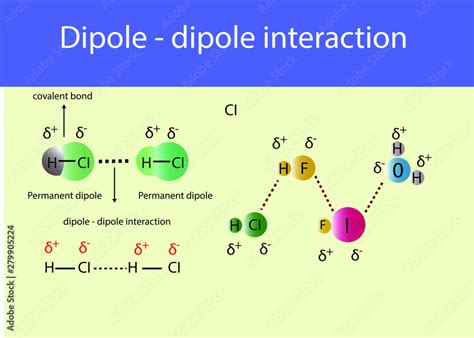
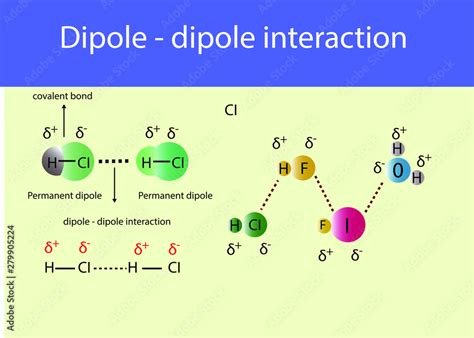
The dipole-dipole interaction is a fundamental concept in chemistry, playing a crucial role in understanding the behavior of molecules and their interactions with each other. This type of interaction occurs between two molecules that have a permanent electric dipole moment, resulting from the unequal sharing of electrons within the molecule. The dipole moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative charges within a molecule, and it is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
In a dipole-dipole interaction, the positive end of one molecule's dipole is attracted to the negative end of another molecule's dipole. This attraction is due to the electrostatic force between the opposite charges, which is a fundamental force of nature. The strength of the dipole-dipole interaction depends on the magnitude of the dipole moments of the interacting molecules and the distance between them. The interaction is stronger when the dipole moments are larger and the distance between the molecules is smaller.
Key Points
- The dipole-dipole interaction is a type of intermolecular force that occurs between molecules with a permanent electric dipole moment.
- The strength of the dipole-dipole interaction depends on the magnitude of the dipole moments and the distance between the molecules.
- Dipole-dipole interactions are responsible for many physical and chemical properties of substances, including melting and boiling points, solubility, and viscosity.
- The dipole-dipole interaction is a key factor in the formation of hydrogen bonds, which are essential for the structure and function of biological molecules.
- Understanding dipole-dipole interactions is crucial for the development of new materials and technologies, such as pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and advanced materials.
Types of Dipole-Dipole Interactions

There are several types of dipole-dipole interactions, including:
- Permanent-Permanent Dipole-Dipole Interaction: This type of interaction occurs between two molecules that have a permanent electric dipole moment. Examples include the interaction between two water molecules (H2O) or between two ammonia molecules (NH3).
- Permanent-Induced Dipole-Dipole Interaction: This type of interaction occurs between a molecule with a permanent electric dipole moment and a molecule that does not have a permanent dipole moment but can be polarized. Examples include the interaction between a water molecule and a carbon dioxide molecule (CO2).
- Induced-Induced Dipole-Dipole Interaction: This type of interaction occurs between two molecules that do not have a permanent electric dipole moment but can be polarized. Examples include the interaction between two methane molecules (CH4).
Factors Affecting Dipole-Dipole Interactions
Several factors can affect the strength and nature of dipole-dipole interactions, including:
- Distance: The strength of the dipole-dipole interaction decreases with increasing distance between the molecules.
- Orientation: The orientation of the molecules relative to each other can affect the strength of the interaction. The interaction is stronger when the dipoles are aligned parallel to each other.
- Temperature: The strength of the dipole-dipole interaction decreases with increasing temperature, as the molecules have more kinetic energy and are less likely to interact with each other.
- Polarity: The polarity of the molecules can affect the strength of the interaction. Polar molecules tend to interact more strongly with each other than non-polar molecules.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Dipole moment of water (H2O) | 1.85 D |
| Dipole moment of ammonia (NH3) | 1.47 D |
| Boiling point of water (H2O) | 100°C |
| Boiling point of ammonia (NH3) | -33°C |
Applications of Dipole-Dipole Interactions

Dipole-dipole interactions have numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Pharmaceuticals: Dipole-dipole interactions play a crucial role in the binding of drugs to their target receptors, which is essential for their therapeutic effect.
- Agrochemicals: Dipole-dipole interactions are involved in the binding of pesticides to their target enzymes, which is essential for their insecticidal or herbicidal activity.
- Advanced Materials: Dipole-dipole interactions can be used to design new materials with specific properties, such as self-healing materials or shape-memory alloys.
What is the difference between a dipole-dipole interaction and a hydrogen bond?
+A dipole-dipole interaction is a type of intermolecular force that occurs between molecules with a permanent electric dipole moment. A hydrogen bond is a specific type of dipole-dipole interaction that occurs between a molecule with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom (such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine) and another molecule that has a lone pair of electrons.
How do dipole-dipole interactions affect the physical properties of substances?
+Dipole-dipole interactions can affect the physical properties of substances, such as melting and boiling points, solubility, and viscosity. The strength of the dipole-dipole interaction can influence the arrangement of molecules in a substance, which can affect its physical properties.
What are some examples of molecules that exhibit dipole-dipole interactions?
+Examples of molecules that exhibit dipole-dipole interactions include water (H2O), ammonia (NH3), and carbon dioxide (CO2). These molecules have a permanent electric dipole moment, which allows them to interact with each other through dipole-dipole interactions.
In conclusion, dipole-dipole interactions are a fundamental concept in chemistry, playing a crucial role in understanding the behavior of molecules and their interactions with each other. By recognizing the factors that affect dipole-dipole interactions and understanding their applications, scientists can design new materials and technologies with specific properties.