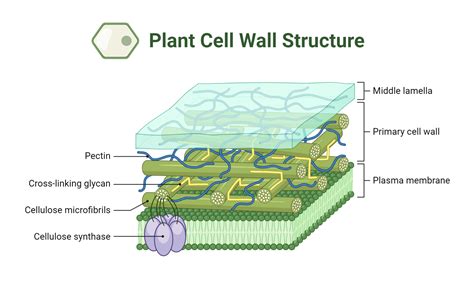
Plants are complex organisms that have evolved over millions of years to thrive in a wide range of environments. One of the key features that distinguish plants from other living things is the presence of cell walls. Cell walls are rigid structures that provide support, protection, and shape to plant cells. They are composed of a variety of materials, including cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin, which are synthesized by the plant cell and deposited outside the cell membrane. In this article, we will explore the structure, function, and importance of plant cell walls, as well as their role in plant growth and development.
The plant cell wall is a dynamic structure that plays a critical role in plant growth and development. It is composed of three main layers: the primary cell wall, the secondary cell wall, and the middle lamella. The primary cell wall is the outermost layer and is composed of a mixture of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin. The secondary cell wall is thicker and more rigid than the primary cell wall and is composed of a higher proportion of cellulose. The middle lamella is a thin layer of pectin that separates adjacent plant cells and helps to hold them together. The composition and structure of the plant cell wall can vary depending on the type of plant, the age of the plant, and the environmental conditions in which it is growing.
Key Points
- Plant cell walls are composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin
- The primary cell wall is the outermost layer and is composed of a mixture of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin
- The secondary cell wall is thicker and more rigid than the primary cell wall and is composed of a higher proportion of cellulose
- The middle lamella is a thin layer of pectin that separates adjacent plant cells and helps to hold them together
- Plant cell walls play a critical role in plant growth and development, providing support, protection, and shape to plant cells
Structure and Function of Plant Cell Walls
The structure and function of plant cell walls are closely linked. The cell wall provides mechanical support to the plant cell, allowing it to maintain its shape and withstand external forces such as wind and rain. It also provides protection to the plant cell, preventing damage from pathogens and insects. In addition, the cell wall plays a critical role in plant growth and development, regulating cell expansion and division. The cell wall is also involved in cell signaling, allowing plant cells to communicate with each other and respond to environmental stimuli.
Cell Wall Composition
The composition of the plant cell wall can vary depending on the type of plant, the age of the plant, and the environmental conditions in which it is growing. However, the main components of the plant cell wall are cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin. Cellulose is a polysaccharide composed of glucose molecules and is the most abundant component of the plant cell wall. Hemicellulose is a polysaccharide composed of xylose, arabinose, and galactose molecules and is present in smaller amounts than cellulose. Pectin is a polysaccharide composed of galacturonic acid molecules and is present in the middle lamella, where it helps to hold adjacent plant cells together.
| Cell Wall Component | Composition |
|---|---|
| Cellulose | Glucose molecules |
| Hemicellulose | Xylose, arabinose, and galactose molecules |
| Pectin | Galacturonic acid molecules |
Importance of Plant Cell Walls
Plant cell walls are essential for plant growth and development. They provide mechanical support to the plant cell, allowing it to maintain its shape and withstand external forces. They also provide protection to the plant cell, preventing damage from pathogens and insects. In addition, plant cell walls play a critical role in plant signaling, allowing plant cells to communicate with each other and respond to environmental stimuli. The plant cell wall is also involved in plant defense, providing a physical barrier against pathogens and insects.
Plant Cell Wall and Plant Defense
The plant cell wall plays a critical role in plant defense, providing a physical barrier against pathogens and insects. The cell wall can be modified in response to pathogen attack, with the deposition of additional cell wall components such as callose and lignin. These modifications can help to prevent pathogen penetration and reduce the spread of disease. The plant cell wall can also be involved in the production of defense-related compounds, such as phytoalexins and terpenes, which can help to deter pathogens and insects.
What is the main component of the plant cell wall?
+The main component of the plant cell wall is cellulose, a polysaccharide composed of glucose molecules.
What is the function of the middle lamella in the plant cell wall?
+The middle lamella is a thin layer of pectin that separates adjacent plant cells and helps to hold them together.
What is the role of the plant cell wall in plant defense?
+The plant cell wall plays a critical role in plant defense, providing a physical barrier against pathogens and insects and involved in the production of defense-related compounds.
In conclusion, plant cell walls are complex structures that play a critical role in plant growth and development. They provide mechanical support, protection, and shape to plant cells, and are involved in plant signaling, defense, and communication. The composition and structure of the plant cell wall can vary depending on the type of plant, the age of the plant, and the environmental conditions in which it is growing. Understanding the structure and function of plant cell walls is essential for understanding plant biology and can have significant implications for agriculture, forestry, and biotechnology.