Diastereomers are a fundamental concept in stereochemistry, representing a crucial aspect of molecular structure that significantly impacts the physical and chemical properties of compounds. Understanding diastereomers is essential in various fields, including organic chemistry, pharmacology, and materials science. This article delves into the intricacies of diastereomers, exploring their definition, formation, properties, and importance in chemical synthesis and biological activity.
Key Points
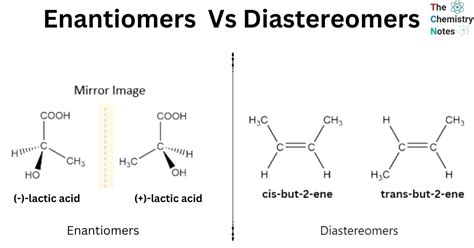
- Diastereomers are stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other, differing in their spatial arrangement of atoms.
- The formation of diastereomers occurs through reactions that create new stereocenters, leading to a mixture of isomers with distinct properties.
- Physical and chemical properties of diastereomers, such as melting points, boiling points, and reactivity, can vary significantly.
- Diastereomers play a critical role in biological systems, where the specific spatial arrangement of molecules can influence their interaction with enzymes, receptors, and other biomolecules.
- The separation and identification of diastereomers are challenging and require sophisticated analytical techniques, including chromatography and spectroscopy.
Introduction to Diastereomers

Diastereomers are a type of stereoisomer, which are molecules that have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms but differ in the three-dimensional arrangement of their atoms. Unlike enantiomers, which are non-superimposable mirror images of each other, diastereomers are not mirror images and can have different physical and chemical properties due to their distinct spatial arrangements.
Formation of Diastereomers
The formation of diastereomers typically occurs in reactions that create new stereocenters, such as asymmetric synthesis or the reaction of a chiral molecule with an achiral reactant. For example, the addition of a chiral auxiliary to an achiral starting material can lead to the formation of diastereomeric products. Understanding the mechanisms of these reactions is crucial for predicting the formation of diastereomers and controlling their ratios in the resulting mixture.
| Type of Reaction | Example | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Asymmetric Synthesis | Sharpless Epoxidation | Formation of chiral epoxides with high enantioselectivity |
| Reaction with Chiral Auxiliary | Evans' Auxiliary | Formation of diastereomeric products with controlled stereoselectivity |

Properties of Diastereomers
Diastereomers can exhibit significantly different physical and chemical properties due to their distinct spatial arrangements. These differences can affect their melting points, boiling points, solubility, and reactivity. For instance, one diastereomer may be more soluble in a particular solvent than its counterpart, or it may react more readily with a specific reagent. Understanding these property differences is crucial for the separation, identification, and application of diastereomers.
Biological Importance of Diastereomers
In biological systems, the spatial arrangement of molecules can have profound effects on their interactions with enzymes, receptors, and other biomolecules. Diastereomers can exhibit different biological activities, such as varying levels of potency or specificity, due to their distinct shapes and orientations. This phenomenon is particularly relevant in pharmacology, where the development of drugs with specific stereochemistries can lead to improved efficacy and reduced side effects.
What are the implications of diastereomerism in drug development?
+The presence of diastereomers in drug candidates can significantly impact their efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics. Understanding and controlling the stereochemistry of drugs is essential for optimizing their therapeutic profiles and minimizing adverse effects.
How are diastereomers separated and identified in a mixture?
+The separation and identification of diastereomers typically involve advanced analytical techniques, such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography (GC), and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. These methods can distinguish between diastereomers based on their unique physical and chemical properties.
In conclusion, diastereomers represent a critical aspect of stereochemistry, with profound implications for the properties and biological activities of molecules. Understanding the formation, properties, and separation of diastereomers is essential for advancing our knowledge of chemical synthesis, pharmacology, and materials science. As research continues to uncover the complexities of diastereomerism, the development of new analytical techniques and synthetic methodologies will be crucial for harnessing the full potential of these intriguing molecules.