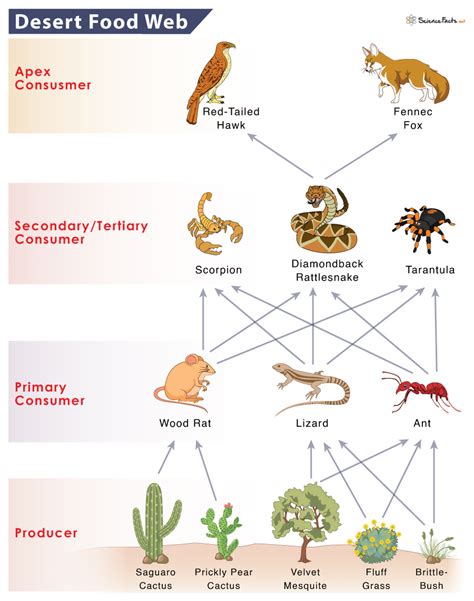
The desert ecosystem, known for its harsh climate and limited vegetation, hosts a fascinating array of life forms that have adapted to survive in these conditions. The food web in the desert is intricate, with each species playing a vital role in the balance of the ecosystem. Understanding the dynamics of the desert food web can provide valuable insights into the interconnectedness of life and the importance of conservation. Here, we delve into five key tips that highlight the complexity and beauty of desert food webs.
Key Points
- Desert food webs are characterized by a reliance on plants that can store water, such as cacti and succulents, which serve as primary producers.
- Herbivores like the desert tortoise and kangaroo rat play a crucial role in dispersing seeds and facilitating the growth of new vegetation.
- Carnivores, including coyotes and bobcats, regulate the population of herbivores, preventing any one species from overgrazing and destroying the plant community.
- Decomposers, such as insects and microorganisms, are essential for breaking down dead organic matter and recycling nutrients back into the soil.
- Human activities, such as urbanization and pollution, can significantly impact desert ecosystems, highlighting the need for sustainable practices and conservation efforts.
Primary Producers in the Desert Ecosystem
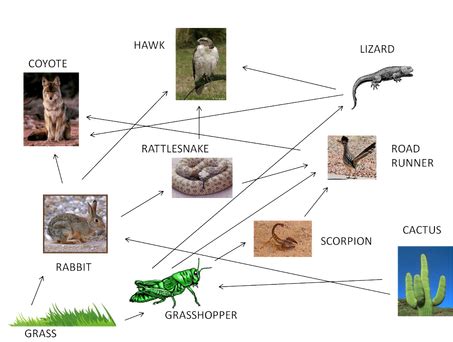
The foundation of the desert food web is laid by primary producers, which in this context, are primarily plants adapted to the arid conditions. Cacti and succulents are notable examples, with their ability to store water enabling them to thrive in environments where water is scarce. These plants not only provide food for herbivores but also offer shelter and habitat for a variety of species. The unique adaptations of these plants, such as deep roots to access groundwater and waxy stems to prevent water loss, demonstrate the remarkable diversity of life in the desert.
Role of Herbivores
Herbivores are the primary consumers in the desert food web, feeding on the plants and, in doing so, contributing to the ecosystem’s balance. Species like the desert tortoise and kangaroo rat are not just consumers; they also play a role in seed dispersal and vegetation regeneration. For example, the desert tortoise helps in spreading the seeds of the cactus it consumes, facilitating the growth of new cacti in different areas. This process is crucial for the expansion and diversification of plant species in the desert.
| Species | Role in Ecosystem |
|---|---|
| Desert Tortoise | Seed dispersal and vegetation regeneration |
| Kangaroo Rat | Seed dispersal and contributing to nutrient cycling |
| Coyote | Predation, regulating herbivore populations |
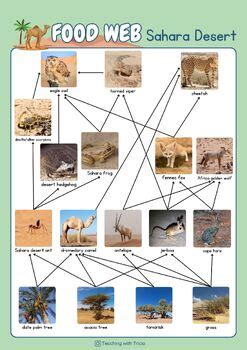
Carnivores and Decomposers in the Desert Ecosystem
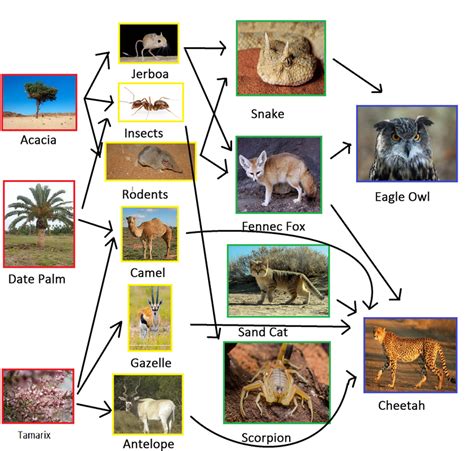
Carnivores, such as coyotes and bobcats, are pivotal in regulating the populations of herbivores. By controlling the numbers of herbivorous species, carnivores prevent overgrazing and ensure that the plant community remains healthy and diverse. Decomposers, including insects and microorganisms, are responsible for breaking down dead organic matter. This process recycles nutrients back into the soil, making them available for plants to use, thus completing the nutrient cycle and sustaining the ecosystem.
Human Impact on Desert Ecosystems
Human activities have a profound impact on desert ecosystems. Urbanization, mining, and pollution can lead to habitat destruction, reduction in biodiversity, and disruption of the food web. For instance, the introduction of invasive species can outcompete native plants for resources, altering the composition of primary producers and cascading through the food web. It is essential to adopt sustainable practices and support conservation efforts to protect these delicate ecosystems.
What is the primary challenge faced by plants in the desert?
+The primary challenge faced by plants in the desert is accessing water. Plants have evolved various adaptations to store water, reduce water loss, and access water deep in the soil.
How do herbivores contribute to the desert ecosystem?
+Herbivores contribute to the desert ecosystem by consuming plants, which helps in regulating plant growth and preventing any one species from dominating. They also play a crucial role in seed dispersal and nutrient cycling.
What can be done to mitigate human impact on desert ecosystems?
+To mitigate human impact, it is crucial to adopt sustainable practices such as reducing pollution, protecting natural habitats, and supporting conservation efforts. Additionally, educating the public about the importance of desert ecosystems and the impact of human activities can foster a sense of responsibility and encourage action.
In conclusion, the desert food web is a complex and fascinating system, with each component playing a vital role in the ecosystem’s balance. Understanding and respecting this balance is crucial for maintaining the health and diversity of desert ecosystems. As we move forward, it is essential to integrate our knowledge of these ecosystems into our actions, striving for a future where human activity and nature coexist in harmony.