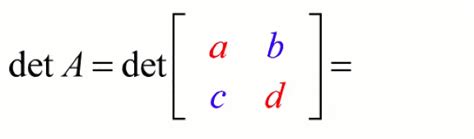The determinant of a 2x2 matrix is a fundamental concept in linear algebra, and it plays a crucial role in various mathematical and real-world applications. The formula for calculating the determinant of a 2x2 matrix is straightforward and easy to apply. Given a 2x2 matrix:
\[ \begin{pmatrix} a & b \\ c & d \end{pmatrix} \]
The determinant, denoted as det(A) or |A|, can be calculated using the following formula:
\[ \text{det(A)} = ad - bc \]
Understanding the Formula
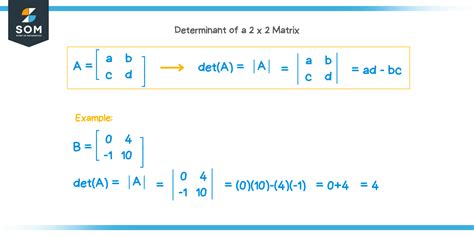
This formula is derived from the concept of determinants in higher-dimensional matrices, but for a 2x2 matrix, it simplifies to the difference between the product of the diagonal elements (a and d) and the product of the anti-diagonal elements (b and c). This calculation provides a scalar value that can be used to describe certain properties of the matrix, such as its invertibility. A non-zero determinant indicates that the matrix is invertible, whereas a determinant of zero signifies that the matrix is singular and does not have an inverse.
Application of the Determinant Formula
The determinant of a 2x2 matrix has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and computer science. For instance, in geometry, it can be used to find the area of a parallelogram formed by two vectors. In linear algebra, it is crucial for solving systems of linear equations and for determining the invertibility of matrices. The formula's simplicity belies its importance and versatility in mathematical and scientific contexts.
| Matrix Element | Description |
|---|---|
| a | Top-left element of the matrix |
| b | Top-right element of the matrix |
| c | Bottom-left element of the matrix |
| d | Bottom-right element of the matrix |
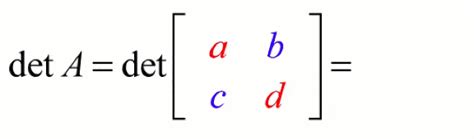
Key Points
- The determinant of a 2x2 matrix is calculated as ad - bc, where a, b, c, and d are the elements of the matrix.
- A non-zero determinant indicates that the matrix is invertible, while a zero determinant means the matrix is singular.
- The determinant has applications in geometry, linear algebra, and other fields for solving systems of equations, finding areas, and determining matrix properties.
- Understanding the determinant of a 2x2 matrix is crucial for progressing to more complex linear algebra concepts and applications.
- The formula's simplicity makes it accessible for manual calculations, but its implications are far-reaching and fundamental to advanced mathematical and scientific analyses.
Calculating the Determinant: Step-by-Step Guide

To calculate the determinant of a 2x2 matrix, follow these steps:
1. Identify the elements of the matrix: a, b, c, and d.
2. Apply the determinant formula: ad - bc.
3. Perform the multiplication operations: ad and bc.
4. Subtract the product of bc from the product of ad: ad - bc.
This step-by-step process ensures that the determinant is calculated accurately and efficiently, providing a clear understanding of the matrix's properties and its potential applications in various mathematical and scientific contexts.
What does a zero determinant signify in a 2x2 matrix?
+A zero determinant signifies that the matrix is singular, meaning it does not have an inverse. This implies that the matrix cannot be used to solve systems of linear equations uniquely.
How is the determinant of a 2x2 matrix used in geometry?
+In geometry, the determinant of a 2x2 matrix can be used to find the area of a parallelogram formed by two vectors. The absolute value of the determinant gives the area of the parallelogram.
What is the significance of a non-zero determinant in a 2x2 matrix?
+A non-zero determinant signifies that the matrix is invertible. This means the matrix can be used to solve systems of linear equations uniquely, and it has a multiplicative inverse.