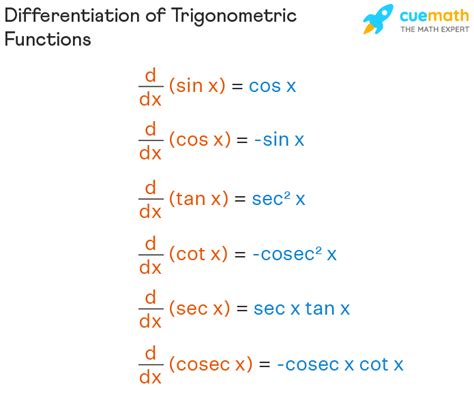
Trigonometric differentiation is a fundamental concept in calculus, allowing us to find the rates of change of trigonometric functions. These functions are crucial in various fields, including physics, engineering, and navigation. Mastering trig differentiation is essential for any student or professional aiming to work with mathematical models that involve periodic phenomena. In this article, we will delve into five key tips for trig differentiation, providing a comprehensive guide to enhance your understanding and proficiency in this area.
Key Points
- Understanding the basic trigonometric derivatives is crucial for more complex calculations.
- Memorization of key derivative formulas can significantly speed up problem-solving.
- Applying the chain rule is essential for differentiating composite trigonometric functions.
- Recognizing the derivative of a function can help in identifying the original function, a process known as antidifferentiation.
- Practice with a variety of problems to develop proficiency and fluency in trigonometric differentiation.
Tip 1: Master the Basic Derivatives
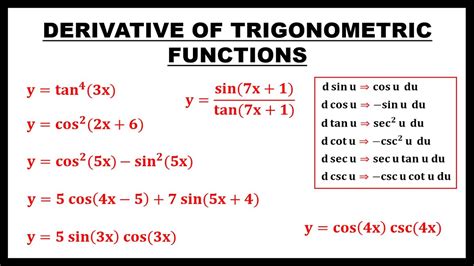
To begin with, it’s vital to memorize the derivatives of the basic trigonometric functions. These include the derivatives of sine, cosine, and tangent, which are: - d(sin(x))/dx = cos(x) - d(cos(x))/dx = -sin(x) - d(tan(x))/dx = sec^2(x) Understanding these basic derivatives is the foundation upon which more complex trigonometric differentiation is built. They are used in various mathematical and real-world applications, from calculating the motion of projectiles to modeling periodic phenomena in economics.
Derivatives of Other Trigonometric Functions
Beyond the basic trigonometric functions, it’s also important to know the derivatives of other related functions, such as: - d(sec(x))/dx = sec(x)tan(x) - d(csc(x))/dx = -csc(x)cot(x) - d(cot(x))/dx = -csc^2(x) These derivatives are essential for tackling problems that involve more complex trigonometric expressions.
Tip 2: Apply the Chain Rule Effectively
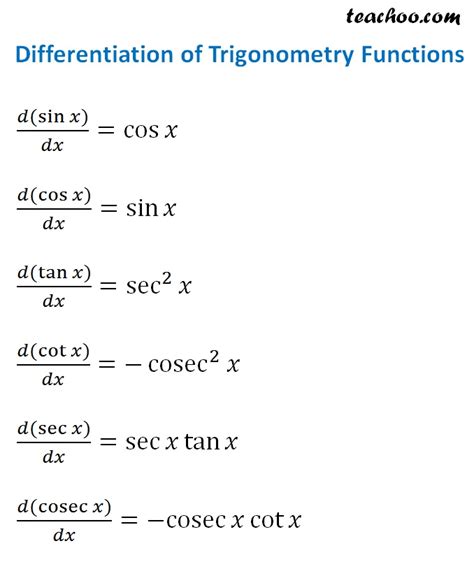
The chain rule is a powerful tool in differentiation that allows us to find the derivative of composite functions. For trigonometric functions, this means we can differentiate functions like sin(2x) or cos(x^2) by applying the chain rule. The formula for the chain rule is: - d(f(g(x)))/dx = f’(g(x)) * g’(x) For example, to differentiate sin(2x), we would use the chain rule as follows: - d(sin(2x))/dx = cos(2x) * d(2x)/dx = 2cos(2x)
Practical Application of the Chain Rule
The chain rule is not only useful for differentiating simple composite functions but also for more complex expressions. For instance, to find the derivative of sin(x^2), we apply the chain rule: - d(sin(x^2))/dx = cos(x^2) * d(x^2)/dx = 2xcos(x^2) This demonstrates how the chain rule can be used to differentiate functions that involve trigonometric functions of other functions.
Tip 3: Use Trigonometric Identities
Trigonometric identities can be very helpful in simplifying expressions before differentiation. For example, using the identity sin^2(x) + cos^2(x) = 1, we can simplify expressions that involve these terms. Additionally, identities like tan(x) = sin(x)/cos(x) can be useful when differentiating functions that involve tangent.
Example: Differentiating Trigonometric Identities
Consider the function f(x) = sin^2(x). To differentiate this, we can use the chain rule and the fact that sin^2(x) + cos^2(x) = 1. However, a more straightforward approach involves recognizing that the derivative of sin^2(x) can be found using the formula for the derivative of a composite function, after rewriting sin^2(x) as (sin(x))^2.
| Function | Derivative |
|---|---|
| sin^2(x) | 2sin(x)cos(x) |
| cos^2(x) | -2sin(x)cos(x) |

Tip 4: Practice with Varied Problems
Practice is key to mastering trigonometric differentiation. It’s essential to work through a variety of problems to become proficient in applying the rules and identities of trigonometric differentiation. This includes practicing differentiation of basic trigonometric functions, composite functions, and functions that involve trigonometric identities.
Developing Problem-Solving Skills
As you practice, focus on developing your problem-solving skills. Start with simple problems and gradually move on to more complex ones. Pay attention to how different rules and identities are applied in different contexts. The more you practice, the more comfortable you will become with recognizing which rules to apply and how to simplify complex expressions.
Tip 5: Review and Apply to Real-World Problems
Finally, it’s crucial to review the concepts regularly and apply them to real-world problems. Trigonometric differentiation has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and other sciences. By applying these concepts to real-world scenarios, you not only reinforce your understanding but also learn to appreciate the practical value of trigonometric differentiation.
Real-World Applications
For example, in physics, the motion of a pendulum can be modeled using trigonometric functions. The derivative of the position function of the pendulum with respect to time gives the velocity, which is crucial for understanding and predicting the pendulum’s behavior. Similarly, in electrical engineering, trigonometric functions are used to model AC circuits, and differentiation is essential for analyzing these circuits.
What is the derivative of the sine function?
+The derivative of the sine function, denoted as d(sin(x))/dx, is cos(x).
How do I differentiate a composite trigonometric function?
+To differentiate a composite trigonometric function, such as sin(2x), you apply the chain rule. The derivative of sin(2x) with respect to x is cos(2x) times the derivative of 2x with respect to x, which equals 2cos(2x).
What are some real-world applications of trigonometric differentiation?
+Trigonometric differentiation has applications in physics, engineering, and other sciences. It is used to model and analyze periodic phenomena, such as the motion of a pendulum or the behavior of AC circuits in electrical engineering.
In conclusion, mastering trigonometric differentiation requires a combination of understanding the basic derivatives, applying the chain rule, using trigonometric identities, practicing with varied problems, and reviewing and applying the concepts to real-world scenarios. By following these tips and dedicating time to practice, you can enhance your proficiency in trigonometric differentiation and unlock a deeper understanding of the mathematical models that underpin many real-world phenomena.