The concept of electric potential is a fundamental aspect of electromagnetism, describing the potential difference in electric potential energy between two points in an electric field. The electric potential equation is a crucial tool for understanding and calculating the behavior of electric charges and fields in various systems. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the principles and applications of the electric potential equation, exploring its derivation, key components, and practical uses.
Key Points
- The electric potential equation is derived from Coulomb's Law and the definition of electric potential.
- The equation relates the electric potential at a point to the distance from a charge and the magnitude of the charge.
- Electric potential is a scalar quantity, measured in volts (V), and is a measure of the potential difference in electric potential energy between two points.
- The electric potential equation has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and technology, including the design of electrical circuits, the calculation of electric fields, and the analysis of electrostatic systems.
- Understanding the electric potential equation is essential for the development of innovative technologies, such as electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and medical devices.
Derivation of the Electric Potential Equation
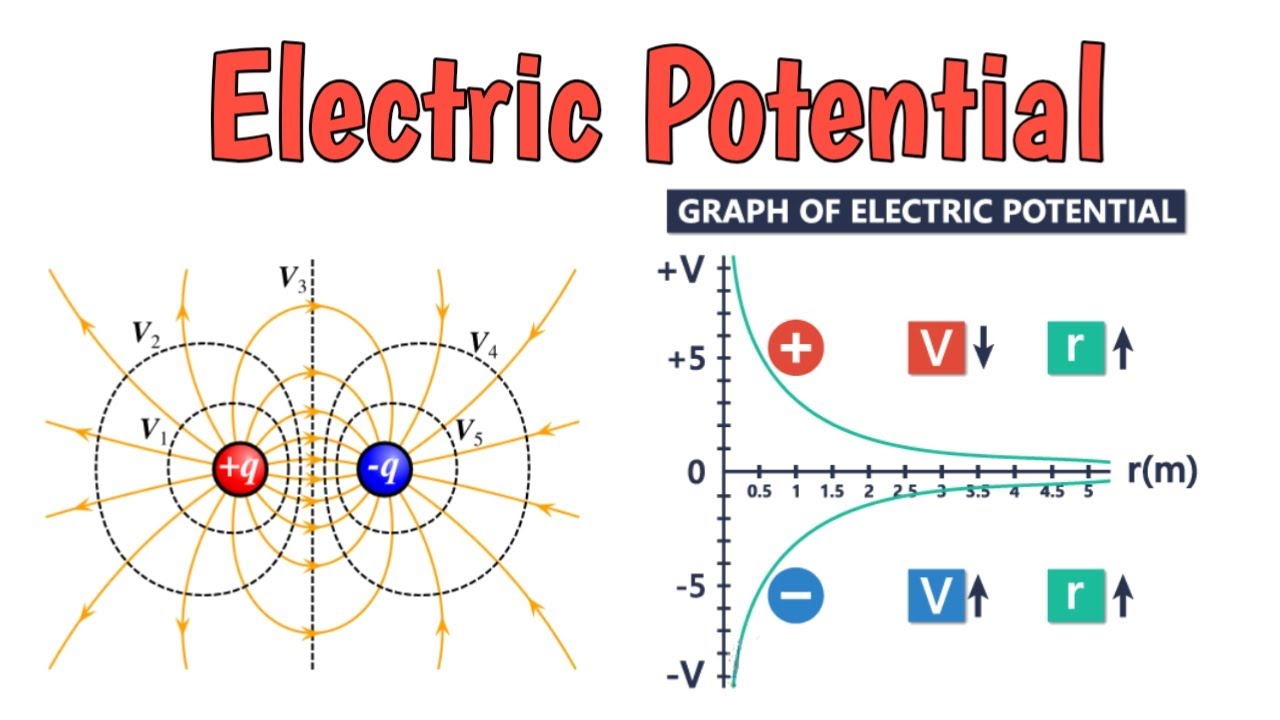
The electric potential equation is derived from Coulomb’s Law, which describes the force between two point charges. By integrating the force over a distance, we can obtain the electric potential energy of a charge in an electric field. The electric potential at a point is defined as the electric potential energy per unit charge, and is given by the equation:
V = k \* q / r, where V is the electric potential, k is Coulomb's constant, q is the magnitude of the charge, and r is the distance from the charge.
Key Components of the Electric Potential Equation
The electric potential equation has several key components that are essential for understanding its behavior and applications. These include:
- Coulomb's constant (k): a fundamental constant of nature that relates the force between two point charges to the product of their magnitudes and the distance between them.
- Charge (q): the magnitude of the charge, which can be positive or negative, and determines the strength of the electric field.
- Distance (r): the distance from the charge, which affects the strength of the electric field and the electric potential.
| Component | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Coulomb's constant (k) | 8.9875 x 10^9 N m^2 C^-2 | N m^2 C^-2 |
| Charge (q) | 1 C (coulomb) | C |
| Distance (r) | 1 m (meter) | m |

Applications of the Electric Potential Equation

The electric potential equation has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and technology. Some of the key areas where the equation is used include:
- Electrical circuits: the electric potential equation is used to calculate the voltage and current in electrical circuits, and to design circuits with specific properties.
- Electric fields: the equation is used to calculate the electric field at a point, and to analyze the behavior of electric fields in various systems.
- Electrostatic systems: the electric potential equation is used to analyze the behavior of electrostatic systems, including the calculation of electric potential and electric field.
The electric potential equation is also essential for the development of innovative technologies, such as electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and medical devices. By understanding the behavior of electric charges and fields, we can design and optimize systems that are more efficient, sustainable, and effective.
Technical Specifications and Contextual Explanation
The electric potential equation is a mathematical representation of the relationship between electric potential and the distance from a charge. The equation is typically expressed in units of volts (V), and is a scalar quantity that can be positive or negative. The electric potential equation is also related to other fundamental equations in physics, such as Ohm’s Law and the Lorentz force equation.
In addition to its theoretical significance, the electric potential equation has numerous practical applications. For example, the equation is used to design electrical circuits, calculate the voltage and current in power systems, and analyze the behavior of electric fields in various systems. The equation is also essential for the development of innovative technologies, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
What is the electric potential equation?
+The electric potential equation is a mathematical representation of the relationship between electric potential and the distance from a charge. The equation is given by V = k \* q / r, where V is the electric potential, k is Coulomb's constant, q is the magnitude of the charge, and r is the distance from the charge.
What are the key components of the electric potential equation?
+The key components of the electric potential equation are Coulomb's constant (k), charge (q), and distance (r). These components are essential for understanding the behavior of electric charges and fields, and are used to calculate the electric potential and electric field in various systems.
What are the applications of the electric potential equation?
+The electric potential equation has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and technology. Some of the key areas where the equation is used include electrical circuits, electric fields, and electrostatic systems. The equation is also essential for the development of innovative technologies, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
In conclusion, the electric potential equation is a fundamental concept in electromagnetism, describing the potential difference in electric potential energy between two points in an electric field. The equation has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and technology, and is essential for the development of innovative technologies. By understanding the key components of the equation and its applications, we can gain insights into the underlying physics and develop innovative solutions for a wide range of applications.



