The concept of electric potential difference is a fundamental aspect of physics and engineering, playing a crucial role in understanding the behavior of electric currents and the design of electrical systems. Electric potential difference, also known as voltage, is the driving force that causes electric current to flow through a circuit. It is defined as the work required to move a unit charge from one point to another against an electric field. The formula for electric potential difference is a key tool in analyzing and designing electrical circuits, and it is essential for understanding various phenomena in physics and engineering.
In the context of electric circuits, the electric potential difference between two points is measured in volts (V) and is denoted by the symbol ΔV or V. It can be calculated using the formula ΔV = W/q, where W is the work done in moving a charge q from one point to another. This formula highlights the relationship between the electric potential difference and the work required to move a charge against an electric field. The electric potential difference is also related to the electric field (E) and the distance (d) between the two points, and it can be calculated using the formula ΔV = E \* d.
Key Points
- The electric potential difference is the driving force that causes electric current to flow through a circuit.
- The formula for electric potential difference is ΔV = W/q, where W is the work done in moving a charge q from one point to another.
- The electric potential difference is related to the electric field (E) and the distance (d) between the two points, and it can be calculated using the formula ΔV = E \* d.
- The unit of electric potential difference is the volt (V), and it is a measure of the work required to move a unit charge from one point to another against an electric field.
- Understanding the electric potential difference formula is essential for analyzing and designing electrical circuits, as well as for understanding various phenomena in physics and engineering.
Electric Potential Difference Formula Derivation
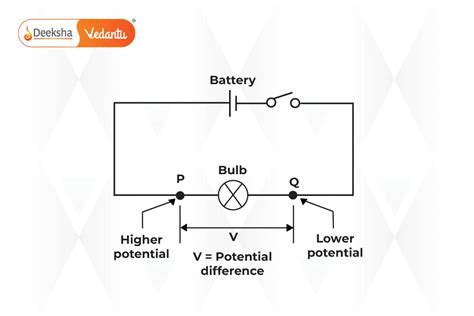
The electric potential difference formula can be derived by considering the work required to move a charge q from one point to another against an electric field. The work done (W) in moving a charge q through a distance d against an electric field E is given by the formula W = F * d, where F is the force exerted on the charge by the electric field. Since the force exerted by the electric field on a charge q is given by F = q * E, the work done can be written as W = q * E * d. The electric potential difference ΔV is then defined as the work required to move a unit charge from one point to another, and it can be calculated using the formula ΔV = W/q = E * d.
Electric Potential Difference Formula for a Uniform Electric Field
In the case of a uniform electric field, the electric potential difference formula can be simplified to ΔV = E * d, where E is the magnitude of the electric field and d is the distance between the two points. This formula is useful for calculating the electric potential difference between two points in a uniform electric field, and it is widely used in the design and analysis of electrical circuits.
| Quantity | Symbol | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Electric potential difference | ΔV or V | Volts (V) |
| Work done | W | Joules (J) |
| Charge | q | Coulombs (C) |
| Electric field | E | Volts per meter (V/m) |
| Distance | d | Meters (m) |
Applications of the Electric Potential Difference Formula
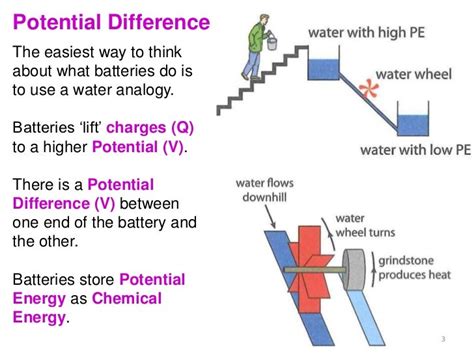
The electric potential difference formula has numerous applications in physics and engineering, including the design and analysis of electrical circuits, the calculation of the voltage drop across a resistor, and the determination of the electric field strength. The formula is also used in the study of electromagnetic induction, where it is used to calculate the induced electromotive force (EMF) in a coil of wire. Additionally, the formula is used in the design of electrical power systems, where it is used to calculate the voltage drop across transmission lines and to determine the required voltage rating of electrical equipment.
Electric Potential Difference Formula in Circuit Analysis
In circuit analysis, the electric potential difference formula is used to calculate the voltage drop across a resistor, and to determine the current flowing through a circuit. The formula is also used to analyze the behavior of complex circuits, including circuits with multiple resistors, capacitors, and inductors. By applying the electric potential difference formula, engineers can design and optimize electrical circuits to meet specific requirements, such as voltage, current, and power.
What is the unit of electric potential difference?
+The unit of electric potential difference is the volt (V), which is defined as the work required to move a unit charge from one point to another against an electric field.
How is the electric potential difference formula derived?
+The electric potential difference formula is derived by considering the work required to move a charge q from one point to another against an electric field. The work done (W) in moving a charge q through a distance d against an electric field E is given by the formula W = F \* d, where F is the force exerted on the charge by the electric field.
What are the applications of the electric potential difference formula?
+The electric potential difference formula has numerous applications in physics and engineering, including the design and analysis of electrical circuits, the calculation of the voltage drop across a resistor, and the determination of the electric field strength.
In conclusion, the electric potential difference formula is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, and it is widely used in the design and analysis of electrical circuits. Understanding the formula and its derivation is essential for working with electrical systems and for understanding various phenomena in physics and engineering. By applying the electric potential difference formula, engineers can design and optimize electrical circuits to meet specific requirements, such as voltage, current, and power.



