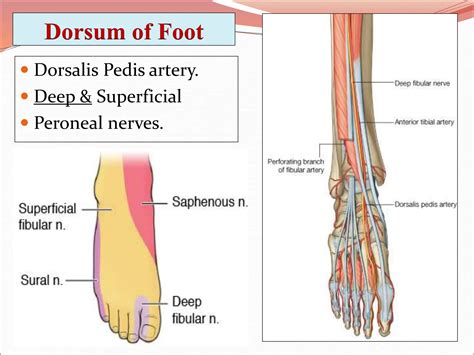
The dorsum of the foot, also known as the top of the foot, is a complex anatomical region that plays a crucial role in our daily activities, including walking, running, and balance. Understanding the anatomy of the dorsum of the foot is essential for diagnosing and treating various foot-related conditions. In this article, we will delve into the details of the dorsum of the foot anatomy, exploring its structure, function, and clinical significance.
Key Points
- The dorsum of the foot is composed of several layers, including skin, fascia, and muscles.
- The extensor tendons, including the extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus, play a crucial role in toe extension.
- The dorsal foot muscles, such as the extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis brevis, contribute to toe movement and stability.
- The dorsum of the foot is richly supplied with blood vessels and nerves, including the dorsal pedal artery and the deep peroneal nerve.
- Understanding the anatomy of the dorsum of the foot is essential for diagnosing and treating various foot-related conditions, such as foot drop and toe deformities.
Layers of the Dorsum of the Foot
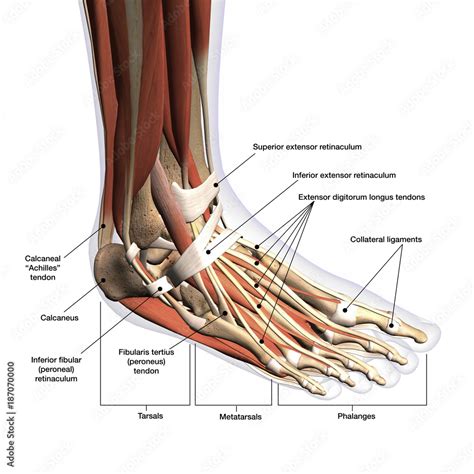
The dorsum of the foot is composed of several layers, each with its unique characteristics and functions. The outermost layer is the skin, which provides a protective barrier against external forces and pathogens. Beneath the skin lies the fascia, a layer of connective tissue that supports the underlying muscles and tendons. The fascia is further divided into two layers: the superficial fascia and the deep fascia.
Superficial Fascia
The superficial fascia is a thin layer of connective tissue that lies just beneath the skin. It is composed of loose areolar tissue and contains a network of blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels. The superficial fascia plays a crucial role in regulating temperature and facilitating the exchange of nutrients and waste products.
Deep Fascia
The deep fascia, also known as the plantar fascia, is a thicker layer of connective tissue that surrounds the muscles and tendons of the foot. It is composed of dense collagen fibers and provides support and stability to the foot. The deep fascia is further divided into two layers: the superficial layer and the deep layer.
| Layer | Description |
|---|---|
| Superficial Fascia | Thin layer of connective tissue beneath the skin |
| Deep Fascia | Thicker layer of connective tissue surrounding muscles and tendons |
| Superficial Layer | Outer layer of the deep fascia |
| Deep Layer | Inner layer of the deep fascia |
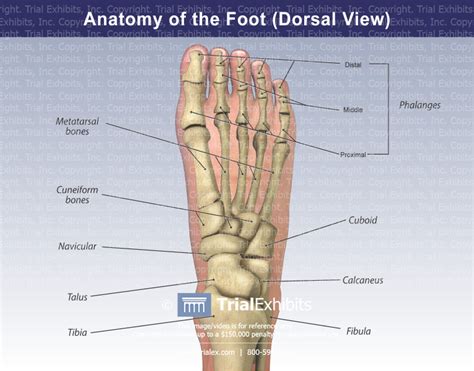
Muscles of the Dorsum of the Foot
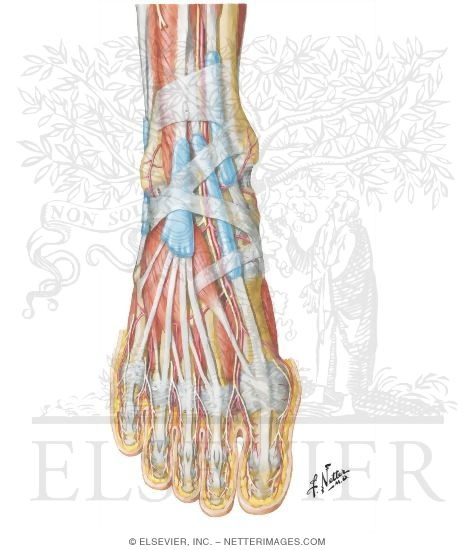
The muscles of the dorsum of the foot play a crucial role in toe movement and stability. The extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis brevis are two of the most important muscles in this region. The extensor digitorum brevis is responsible for extending the toes, while the extensor hallucis brevis is responsible for extending the big toe.
Extensor Tendons
The extensor tendons, including the extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus, play a crucial role in toe extension. These tendons are located on the dorsal surface of the foot and are surrounded by a synovial sheath. The extensor hallucis longus tendon is responsible for extending the big toe, while the extensor digitorum longus tendon is responsible for extending the other toes.
Blood Supply and Nerve Innervation
The dorsum of the foot is richly supplied with blood vessels and nerves. The dorsal pedal artery, which arises from the anterior tibial artery, is the main blood vessel that supplies the dorsum of the foot. The deep peroneal nerve, which arises from the common peroneal nerve, is the main nerve that innervates the muscles of the dorsum of the foot.
Clinical Significance
Understanding the anatomy of the dorsum of the foot is essential for diagnosing and treating various foot-related conditions. Foot drop, a condition characterized by weakness or paralysis of the muscles that control toe movement, is a common condition that affects the dorsum of the foot. Toe deformities, such as hammertoes and claw toes, are also common conditions that affect the dorsum of the foot.
What is the main function of the extensor digitorum brevis muscle?
+The main function of the extensor digitorum brevis muscle is to extend the toes.
What is the name of the main blood vessel that supplies the dorsum of the foot?
+The main blood vessel that supplies the dorsum of the foot is the dorsal pedal artery.
What is the name of the condition characterized by weakness or paralysis of the muscles that control toe movement?
+The condition characterized by weakness or paralysis of the muscles that control toe movement is called foot drop.
In conclusion, the dorsum of the foot is a complex anatomical region that plays a crucial role in our daily activities. Understanding the anatomy of the dorsum of the foot, including its layers, muscles, and blood supply, is essential for diagnosing and treating various foot-related conditions. By recognizing the importance of the dorsum of the foot, we can take steps to prevent injuries and promote overall foot health.