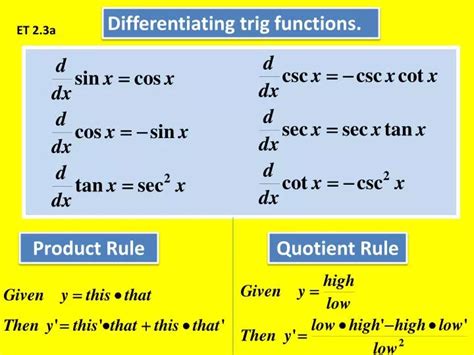
Trigonometric functions, commonly referred to as trig functions, are a fundamental component of mathematics and play a crucial role in various fields, including physics, engineering, and computer science. The primary trig functions include sine, cosine, and tangent, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Understanding the differences between these functions is essential for solving problems and applying trigonometry in real-world scenarios.
At the core of trigonometry lies the unit circle, a circle with a radius of 1 centered at the origin of a coordinate plane. The unit circle serves as a visual representation of trig functions, allowing for the illustration of key concepts such as angles, triangles, and wave patterns. By examining the unit circle and the relationships between angles and side lengths of triangles, one can develop a deep understanding of trig functions and their interconnections.
Key Points
- The sine function relates to the y-coordinate of a point on the unit circle and is defined as the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle.
- The cosine function corresponds to the x-coordinate of a point on the unit circle and is defined as the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle.
- The tangent function is defined as the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side in a right-angled triangle and can be expressed as the ratio of sine to cosine.
- Trigonometric identities, such as the Pythagorean identity (sin^2(x) + cos^2(x) = 1), are essential for simplifying expressions and solving equations involving trig functions.
- Graphical representations of trig functions provide valuable insights into their periodic nature and can be used to analyze and visualize complex phenomena.
Understanding Sine, Cosine, and Tangent
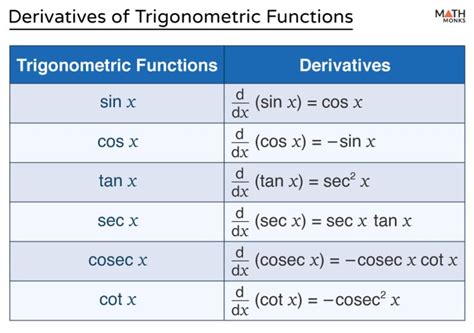
The sine, cosine, and tangent functions are defined in terms of the ratios of the sides of a right-angled triangle. The sine of an angle is equal to the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the hypotenuse, while the cosine is equal to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. The tangent, on the other hand, is equal to the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side.
These definitions can be expressed mathematically as follows: sin(x) = opposite side / hypotenuse, cos(x) = adjacent side / hypotenuse, and tan(x) = opposite side / adjacent side. By recognizing the relationships between these ratios, one can easily differentiate between the sine, cosine, and tangent functions and apply them to solve problems in trigonometry.
Visualizing Trig Functions with the Unit Circle
The unit circle provides a powerful visual tool for understanding trig functions. By plotting points on the unit circle and examining their coordinates, one can see the relationships between angles and trig functions. For example, the sine of an angle corresponds to the y-coordinate of the point on the unit circle, while the cosine corresponds to the x-coordinate.
Using the unit circle, one can also visualize the periodic nature of trig functions, which repeat every 2π radians or 360 degrees. This periodicity is essential for understanding and working with trig functions in various applications, including physics, engineering, and computer science.
| Trig Function | Definition | Unit Circle Representation |
|---|---|---|
| Sine | opposite side / hypotenuse | y-coordinate of a point on the unit circle |
| Cosine | adjacent side / hypotenuse | x-coordinate of a point on the unit circle |
| Tangent | opposite side / adjacent side | ratio of y-coordinate to x-coordinate of a point on the unit circle |
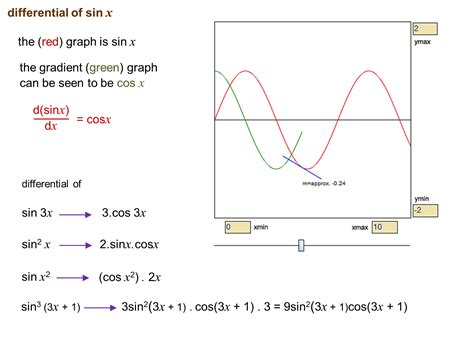
Applying Trig Functions in Real-World Scenarios
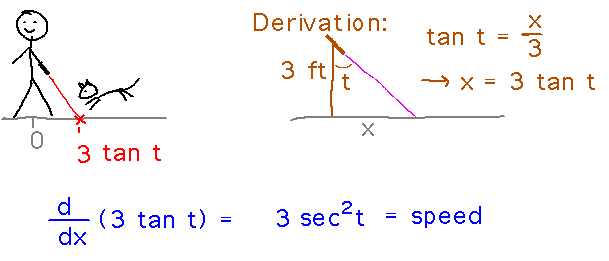
Trigonometric functions have numerous applications in physics, engineering, and computer science. In physics, trig functions are used to describe the motion of objects, including the trajectory of projectiles and the vibration of strings. In engineering, trig functions are used to design and analyze systems, such as bridges and electronic circuits.
In computer science, trig functions are used in graphics and game development to create realistic simulations and animations. For example, the sine and cosine functions can be used to generate wave patterns and simulate the motion of objects in a virtual environment.
Solving Trig Equations and Identities
Solving trig equations and identities requires a deep understanding of trig functions and their relationships. One essential tool for solving trig equations is the use of trig identities, such as the Pythagorean identity (sin^2(x) + cos^2(x) = 1). By applying these identities, one can simplify expressions and solve equations involving trig functions.
Another important technique for solving trig equations is the use of graphical methods, such as plotting the graphs of trig functions and examining their intersections. By combining these techniques with a strong understanding of trig functions and their relationships, one can develop a powerful toolkit for solving trig equations and identities.
What is the difference between sine, cosine, and tangent?
+The sine, cosine, and tangent functions are defined in terms of the ratios of the sides of a right-angled triangle. The sine of an angle is equal to the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the hypotenuse, while the cosine is equal to the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. The tangent, on the other hand, is equal to the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side.
How are trig functions used in real-world applications?
+Trigonometric functions have numerous applications in physics, engineering, and computer science. In physics, trig functions are used to describe the motion of objects, including the trajectory of projectiles and the vibration of strings. In engineering, trig functions are used to design and analyze systems, such as bridges and electronic circuits. In computer science, trig functions are used in graphics and game development to create realistic simulations and animations.
What is the importance of the unit circle in trigonometry?
+The unit circle provides a powerful visual tool for understanding trig functions. By plotting points on the unit circle and examining their coordinates, one can see the relationships between angles and trig functions. The unit circle also illustrates the periodic nature of trig functions, which repeat every 2π radians or 360 degrees.
Meta Description: Differentiate between trig functions easily by understanding their definitions, relationships, and applications. Learn how to apply trig functions in real-world scenarios and solve trig equations and identities with confidence.