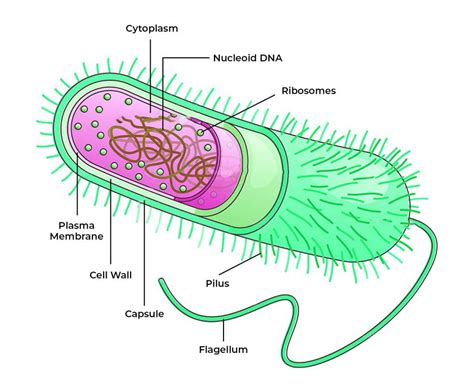
The bacterium, a type of microscopic, single-celled organism, has been a subject of fascination for scientists and researchers for centuries. One of the most distinctive features of bacteria is the lack of a true nucleus, which sets them apart from other types of cells, such as eukaryotic cells. In this article, we will delve into the world of bacteria and explore the implications of not having a nucleus, as well as the unique characteristics that have allowed these organisms to thrive in a wide range of environments.
Cell Structure and Function

Bacteria are prokaryotic cells, meaning that they do not have a membrane-bound nucleus. Instead, their genetic material, which is composed of a single circular chromosome, is found in a region of the cell called the nucleoid. The nucleoid is not surrounded by a membrane and is often attached to the cell wall. This lack of a nucleus has significant implications for the way that bacteria function and interact with their environment. For example, bacteria are able to reproduce quickly and efficiently, with some species able to divide and form new cells in as little as 20 minutes.
Reproduction and Genetics
The lack of a nucleus in bacteria also affects their reproductive processes. Bacteria reproduce through a process called binary fission, in which the cell divides into two identical daughter cells. This process is relatively simple and does not involve the complex mechanisms of mitosis and meiosis that are found in eukaryotic cells. Additionally, bacteria are able to exchange genetic material with other bacteria through a process called conjugation, which allows them to share genes and acquire new traits.
| Characteristics | Bacteria | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | No true nucleus | Membrane-bound nucleus |
| Genetic Material | Single circular chromosome | Multiple linear chromosomes |
| Reproduction | Binary fission | Mitosis and meiosis |
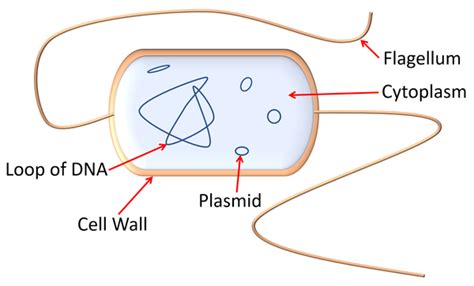
Key Points
- Bacteria do not have a true nucleus, but instead have a nucleoid that contains their genetic material.
- The lack of a nucleus affects the way that bacteria function and interact with their environment.
- Bacteria reproduce through a process called binary fission, which is relatively simple and efficient.
- Bacteria are able to exchange genetic material with other bacteria through a process called conjugation.
- The unique characteristics of bacteria have allowed them to thrive in a wide range of environments.
Evolutionary History
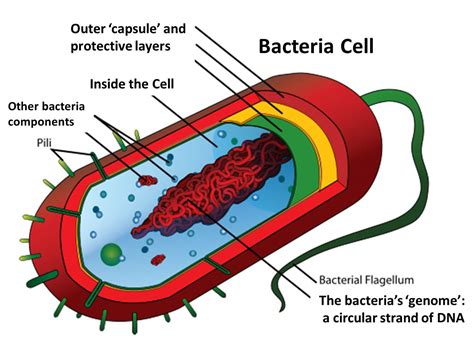
Bacteria have been on the planet for billions of years, and their evolutionary history is complex and fascinating. The earliest bacteria are thought to have evolved around 3.5 billion years ago, during a time when the Earth’s atmosphere was very different from what it is today. Over time, bacteria have evolved and adapted to their environments, developing new traits and characteristics that have allowed them to thrive in a wide range of ecosystems.
Phylogeny and Classification
Bacteria are classified into different groups based on their phylogeny, or evolutionary history. There are several different types of bacteria, including Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, which are distinguished by the composition of their cell walls. Additionally, bacteria can be classified based on their metabolism, with some species able to photosynthesize and others able to degrade complex organic molecules.
Understanding the evolutionary history and classification of bacteria is important for a number of reasons. For example, it can help us to understand the origins of antibiotic resistance, which is a major public health concern. Additionally, it can help us to develop new treatments and therapies for bacterial infections, which are a major cause of morbidity and mortality around the world.
What is the main difference between bacteria and eukaryotic cells?
+The main difference between bacteria and eukaryotic cells is the presence or absence of a true nucleus. Bacteria do not have a membrane-bound nucleus, while eukaryotic cells do.
How do bacteria reproduce?
+Bacteria reproduce through a process called binary fission, in which the cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
What is conjugation in bacteria?
+Conjugation is a process by which bacteria exchange genetic material with other bacteria. This allows them to share genes and acquire new traits.
In conclusion, the bacterium’s lack of a nucleus is a unique characteristic that has significant implications for its function and behavior. Through their ability to reproduce quickly and efficiently, exchange genetic material, and adapt to their environments, bacteria have been able to thrive in a wide range of ecosystems. Understanding the biology and evolution of bacteria is essential for developing new treatments and therapies for bacterial infections, and for appreciating the important role that these organisms play in our world.