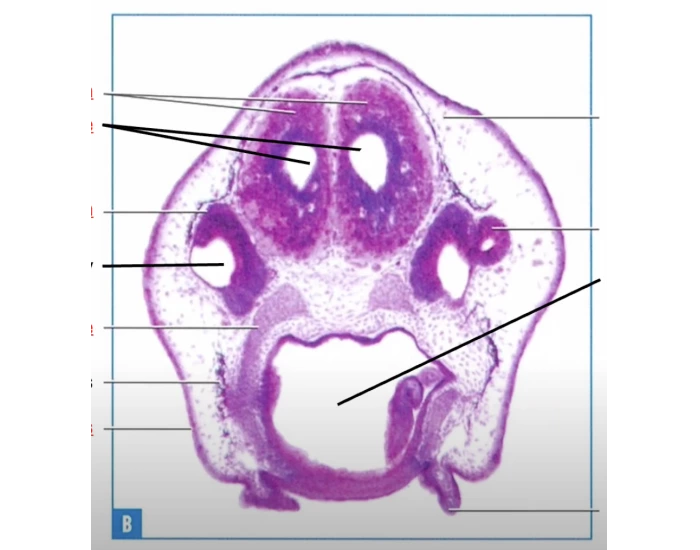
The study of tadpole development, particularly focusing on their dorsal aspects, offers fascinating insights into the biology and evolution of amphibians. Tadpoles, the larval stage of frogs and toads, undergo a dramatic transformation as they develop into adult forms. Here, we delve into five key facts about the dorsal aspects of tadpoles, exploring their development, anatomy, and the significance of these characteristics in their survival and metamorphosis.
Introduction to Tadpole Dorsal Anatomy
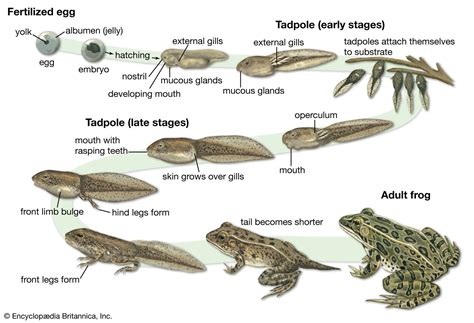
Understanding the dorsal anatomy of tadpoles is essential for appreciating their development and evolutionary adaptations. The dorsal side of a tadpole refers to its back or upper side, contrasting with the ventral side, which is the belly or lower side. This anatomy is crucial for tadpoles’ locomotion, feeding, and defense mechanisms. For instance, the dorsal fin, a prominent feature in many tadpole species, plays a significant role in swimming and maneuverability. The dorsal fin’s size and shape can vary significantly among species, influencing the tadpole’s ability to navigate through different aquatic environments.
Dorsal Developmental Stages
The development of tadpoles’ dorsal features is a complex process, influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. From the moment of hatching, tadpoles begin to develop their dorsal structures, including the neural tube, which eventually gives rise to the brain and spinal cord. As they grow, the dorsal fin becomes more pronounced, and in some species, additional dorsal features such as the formation of the vertebral column and the development of skin and muscle layers occur. The rate and pattern of this development can be affected by factors such as water temperature, availability of food, and the presence of predators, highlighting the intricate relationship between the tadpole’s biology and its environment.
| Developmental Stage | Dorsal Feature Development |
|---|---|
| Early Hatchling | Neural tube formation, initial dorsal fin development |
| Late Hatchling | Expansion of dorsal fin, initial formation of vertebral column |
| Feeding Tadpole | Further development of dorsal fin, muscle and skin layer formation |
| Metamorphic Tadpole | Regression of dorsal fin, completion of vertebral column and skin development |

Adaptations and Survival Strategies
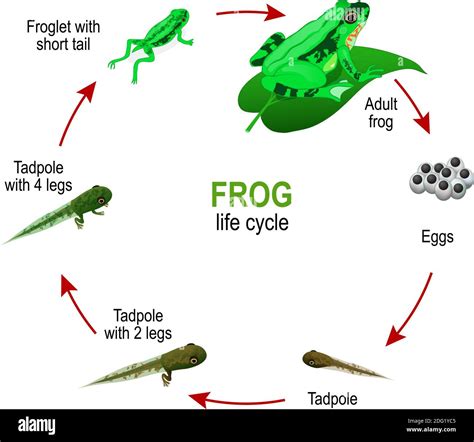
Tadpoles’ dorsal adaptations are not merely developmental stages but also critical survival strategies. The dorsal fin, for example, aids in balance and maneuverability, allowing tadpoles to evade predators more effectively. In addition, the skin on the dorsal side of many tadpole species contains toxic secretions or camouflage patterns, further enhancing their defense against predators. These adaptations highlight the complex interplay between the tadpole’s biology and its environment, where dorsal features play a pivotal role in survival and successful metamorphosis into adult amphibians.
Evidence of Evolutionary Divergence
The study of tadpoles’ dorsal features also provides valuable insights into evolutionary biology. Different species of tadpoles exhibit a wide range of dorsal adaptations, reflecting their evolutionary history and the pressures of their environments. For instance, tadpoles living in fast-flowing streams may develop more pronounced dorsal fins to improve their swimming abilities, whereas those in still waters may have less need for such adaptations. This diversity in dorsal anatomy is a testament to the evolutionary flexibility of amphibians and their ability to thrive in a variety of ecosystems.
Key Points
- The dorsal anatomy of tadpoles is crucial for their locomotion, feeding, and defense mechanisms.
- The development of dorsal features in tadpoles is influenced by genetic and environmental factors.
- Dorsal adaptations in tadpoles, such as the dorsal fin and toxic skin secretions, are key survival strategies.
- The diversity in dorsal anatomy among tadpole species reflects their evolutionary history and environmental pressures.
- Understanding tadpole dorsal anatomy and development is essential for appreciating the biology and evolution of amphibians.
In conclusion, the dorsal aspects of tadpoles offer a fascinating area of study, revealing not only the intricacies of amphibian development but also the evolutionary adaptations that have allowed these creatures to thrive in diverse aquatic environments. By examining the development, anatomy, and significance of dorsal features in tadpoles, we gain a deeper understanding of the complex interplay between biology, environment, and evolution.
What is the primary function of the dorsal fin in tadpoles?
+The primary function of the dorsal fin in tadpoles is to aid in balance and maneuverability, enhancing their swimming abilities and helping them evade predators.
How do environmental factors influence the development of dorsal features in tadpoles?
+Environmental factors such as water temperature, availability of food, and the presence of predators can influence the rate and pattern of dorsal feature development in tadpoles, highlighting the intricate relationship between the tadpole’s biology and its environment.
What is the significance of studying the dorsal anatomy of tadpoles?
+Studying the dorsal anatomy of tadpoles provides valuable insights into their development, evolutionary adaptations, and survival strategies, offering a deeper understanding of the biology and evolution of amphibians.