Poetry, a timeless and versatile form of expression, has evolved over centuries, branching out into numerous styles and forms. Among these, seven types of poetry stand out for their distinct characteristics, each offering a unique lens through which poets can convey emotions, thoughts, and experiences. Understanding these forms not only enriches one's appreciation of poetry but also provides poets with a diverse palette of creative expression.
Introduction to Poetry Forms
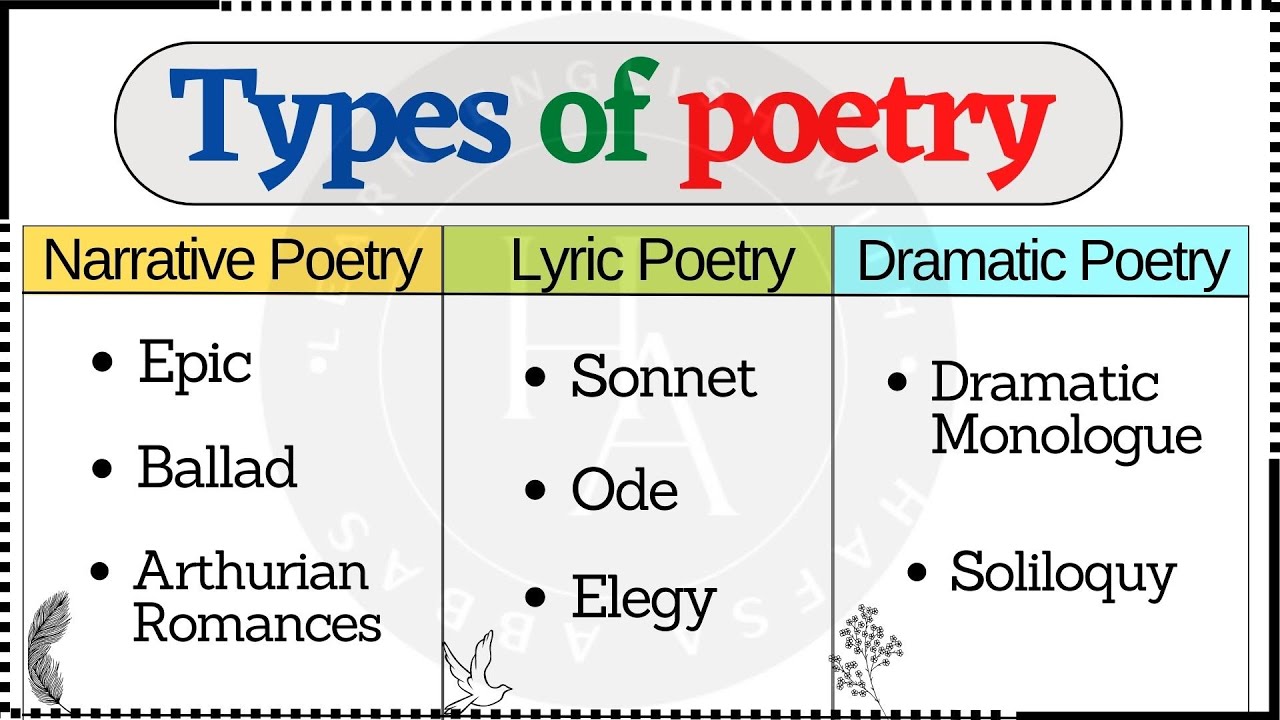
The world of poetry is vast and intricate, with various forms emerging from different cultures and historical periods. From the sonnets of Shakespeare to the free verse of modern poets, each form of poetry has its own set of rules, structures, and emotional resonance. This article will delve into seven significant types of poetry, exploring their origins, characteristics, and examples, to provide a comprehensive overview of the poetic landscape.
1. Sonnet
A sonnet, one of the most recognizable forms of poetry, is a 14-line poem that follows a specific rhyme scheme. There are two main forms of sonnets: the Shakespearean sonnet, which consists of three quatrains and a final couplet, and the Italian sonnet, which is divided into an octave and a sestet. Sonnets traditionally explore themes of love, beauty, and the passage of time, with each line meticulously crafted to contribute to the overall emotional impact of the poem.
| Poetry Form | Description |
|---|---|
| Sonnet | 14-line poem with a specific rhyme scheme, traditionally dealing with themes of love and beauty |
| Free Verse | Poetry that doesn't follow a specific rhyme or meter, allowing for a wide range of creative expression |
| Haiku | A short, three-line poem originating from Japan, focusing on nature and the seasons |
| Ode | A poem written in praise of a person, place, or thing, typically formal and expressive |
| Ballad | A narrative poem that tells a story, often with a folkloric or legendary theme, and a strong rhythm |
| Elegy | A poem of mourning, expressing sorrow or loss, usually formal and reflective |
| Limerick | A humorous, five-line poem with a specific rhyme scheme and meter, often featuring a punchline or joke |

Exploring Poetry Forms

Beyond the sonnet, there are numerous other forms of poetry, each with its unique characteristics and challenges. Free verse, for example, offers poets the freedom to express themselves without adhering to any specific rhyme or meter, resulting in highly personal and expressive works. On the other hand, forms like haiku and limerick, with their strict syllable counts and rhyme schemes, require poets to be concise and creative within defined boundaries.
2. Free Verse
Free verse poetry is characterized by its lack of a regular rhythm, meter, or rhyme. This form of poetry allows the poet to express themselves freely without adhering to any specific structural guidelines, making it a popular choice for contemporary poets who seek to explore new modes of expression and connect with readers on a deeper, more personal level.
Key Points
- Sonnets are 14-line poems that follow a specific rhyme scheme and traditionally deal with themes of love and beauty.
- Free verse poetry does not follow a specific rhyme or meter, offering poets a wide range of creative expression.
- Haiku is a short, three-line poem that focuses on nature and the seasons, originating from Japan.
- Odes are formal and expressive poems written in praise of a person, place, or thing.
- Ballads are narrative poems that tell stories, often with a folkloric or legendary theme and a strong rhythm.
Understanding Poetry
Understanding and appreciating poetry involves not just recognizing its various forms but also delving into the historical, cultural, and personal contexts in which poems are written. Poetry, in all its forms, serves as a mirror to society, reflecting the joys, sorrows, and complexities of human experience. By exploring the different types of poetry, readers can gain a deeper understanding of the world and their place within it.
3. Haiku
Haiku, a traditional form of Japanese poetry, consists of three lines with a syllable count of 5, 7, and 5. Haiku poems often capture moments in time or express a feeling or image, with a seasonal reference included to help establish the time and setting of the poem. The simplicity and clarity of haiku make it a beloved form of poetry worldwide, offering insights into the natural world and the human condition.
4. Ode
An ode is a poem written in praise of a person, place, or thing. It is typically formal and expresses deep emotion, with the structure and style varying depending on the poet and the subject. Odes can be expressive and personal, or they can be formal and public, serving as a way to honor and celebrate the subjects they extol.
5. Ballad
A ballad is a narrative poem that tells a story, often with a folkloric or legendary theme. Ballads are typically written in quatrains (four-line stanzas) with a strong rhythm and rhyme scheme, making them musical and engaging. They can be tragic, romantic, or humorous, and their narrative structure makes them popular for storytelling.
6. Elegy
An elegy is a poem of mourning, expressing sorrow or loss. It is typically formal and reflective, with the poet exploring themes of death, grief, and memory. Elegies can be personal, mourning the loss of a loved one, or public, commemorating a significant event or figure.
7. Limerick
A limerick is a humorous, five-line poem with a specific rhyme scheme and meter. The first, second, and last lines rhyme with each other, while the third and fourth lines rhyme with each other. Limericks often feature a punchline or joke and are known for their light, playful nature, making them a delightful form of poetry for both children and adults.
What is the main characteristic of a sonnet?
+A sonnet is characterized by its 14 lines and a specific rhyme scheme, traditionally dealing with themes of love and beauty.
What distinguishes free verse poetry from other forms?
+Free verse poetry is distinguished by its lack of a regular rhythm, meter, or rhyme, offering poets the freedom to express themselves without adhering to any specific structural guidelines.
What is the traditional structure of a haiku?
+A traditional haiku consists of three lines with a syllable count of 5, 7, and 5, often capturing moments in time or expressing a feeling or image, with a seasonal reference included.
In conclusion, the world of poetry is rich and diverse, with each form offering a unique perspective and mode of expression. From the structured sonnet to the free-flowing free verse, and from the traditional haiku to the narrative ballad, understanding and appreciating these forms can deepen our connection to poetry and to the world around us. Whether you are a seasoned poet or just beginning to explore the realm of poetry, there is a form out there waiting to be discovered, offering a voice and a perspective that resonates with your own.



