Ear infections, also known as otitis media, are a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. The primary cause of ear infections is bacterial or viral pathogens that invade the middle ear, leading to inflammation and fluid buildup. Amoxicillin, a broad-spectrum antibiotic, is often prescribed to treat ear infections. However, the effectiveness of amoxicillin in treating ear infections depends on various factors, including the type of infection, severity, and patient's overall health.
Understanding Ear Infections
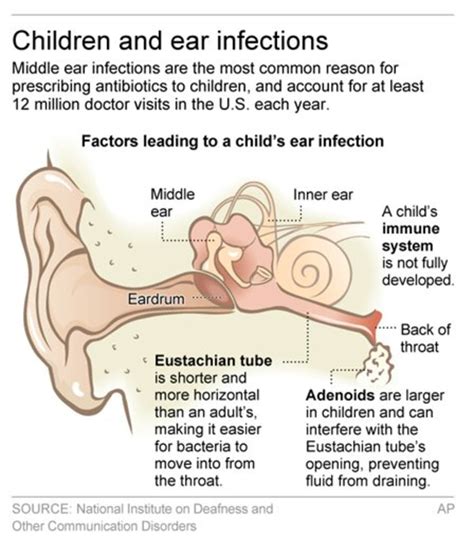
Ear infections can be categorized into three main types: acute otitis media (AOM), otitis media with effusion (OME), and chronic otitis media. AOM is a sudden onset of ear infection, often accompanied by fever, ear pain, and discharge. OME is a condition where fluid accumulates in the middle ear, often without symptoms. Chronic otitis media is a recurring or persistent ear infection. The primary cause of ear infections is bacterial pathogens, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis.
Amoxicillin: Mechanism of Action
Amoxicillin is a beta-lactam antibiotic that works by inhibiting the growth of bacterial cell walls. It is effective against a wide range of bacterial pathogens, including those that cause ear infections. Amoxicillin is often prescribed in combination with clavulanic acid, a beta-lactamase inhibitor, to enhance its effectiveness against beta-lactamase-producing bacteria.
| Antibiotic | Effectiveness against Ear Infection Pathogens |
|---|---|
| Amoxicillin | Effective against S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, and M. catarrhalis |
| Amoxicillin-Clavulanic Acid | Effective against beta-lactamase-producing H. influenzae and M. catarrhalis |
Treatment Guidelines and Recommendations
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) provide guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of ear infections. According to these guidelines, amoxicillin is recommended as a first-line treatment for AOM in children and adults. However, the guidelines also emphasize the importance of watchful waiting and symptom management for mild cases of ear infections.
Key Considerations and Limitations
While amoxicillin is effective in treating ear infections, there are limitations and considerations to be aware of. Resistance to amoxicillin is increasing among certain bacterial pathogens, such as S. pneumoniae. Additionally, amoxicillin may not be effective against viral ear infections, and its use in such cases may contribute to antibiotic resistance. It is essential to use amoxicillin judiciously and only when necessary, as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Key Points
- Amoxicillin is effective against bacterial ear infections, including those caused by S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, and M. catarrhalis
- Amoxicillin is not effective against viral ear infections, which account for approximately 60% of all ear infections
- Accurate diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent unnecessary antibiotic use and promote effective management of ear infections
- The AAP and AAFP recommend amoxicillin as a first-line treatment for AOM in children and adults
- Watchful waiting and symptom management are recommended for mild cases of ear infections
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, amoxicillin is a commonly prescribed antibiotic for the treatment of ear infections. While it is effective against bacterial pathogens, its use should be judicious and guided by accurate diagnosis and treatment guidelines. As antibiotic resistance continues to rise, it is essential to promote responsible antibiotic use and develop new treatment strategies for ear infections. Further research is needed to explore alternative treatments, such as vaccines and probiotics, and to improve our understanding of the complex interactions between the host, pathogen, and environment in ear infections.
What are the common causes of ear infections?
+Ear infections are commonly caused by bacterial pathogens, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis, as well as viral pathogens.
How effective is amoxicillin in treating ear infections?
+Amoxicillin is effective against bacterial ear infections, including those caused by S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, and M. catarrhalis. However, its effectiveness depends on various factors, including the type of infection, severity, and patient's overall health.
What are the potential limitations and risks of using amoxicillin to treat ear infections?
+The potential limitations and risks of using amoxicillin to treat ear infections include antibiotic resistance, side effects, and the potential for unnecessary antibiotic use. It is essential to use amoxicillin judiciously and only when necessary, as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Meta Description: Amoxicillin is a commonly prescribed antibiotic for ear infections, but its effectiveness depends on various factors. Learn about the causes, diagnosis, and treatment of ear infections, as well as the potential limitations and risks of using amoxicillin. (147 characters)