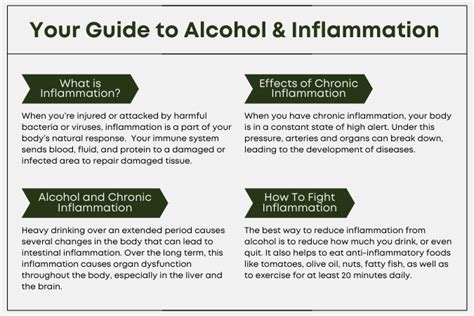
Alcohol consumption has been a longstanding aspect of human culture, with its effects on the body being a subject of extensive study. One of the critical areas of interest is the relationship between alcohol and inflammation. Inflammation is a natural response of the body's immune system, intended to protect against harm, such as infections and injuries. However, chronic inflammation can lead to various health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and even certain types of cancer. The question of whether alcohol causes inflammation is complex, as the answer depends on several factors, including the amount and frequency of alcohol consumption, the type of alcoholic beverage, and individual differences in metabolism and health status.
Understanding Alcohol and Inflammation

Research has shown that moderate alcohol consumption may have anti-inflammatory effects in some cases, while excessive drinking can lead to increased inflammation. Moderate drinking is typically defined as up to one drink a day for women and up to two drinks a day for men. A drink is usually considered to be 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1.5 ounces of distilled spirits. The anti-inflammatory effects of moderate alcohol consumption are thought to be due to its ability to increase levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), the “good” cholesterol, and to reduce levels of fibrinogen, a protein that can contribute to blood clotting and inflammation.
The Impact of Excessive Alcohol Consumption
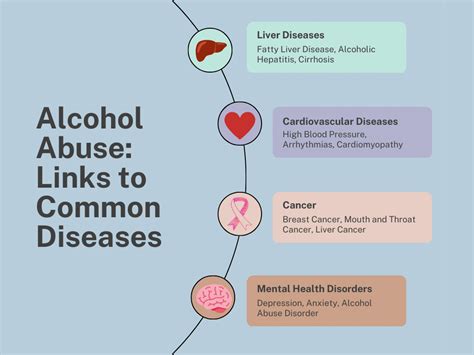
On the other hand, excessive alcohol consumption is associated with increased inflammation. This is because alcohol can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome, leading to the release of pro-inflammatory substances into the bloodstream. Furthermore, alcohol can directly damage liver cells, leading to the release of inflammatory chemicals. Chronic inflammation caused by excessive alcohol consumption can lead to a range of health problems, including alcoholic liver disease, which can progress from fatty liver to cirrhosis and even liver cancer.
| Alcohol Consumption Level | Inflammation Effect |
|---|---|
| Moderate | Potential anti-inflammatory effects |
| Excessive | Increased inflammation |
| Chronic | Lead to health issues like liver disease and cancer |
Key Points
- Moderate alcohol consumption may have anti-inflammatory effects, but excessive drinking leads to increased inflammation.
- The type of alcoholic beverage and individual differences in metabolism and health status can influence the impact of alcohol on inflammation.
- Excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt the gut microbiome and directly damage liver cells, contributing to chronic inflammation.
- Chronic inflammation associated with alcohol consumption can lead to serious health issues, including liver disease and certain types of cancer.
- Understanding the relationship between alcohol and inflammation is crucial for making informed decisions about alcohol consumption and maintaining overall health.
Reducing Inflammation through Lifestyle Changes

For individuals who choose to consume alcohol, reducing the risk of inflammation involves maintaining a moderate consumption level and adopting a healthy lifestyle. This includes a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, regular physical activity, not smoking, and managing stress. Additionally, ensuring adequate sleep and staying hydrated are important for overall health and can help mitigate the negative effects of alcohol on the body.
Nutritional Considerations
Certain nutrients have anti-inflammatory properties and can help counteract the inflammatory effects of alcohol. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, and antioxidants such as vitamins C and E, can be beneficial. Furthermore, a diet high in fiber can support the health of the gut microbiome, potentially reducing the inflammatory impact of alcohol.
It's also important to consider the role of alcohol in the context of other lifestyle factors. For example, smoking and alcohol consumption can have synergistic harmful effects on health, increasing the risk of certain cancers and cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake are critical for reducing overall health risks.
Can moderate alcohol consumption be part of a healthy lifestyle?
+For some individuals, moderate alcohol consumption may not have significant negative health effects and can even be associated with certain health benefits. However, it's essential to consider individual health status, family history, and other lifestyle factors.
How can I reduce the risk of inflammation associated with alcohol consumption?
+Maintaining a moderate drinking level, adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and not smoking are key strategies. Additionally, managing stress and ensuring adequate sleep can help reduce overall inflammation.
Is it possible to reverse the inflammatory effects of chronic alcohol consumption?
+Stopping or significantly reducing alcohol consumption can help mitigate the inflammatory effects over time. Combining this with a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can support the body's natural healing processes and reduce inflammation.
In conclusion, the relationship between alcohol and inflammation is complex and influenced by a variety of factors. While moderate alcohol consumption may have anti-inflammatory effects for some, excessive drinking can lead to chronic inflammation and serious health issues. By understanding this relationship and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can make informed decisions about alcohol consumption and work towards reducing their risk of inflammation-related health problems.