The concept of the effective annual rate (EAR) is a crucial aspect of finance, as it provides a more accurate representation of the interest earned on an investment or paid on a loan over a year. Unlike the nominal interest rate, which is the stated interest rate, the effective annual rate takes into account the compounding effect of interest, resulting in a more comprehensive understanding of the actual cost or return. In this article, we will delve into the effective annual rate formula, exploring its components, applications, and implications.
Understanding the Effective Annual Rate Formula
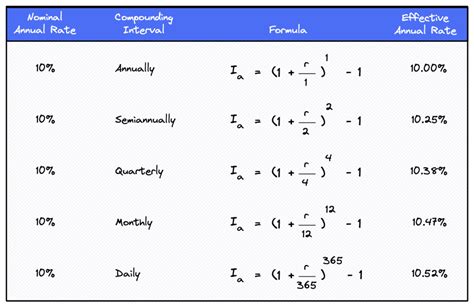
The effective annual rate formula is given by: EAR = (1 + (nominal interest rate/n))^(n) - 1, where n is the number of compounding periods per year. This formula highlights the importance of compounding frequency, as it significantly impacts the effective annual rate. For instance, if the nominal interest rate is 10% and interest is compounded annually, the effective annual rate will also be 10%. However, if the interest is compounded monthly, the effective annual rate will be approximately 10.47%, demonstrating the impact of compounding frequency on the actual interest earned.
Components of the Effective Annual Rate Formula
To accurately calculate the effective annual rate, it is essential to understand the components of the formula. The nominal interest rate, often referred to as the stated interest rate, is the rate at which interest is accrued. The compounding frequency, represented by n, determines how often interest is compounded per year. Common compounding frequencies include annual, semi-annual, quarterly, and monthly. The effective annual rate formula requires the nominal interest rate to be divided by the compounding frequency, resulting in the periodic interest rate. This periodic rate is then raised to the power of the compounding frequency, and 1 is subtracted from the result to obtain the effective annual rate.
| Compounding Frequency | Effective Annual Rate Formula |
|---|---|
| Annually | (1 + 0.10)^1 - 1 = 10% |
| Semi-Annually | (1 + 0.05)^2 - 1 = 10.25% |
| Quarterly | (1 + 0.025)^4 - 1 = 10.38% |
| Monthly | (1 + 0.008333)^12 - 1 = 10.47% |
Applications of the Effective Annual Rate Formula

The effective annual rate formula has numerous applications in finance, including evaluating investment opportunities, assessing loan options, and comparing credit card offers. By calculating the effective annual rate, individuals can make informed decisions about their financial resources, taking into account the actual cost or return on their investments. For instance, when comparing two investment options with different compounding frequencies, the effective annual rate formula can help determine which option provides the highest return.
Comparing Effective Annual Rates
When comparing effective annual rates, it is essential to consider the compounding frequency and the nominal interest rate. A higher effective annual rate indicates a higher actual interest earned or paid, taking into account the compounding effect. However, it is crucial to also consider other factors, such as fees, risks, and liquidity, when evaluating investment or loan options.
Key Points
- The effective annual rate formula takes into account the compounding effect of interest, providing a more accurate representation of the actual cost or return.
- Compounding frequency significantly impacts the effective annual rate, with more frequent compounding resulting in a higher effective annual rate.
- The effective annual rate formula assumes constant interest rates and compounding frequencies, which may not reflect real-world scenarios.
- Calculating the effective annual rate is essential for evaluating investment opportunities, assessing loan options, and comparing credit card offers.
- Other factors, such as fees, risks, and liquidity, should also be considered when evaluating investment or loan options.
Implications of the Effective Annual Rate Formula
The effective annual rate formula has significant implications for financial decision-making. By understanding the impact of compounding frequency on the effective annual rate, individuals can optimize their investment strategies and minimize their borrowing costs. Furthermore, the effective annual rate formula highlights the importance of considering the actual cost or return on investments, rather than relying solely on the nominal interest rate.
Forward-Looking Implications
As the financial landscape continues to evolve, the effective annual rate formula will remain a vital tool for evaluating investment opportunities and assessing loan options. With the increasing complexity of financial products and the growing importance of compounding frequency, the effective annual rate formula will play a critical role in helping individuals make informed decisions about their financial resources.
What is the primary difference between the nominal interest rate and the effective annual rate?
+The primary difference between the nominal interest rate and the effective annual rate is that the effective annual rate takes into account the compounding effect of interest, providing a more accurate representation of the actual cost or return.
How does compounding frequency impact the effective annual rate?
+Compounding frequency significantly impacts the effective annual rate, with more frequent compounding resulting in a higher effective annual rate. This is because more frequent compounding allows interest to be accrued more rapidly, resulting in a higher actual interest earned or paid.
What are the implications of the effective annual rate formula for financial decision-making?
+The effective annual rate formula has significant implications for financial decision-making, as it provides a more accurate representation of the actual cost or return on investments. By understanding the impact of compounding frequency on the effective annual rate, individuals can optimize their investment strategies and minimize their borrowing costs.
Meta Description: Understand the effective annual rate formula and its significance in finance. Learn how to calculate the effective annual rate and its implications for financial decision-making. (150 characters)



