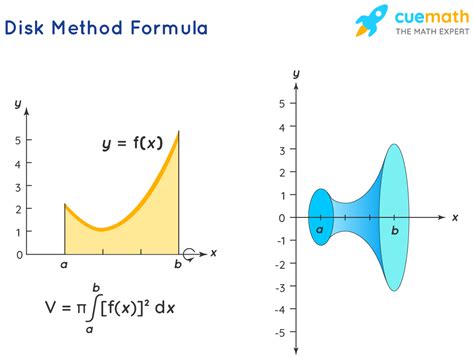
The disk method, also known as the method of disks or washers, is a technique used in calculus to find the volume of a solid of revolution. This method is employed when a region bounded by a curve is rotated about an axis, generating a solid. The disk method formulas are fundamental in calculating the volumes of such solids, and they vary based on the axis of rotation and the function being rotated.
Introduction to Disk Method Formulas
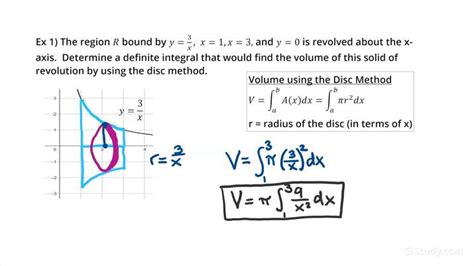
The disk method involves integrating the area of disks formed when the region under a curve is rotated. The formula for the volume of a solid formed by revolving a region about the x-axis is given by (V = \pi \int_{a}^{b} [f(x)]^2 dx), where (f(x)) is the function being rotated, and (a) and (b) are the limits of integration that define the region. This formula is derived from the concept that the volume of each disk is (\pi r^2 h), where (r) is the radius of the disk (given by (f(x)) in this case) and (h) is the thickness of the disk (given by (dx)).
Disk Method Formula for Rotation About the X-axis
When a region bounded by a curve (y = f(x)) and the x-axis is rotated about the x-axis, from (x = a) to (x = b), the volume (V) of the solid formed is given by:
[V = \pi \int_{a}^{b} [f(x)]^2 dx]This formula is widely used and is a direct application of the disk method. For example, if (f(x) = x^2) and the region is from (x = 0) to (x = 2), the volume of the solid formed by rotating this region about the x-axis would be calculated using this formula.
Disk Method Formula for Rotation About the Y-axis
When the region bounded by a curve (x = f(y)) and the y-axis is rotated about the y-axis, from (y = a) to (y = b), the volume (V) of the solid formed is given by:
[V = \pi \int_{a}^{b} [f(y)]^2 dy]This scenario involves functions of (y) and rotation about the y-axis, which is a common variation of the disk method. The approach remains similar, with the integration now being with respect to (y).
Disk Method with Hollow Cylinders (Washer Method)
In cases where the region is bounded by two curves, (f(x)) and (g(x)), and rotated about the x-axis, the volume of the solid formed can be calculated using the washer method, a variation of the disk method. The formula is:
[V = \pi \int_{a}^{b} ([f(x)]^2 - [g(x)]^2) dx]This formula accounts for the hollow center of the solid, subtracting the volume of the inner solid from the outer solid to find the volume of the shell.
| Rotation Axis | Formula |
|---|---|
| X-axis | V = \pi \int_{a}^{b} [f(x)]^2 dx |
| Y-axis | V = \pi \int_{a}^{b} [f(y)]^2 dy |
| Washer Method | V = \pi \int_{a}^{b} ([f(x)]^2 - [g(x)]^2) dx |

Key Points
- The disk method is used for finding the volume of a solid of revolution when a region under a curve is rotated about an axis.
- The formula for rotation about the x-axis is V = \pi \int_{a}^{b} [f(x)]^2 dx.
- The formula for rotation about the y-axis is V = \pi \int_{a}^{b} [f(y)]^2 dy.
- The washer method, for rotation about the x-axis with a hollow center, uses the formula V = \pi \int_{a}^{b} ([f(x)]^2 - [g(x)]^2) dx.
- Correct identification of the function and axis of rotation is key to applying the disk method formulas correctly.
Understanding and applying these disk method formulas requires a solid grasp of calculus principles, particularly integration, and the ability to visualize the solids formed by rotating regions about different axes. With practice, these formulas become essential tools for solving a wide range of problems in mathematics and physics.
What is the primary difference between the disk and washer methods?
+The primary difference lies in the scenario they are applied to. The disk method is used when rotating a single region about an axis, while the washer method is used when the region has a hollow center, bounded by two curves.
How do you choose between rotating about the x-axis or y-axis?
+The choice depends on the function and the region being rotated. If the function is given in terms of x and the region is bounded below and above by curves or the x-axis, rotation about the x-axis is considered. If the function is given in terms of y, rotation about the y-axis is considered.
What are common applications of the disk method?
+The disk method has various applications in physics and engineering, such as calculating volumes of tanks, volumes of solids of revolution in manufacturing, and volumes of irregularly shaped objects.