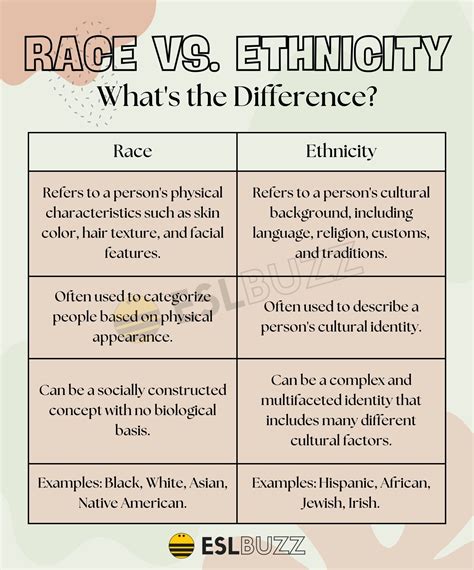
The concepts of nationality and ethnicity are often intertwined, yet they hold distinct meanings that are essential to understanding the complexities of human identity. Nationality refers to the legal relationship between an individual and a nation-state, typically denoted by citizenship. It encompasses the rights, privileges, and responsibilities that come with being a member of a particular country. On the other hand, ethnicity pertains to a person's cultural, social, and historical heritage, which may include their ancestry, language, traditions, and values.
While nationality is often tied to a specific geographic location and is usually acquired through birth or naturalization, ethnicity is a more fluid and multifaceted concept. Ethnicity can be influenced by a variety of factors, including a person's family background, community affiliations, and personal experiences. It is not uncommon for individuals to identify with multiple ethnicities, reflecting the diverse and complex nature of human identity. For instance, a person may hold the nationality of one country but identify with the ethnicity of another, due to their ancestral roots or cultural practices.
The distinction between nationality and ethnicity becomes particularly significant in the context of globalization, migration, and cultural exchange. As people move across borders and interact with different cultures, their sense of nationality and ethnicity may evolve, leading to the creation of new identities and affiliations. Furthermore, the intersection of nationality and ethnicity can have profound implications for social justice, equality, and human rights, as individuals from diverse backgrounds navigate complex power dynamics and societal expectations.
Key Points
- Nationality refers to the legal relationship between an individual and a nation-state, denoted by citizenship.
- Ethnicity pertains to a person's cultural, social, and historical heritage, including ancestry, language, traditions, and values.
- Nationality is often tied to a specific geographic location, while ethnicity is a more fluid and multifaceted concept.
- Individuals may identify with multiple ethnicities, reflecting the diverse and complex nature of human identity.
- The distinction between nationality and ethnicity has significant implications for social justice, equality, and human rights.
Nationality: Understanding the Concept

Nationality is a fundamental aspect of a person’s identity, as it determines their legal rights, privileges, and responsibilities within a nation-state. It is typically acquired through birth, descent, or naturalization, and is usually documented through official records such as passports, birth certificates, and nationality certificates. Nationality can also be influenced by a person’s place of residence, language, and cultural affiliations. For example, a person may hold the nationality of a country where they were born, but later acquire the nationality of another country through naturalization.
The concept of nationality has evolved over time, with modern nation-states recognizing the importance of nationality in shaping individual and collective identities. Nationality laws and regulations vary across countries, reflecting different historical, cultural, and political contexts. Some countries have relatively straightforward nationality laws, while others have more complex and nuanced regulations. For instance, some countries recognize dual nationality, while others do not.
Nationality and Citizenship: Interconnected Concepts
Nationality and citizenship are often used interchangeably, but they hold distinct meanings. Citizenship refers to the relationship between an individual and a state, where the individual has certain rights, privileges, and responsibilities. Nationality, on the other hand, refers to the legal relationship between an individual and a nation-state, denoted by citizenship. In other words, nationality is a broader concept that encompasses citizenship, as well as other aspects of a person’s identity and affiliation with a nation-state.
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Nationality | Legal relationship between an individual and a nation-state |
| Citizenship | Relationship between an individual and a state, with certain rights and responsibilities |
| Ethnicity | Cultural, social, and historical heritage, including ancestry, language, traditions, and values |
Ethnicity: Understanding the Concept
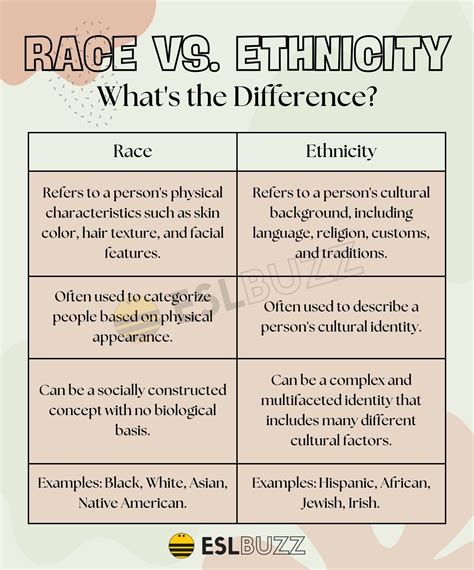
Ethnicity is a multifaceted concept that encompasses a person’s cultural, social, and historical heritage. It is shaped by a variety of factors, including ancestry, language, traditions, and values. Ethnicity can be influenced by a person’s family background, community affiliations, and personal experiences. For example, a person may identify with a particular ethnicity due to their ancestral roots, cultural practices, or language.
Ethnicity is a dynamic and evolving concept, as individuals and groups navigate complex power dynamics and societal expectations. Ethnicity can be a source of pride, identity, and belonging, as well as a site of conflict, marginalization, and exclusion. The recognition and respect of ethnic diversity are essential for promoting social justice, equality, and human rights.
Ethnicity and Identity: Interconnected Concepts
Ethnicity and identity are deeply intertwined, as ethnicity shapes a person’s sense of self and belonging. Identity refers to the complex and multifaceted nature of a person’s self-concept, encompassing various aspects of their personality, experiences, and affiliations. Ethnicity is a critical component of identity, as it influences a person’s values, beliefs, and practices. For instance, a person’s ethnicity may shape their language, customs, and traditions, which in turn influence their sense of identity and belonging.
The intersection of ethnicity and identity has significant implications for social justice, equality, and human rights. As individuals and groups navigate complex power dynamics and societal expectations, it is essential to recognize and respect ethnic diversity. This requires a nuanced understanding of the complexities of human identity, as well as a commitment to promoting social justice and equality.
What is the difference between nationality and ethnicity?
+Nationality refers to the legal relationship between an individual and a nation-state, denoted by citizenship. Ethnicity, on the other hand, pertains to a person's cultural, social, and historical heritage, including ancestry, language, traditions, and values.
Can a person have multiple ethnicities?
+Yes, individuals may identify with multiple ethnicities, reflecting the diverse and complex nature of human identity. This can be due to their ancestral roots, cultural practices, or language.
What is the relationship between nationality and citizenship?
+Nationality and citizenship are interconnected concepts, where nationality refers to the legal relationship between an individual and a nation-state, and citizenship refers to the relationship between an individual and a state, with certain rights and responsibilities.
Meta Description: Discover the difference between nationality and ethnicity, and how these concepts shape individual and collective identities. Learn about the complexities of human identity and the importance of recognizing and respecting ethnic diversity. (149 characters)



