The cell wall is a critical component of plant, bacterial, and fungal cells, providing structural support, protection, and maintaining cellular shape. In this article, we'll delve into the fascinating world of cell walls, exploring their composition, functions, and significance in various biological contexts. With a deep understanding of cell wall biology, researchers and scientists can better appreciate the intricacies of cellular life and develop innovative solutions for various applications, from agriculture to biotechnology.
Cell Wall Composition and Structure
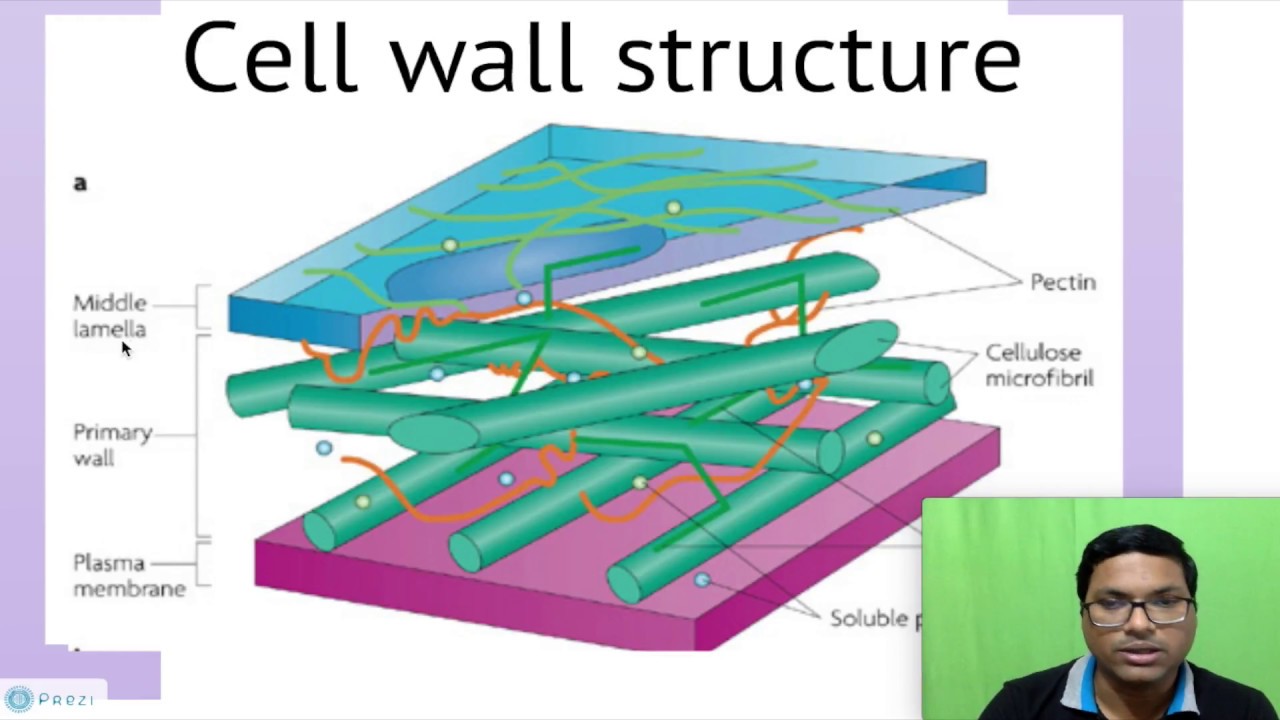
The cell wall is a complex structure composed of various biomolecules, including carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. In plant cells, the primary components of the cell wall are cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin, which provide rigidity, flexibility, and adhesion, respectively. The cellulose microfibrils, in particular, are embedded in a matrix of hemicellulose and pectin, forming a strong yet dynamic network. This intricate structure allows plant cells to withstand mechanical stress, maintain their shape, and regulate cellular growth. Cell wall composition can vary significantly between different species, tissues, and even cell types, reflecting the diverse functional requirements of various biological systems.
Functions of the Cell Wall
Beyond its structural role, the cell wall plays a crucial part in cellular communication, defense, and environmental interactions. In plants, the cell wall acts as a barrier against pathogens, insects, and abiotic stresses, such as drought and extreme temperatures. The cell wall also regulates the exchange of nutrients, water, and signaling molecules between the cell and its surroundings. Furthermore, the cell wall is involved in cell-cell interactions, influencing tissue development, patterning, and differentiation. By understanding the multifaceted functions of the cell wall, researchers can develop novel strategies for improving crop yields, enhancing plant disease resistance, and optimizing biotechnological applications.
| Cell Wall Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Cellulose | Provides structural support and rigidity |
| Hemicellulose | Contributes to cell wall flexibility and adhesion |
| Pectin | Regulates cell-cell adhesion and cellular growth |
Key Points
- The cell wall is a critical component of plant, bacterial, and fungal cells, providing structural support, protection, and maintaining cellular shape.
- Cell wall composition can vary significantly between different species, tissues, and even cell types, reflecting the diverse functional requirements of various biological systems.
- The cell wall plays a crucial part in cellular communication, defense, and environmental interactions, regulating the exchange of nutrients, water, and signaling molecules between the cell and its surroundings.
- Understanding the multifaceted functions of the cell wall can inform the development of novel strategies for improving crop yields, enhancing plant disease resistance, and optimizing biotechnological applications.
- The cell wall is a dynamic, responsive structure that plays a vital role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating interactions with the environment.
Cell Wall Biology in Different Organisms

While the cell wall is a ubiquitous feature of plant, bacterial, and fungal cells, its composition, structure, and function can vary significantly between different organisms. In bacteria, the cell wall is composed of peptidoglycan, which provides structural support and maintains cellular shape. In fungi, the cell wall is composed of chitin, glucan, and other polysaccharides, which regulate cellular growth, differentiation, and interactions with the environment. By exploring the diversity of cell wall biology across different organisms, researchers can gain insights into the evolution of cellular structures and develop novel strategies for biotechnological innovation.
Biotechnological Applications of Cell Wall Research
Cell wall research has numerous biotechnological applications, ranging from the development of novel biofuels and biomaterials to the improvement of crop yields and disease resistance. By understanding the complex interactions between cell wall components and cellular processes, researchers can engineer microorganisms for the production of biofuels, such as ethanol and butanol. Additionally, cell wall research can inform the development of novel biomaterials, such as bioplastics and biocomposites, which have potential applications in packaging, textiles, and construction. Biotechnological innovation in the field of cell wall research can have significant economic, environmental, and social impacts, contributing to a more sustainable and equitable future.
What is the primary function of the cell wall in plant cells?
+The primary function of the cell wall in plant cells is to provide structural support, protection, and maintain cellular shape, while also regulating cellular growth, differentiation, and interactions with the environment.
How does the cell wall composition vary between different species and tissues?
+Cell wall composition can vary significantly between different species, tissues, and even cell types, reflecting the diverse functional requirements of various biological systems. For example, plant cell walls are composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin, while bacterial cell walls are composed of peptidoglycan.
What are some biotechnological applications of cell wall research?
+Cell wall research has numerous biotechnological applications, ranging from the development of novel biofuels and biomaterials to the improvement of crop yields and disease resistance. By understanding the complex interactions between cell wall components and cellular processes, researchers can engineer microorganisms for the production of biofuels, such as ethanol and butanol.
Meta description suggestion: “Discover the fascinating world of cell walls, exploring their composition, functions, and significance in various biological contexts, from plant and bacterial cells to biotechnological applications.” (150 characters)