functions in arcsinx | $\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}$ |

What is the derivative of arcsinx used for?
+The derivative of arcsinx is used in optimization problems, physics, and engineering, particularly when dealing with periodic phenomena or right-angled trigonometry.
Why are there multiple methods to derive the derivative of arcsinx?
+Multiple methods exist to cater to different learning styles and to illustrate the versatility and depth of calculus. Each method provides a unique insight into mathematical principles and problem-solving strategies.
How does the derivative of arcsinx relate to other inverse trigonometric functions?
+The derivative of arcsinx is closely related to the derivatives of other inverse trigonometric functions, such as arccosx and arctanx, through trigonometric identities and the unit circle. Understanding one helps in understanding the others.
In conclusion, the derivative of arcsinx, \frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}, can be derived through various methods, each offering a distinct perspective on calculus and the properties of inverse trigonometric functions. Whether through geometric interpretation, implicit differentiation, the definition of a derivative, trigonometric identities, or the chain rule, understanding these derivations is essential for a deep appreciation of calculus and its applications. As calculus continues to play a pivotal role in science, engineering, and mathematics, the ability to derive and apply the derivative of arcsinx and other functions remains a fundamental skill for problem-solving and analytical thinking.