The electric field is a fundamental concept in physics, and understanding its formula is crucial for grasping various phenomena in the natural world. The electric field is a vector field that surrounds charged particles and exerts a force on other charged particles. In this article, we will delve into the electric field formula, exploring its components, applications, and implications. Our goal is to provide a comprehensive and accessible explanation, making the electric field formula simple to understand and apply.
Key Points
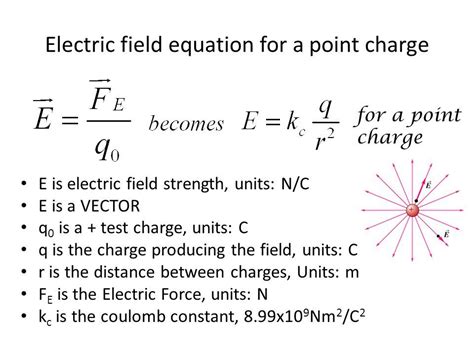
- The electric field formula is given by E = k \* q / r^2, where E is the electric field strength, k is Coulomb's constant, q is the charge, and r is the distance from the charge.
- The electric field is a vector field that surrounds charged particles and exerts a force on other charged particles.
- The electric field formula has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and technology, including the design of electrical circuits, antennas, and motors.
- Understanding the electric field formula is essential for grasping various phenomena, such as electromagnetic induction, electromagnetic waves, and the behavior of charged particles.
- The electric field formula can be used to calculate the electric field strength at a given point in space, allowing us to predict the behavior of charged particles and design electrical systems.
Electric Field Formula: A Comprehensive Overview
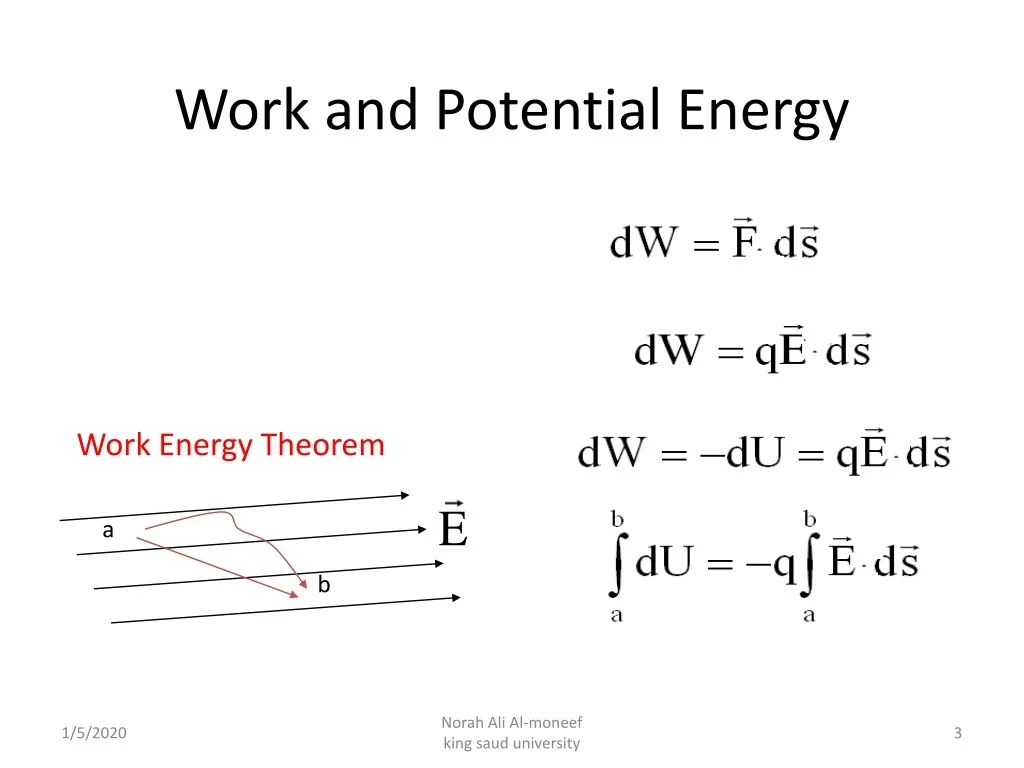
The electric field formula is a mathematical expression that describes the electric field surrounding a charged particle. The formula is given by E = k * q / r^2, where E is the electric field strength, k is Coulomb’s constant (approximately 8.99 x 10^9 N m^2 C^-2), q is the charge, and r is the distance from the charge. This formula is a fundamental concept in physics and has numerous applications in various fields.
Components of the Electric Field Formula
To understand the electric field formula, it’s essential to grasp its components. The electric field strength (E) is a vector quantity that describes the force exerted on a charged particle per unit charge. Coulomb’s constant (k) is a fundamental constant of nature that relates the electric field to the charge and distance. The charge (q) is a measure of the amount of electric charge, and the distance ® is the distance from the charge to the point where the electric field is being measured.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Electric Field Strength (E) | A vector quantity that describes the force exerted on a charged particle per unit charge |
| Coulomb's Constant (k) | A fundamental constant of nature that relates the electric field to the charge and distance |
| Charge (q) | A measure of the amount of electric charge |
| Distance (r) | The distance from the charge to the point where the electric field is being measured |
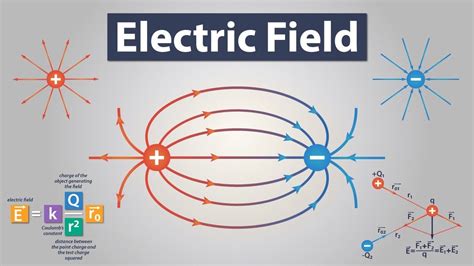
Applications of the Electric Field Formula

The electric field formula has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and technology. Some of the most significant applications include:
- Electrical Circuits: The electric field formula is used to design and analyze electrical circuits, including resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
- Antennas: The electric field formula is used to design and optimize antennas for wireless communication systems.
- Motors and Generators: The electric field formula is used to design and analyze motors and generators, which are crucial components of many electrical systems.
Calculating the Electric Field Strength
To calculate the electric field strength at a given point in space, you can use the electric field formula. For example, suppose you want to calculate the electric field strength at a distance of 1 meter from a charge of 1 coulomb. Using the formula E = k * q / r^2, you can plug in the values and solve for E.
E = (8.99 x 10^9 N m^2 C^-2) \* (1 C) / (1 m)^2 = 8.99 x 10^9 N/C
This calculation shows that the electric field strength at a distance of 1 meter from a charge of 1 coulomb is approximately 8.99 x 10^9 N/C.
What is the electric field formula?
+The electric field formula is given by E = k \* q / r^2, where E is the electric field strength, k is Coulomb's constant, q is the charge, and r is the distance from the charge.
What are the components of the electric field formula?
+The components of the electric field formula are the electric field strength (E), Coulomb's constant (k), charge (q), and distance (r).
What are some applications of the electric field formula?
+The electric field formula has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and technology, including the design of electrical circuits, antennas, and motors.
Meta Description: Learn about the electric field formula, its components, and applications. Understand how to calculate the electric field strength and its significance in physics and engineering. (145 characters)