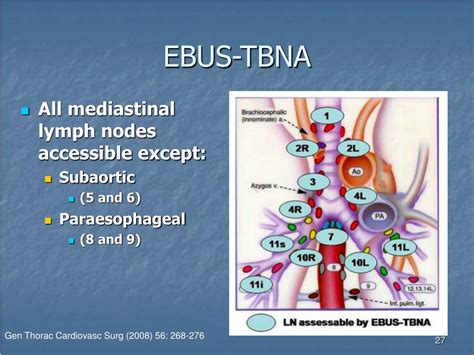
The medical field is replete with abbreviations, each serving a specific purpose to streamline communication among healthcare professionals. One such abbreviation is EBUS, which stands for Endobronchial Ultrasound. EBUS is a minimally invasive procedure used to diagnose and stage lung cancer, as well as other diseases affecting the lungs and mediastinum. It combines endoscopy and ultrasound imaging, allowing physicians to visualize the airways and surrounding structures in real-time.
Understanding EBUS
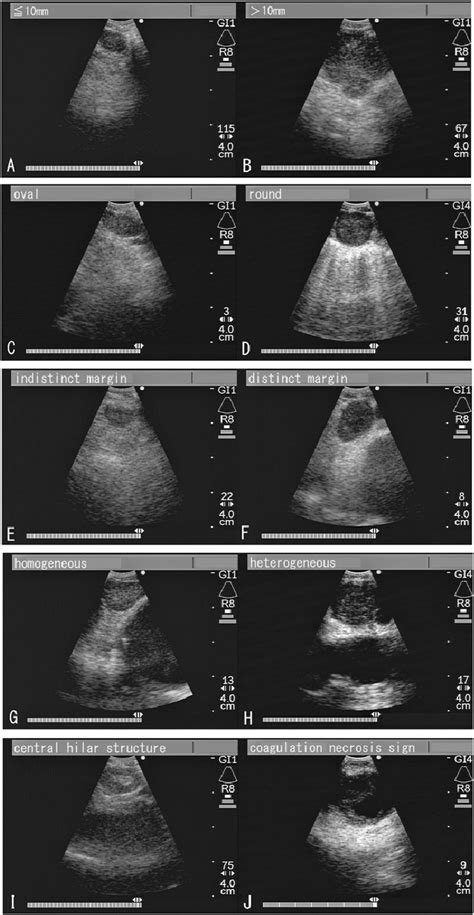
EBUS is primarily utilized for the diagnosis and staging of lung cancer, particularly for assessing mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes. The procedure involves the insertion of a flexible bronchoscope, equipped with an ultrasound probe at its tip, through the mouth or nose into the lungs. This allows for the examination of the airway walls and parabronchial structures. The ultrasound component provides high-resolution images that help in identifying abnormalities, such as enlarged lymph nodes, which can then be sampled for cytological examination using fine-needle aspiration (FNA) under real-time ultrasound guidance.
Technical Specifications and Procedure
The technical specifications of EBUS equipment include high-frequency ultrasound probes that operate within the range of 5-12 MHz, providing detailed images of the structures surrounding the airways. The procedure is typically performed under conscious sedation or general anesthesia, ensuring patient comfort. During the procedure, the physician navigates the bronchoscope to the target area, uses the ultrasound to locate the lymph nodes or lesions of interest, and then performs FNA to collect tissue samples for pathological examination. The samples are then analyzed to determine the presence of cancer cells, which aids in diagnosing and staging the disease.
| EBUS Procedure Steps | Description |
|---|---|
| Preparation | Patient evaluation, informed consent, and preparation for sedation or anesthesia |
| Procedure | Insertion of the bronchoscope, ultrasound imaging, and sampling of lymph nodes or lesions |
| Post-procedure | Monitoring for complications, patient recovery, and analysis of collected samples |

Benefits and Limitations of EBUS
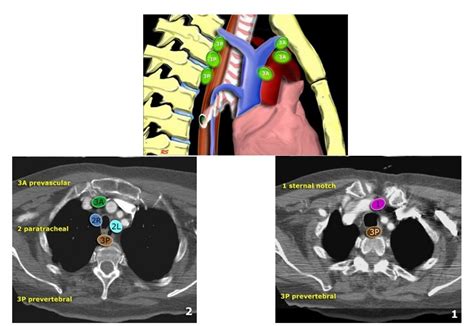
EBUS offers several benefits, including its minimally invasive nature, which leads to less discomfort and fewer complications for patients compared to traditional surgical methods. It also allows for real-time imaging and sampling, enhancing the accuracy of diagnoses. However, EBUS is not without limitations. The procedure requires specialized training and equipment, and the interpretation of ultrasound images demands a high level of expertise. Furthermore, the availability of EBUS might be limited in some regions due to resource constraints.
Future Perspectives and Technological Advancements
Looking forward, advancements in EBUS technology, such as improvements in image resolution and the development of more versatile and user-friendly equipment, are expected to further enhance its diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities. Additionally, the integration of EBUS with other diagnostic modalities, such as positron emission tomography (PET) and computed tomography (CT), may offer even more comprehensive assessments of lung diseases. The future of EBUS also involves its potential application in therapeutic interventions, such as the delivery of drugs or therapies directly to the site of disease under ultrasound guidance.
Key Points
- EBUS stands for Endobronchial Ultrasound, a procedure used for diagnosing and staging lung cancer and other lung diseases.
- The procedure involves using a bronchoscope with an ultrasound probe to visualize the airways and surrounding structures.
- EBUS allows for real-time imaging and sampling of lymph nodes or lesions under ultrasound guidance.
- It offers a minimally invasive alternative to surgical methods, reducing risks and complications for patients.
- The interpretation of EBUS images and the performance of the procedure require specialized training and expertise.
In conclusion, EBUS has emerged as a valuable tool in the diagnosis and staging of lung cancer, providing a minimally invasive approach that enhances patient outcomes. Its integration into clinical practice reflects the ongoing evolution of medical technology and the commitment to improving diagnostic and therapeutic strategies in pulmonology.
What is the primary use of EBUS in medical practice?
+The primary use of EBUS is for the diagnosis and staging of lung cancer, allowing for the visualization of the airways and the sampling of mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes under real-time ultrasound guidance.
What are the benefits of EBUS compared to traditional diagnostic methods?
+EBUS is minimally invasive, reduces the risk of complications, and allows for real-time imaging and sampling, making it a more comfortable and potentially more accurate diagnostic tool for patients compared to surgical methods.
Are there any limitations to the use of EBUS?
+Yes, EBUS requires specialized training and equipment, and its availability might be limited in some regions. Additionally, the interpretation of EBUS images demands a high level of expertise, which can be a limiting factor in its widespread adoption.