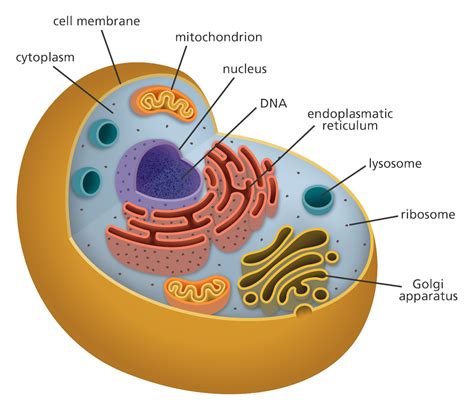
The discovery of DNA in various organelles has revolutionized our understanding of cellular biology. While it's well-known that the nucleus houses the majority of a cell's genetic material, other organelles also contain DNA, playing crucial roles in the cell's functioning and survival. This article delves into the world of five organelles that contain DNA, exploring their structures, functions, and the significance of their genetic material.
Key Points
- The nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, centrioles, and kinetoplasts are organelles that contain DNA.
- Each of these organelles has a unique function and plays a vital role in the cell's overall functioning.
- DNA in these organelles is crucial for the synthesis of proteins, the transmission of genetic information, and the regulation of cellular processes.
- The study of DNA in these organelles has significant implications for our understanding of cellular biology, genetics, and the evolution of life on Earth.
- Understanding the functions and interactions of these organelles can provide insights into various diseases and disorders, including those related to mitochondrial dysfunction and chloroplast abnormalities.
Nucleus: The Control Center of the Cell

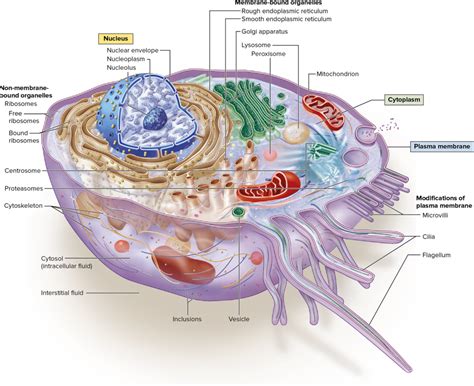
The nucleus is the most prominent organelle containing DNA, often referred to as the “control center” of the cell. It houses the majority of the cell’s genetic material, which is organized into structures called chromosomes. The DNA in the nucleus is responsible for encoding the instructions for the synthesis of proteins, the regulation of cellular processes, and the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which regulates the movement of materials in and out of the nucleus.
Structure and Function of the Nucleus
The nucleus is a complex organelle with a highly organized structure. It contains various subdomains, including the nucleolus, where ribosome synthesis occurs, and the chromatin, which is the complex of DNA and proteins that make up the chromosomes. The nucleus is also the site of transcription, where the information in the DNA is copied into RNA molecules, and translation, where the RNA molecules are used to synthesize proteins.
Mitochondria: The Powerhouses of the Cell
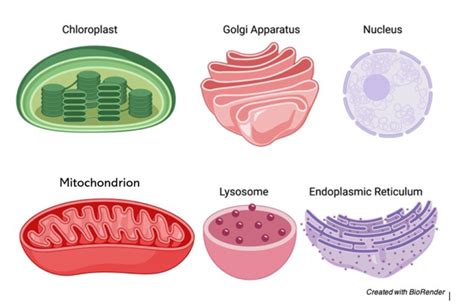
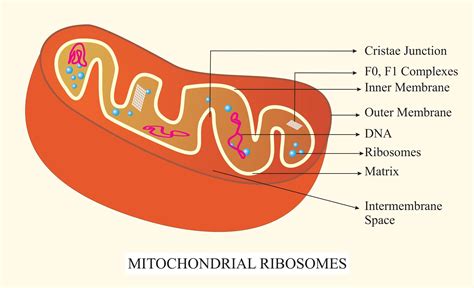
Mitochondria are organelles found in the cells of most eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. They are often referred to as the “powerhouses” of the cell because they generate most of the energy that the cell needs to function. Mitochondria contain their own DNA, known as mtDNA, which is separate from the DNA found in the nucleus. The mtDNA is responsible for encoding some of the proteins involved in energy production, as well as the synthesis of transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules.
Structure and Function of Mitochondria
Mitochondria have a unique structure, with two membranes: an outer membrane and an inner membrane. The inner membrane is folded into a series of cristae, which increase the surface area of the mitochondria and allow for more efficient energy production. Mitochondria are the site of cellular respiration, where the energy from the food we eat is converted into a molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is used to power the cell’s various functions.
Chloroplasts: The Organelles of Photosynthesis
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and some algae, responsible for photosynthesis, the process of converting light energy into chemical energy. Like mitochondria, chloroplasts contain their own DNA, known as cpDNA, which is responsible for encoding some of the proteins involved in photosynthesis. The cpDNA is also responsible for the synthesis of tRNA and rRNA molecules.
Structure and Function of Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts have a complex structure, with two membranes and a series of flattened sacs called thylakoids, where photosynthesis occurs. The thylakoids are stacked into structures called grana, which increase the surface area of the chloroplast and allow for more efficient photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are responsible for producing the energy that plants need to grow and develop, and are also involved in the production of oxygen, which is released into the atmosphere as a byproduct of photosynthesis.
Centrioles: The Organelles of Cilia and Flagella
Centrioles are small, cylindrical organelles found in the cells of most eukaryotes. They are involved in the formation of cilia and flagella, which are hair-like structures that project from the surface of the cell and are used for movement and sensing the environment. Centrioles contain a small amount of DNA, which is responsible for encoding some of the proteins involved in the formation and maintenance of cilia and flagella.
Structure and Function of Centrioles
Centrioles have a highly organized structure, with a series of microtubules that are arranged in a specific pattern. They are involved in the formation of the axoneme, which is the core structure of cilia and flagella. Centrioles are also involved in the regulation of the cell cycle, and play a role in the formation of the spindle fibers that separate the chromosomes during cell division.
Kinetoplasts: The Organelles of Trypanosomes
Kinetoplasts are organelles found in the cells of trypanosomes, which are a type of protozoan parasite. They contain a large amount of DNA, which is responsible for encoding some of the proteins involved in the metabolism and survival of the parasite. Kinetoplasts are unique in that they contain a network of interlocked DNA molecules, which are responsible for the parasite’s ability to evade the host’s immune system.
Structure and Function of Kinetoplasts
Kinetoplasts have a complex structure, with a series of DNA molecules that are interlocked and twisted together. They are involved in the regulation of the parasite’s metabolism, and play a role in the parasite’s ability to survive and thrive in the host. Kinetoplasts are also involved in the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next, and are responsible for the parasite’s ability to evolve and adapt to changing environments.
| Organelle | Function | DNA Content |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Control center of the cell | Majority of cellular DNA |
| Mitochondria | Energy production | mtDNA, responsible for encoding some proteins involved in energy production |
| Chloroplasts | Photosynthesis | cpDNA, responsible for encoding some proteins involved in photosynthesis |
| Centrioles | Formation of cilia and flagella | Small amount of DNA, responsible for encoding some proteins involved in cilia and flagella formation |
| Kinetoplasts | Metabolism and survival of trypanosomes | Large amount of DNA, responsible for encoding some proteins involved in metabolism and survival |
What is the function of the nucleus in a cell?
+The nucleus is the control center of the cell, responsible for housing the majority of the cell’s genetic material and regulating the cell’s growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
What is the role of mitochondria in energy production?
+Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, responsible for generating most of the energy that the cell needs to function through the process of cellular respiration.
What is the function of chloroplasts in plant cells?
+Chloroplasts are the organelles responsible for photosynthesis, the process of converting light energy into chemical energy, which is used to power the plant’s growth and development.
What is the role of centrioles in the formation of cilia and flagella?
+Centrioles are involved in the formation of cilia and flagella, which are hair-like structures that project from the surface of the cell and are used for movement and sensing the environment.
What is the function of kinetoplasts in trypanosomes?
+Kinetoplasts are involved in the regulation of the parasite’s metabolism and survival, and play a role in the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.