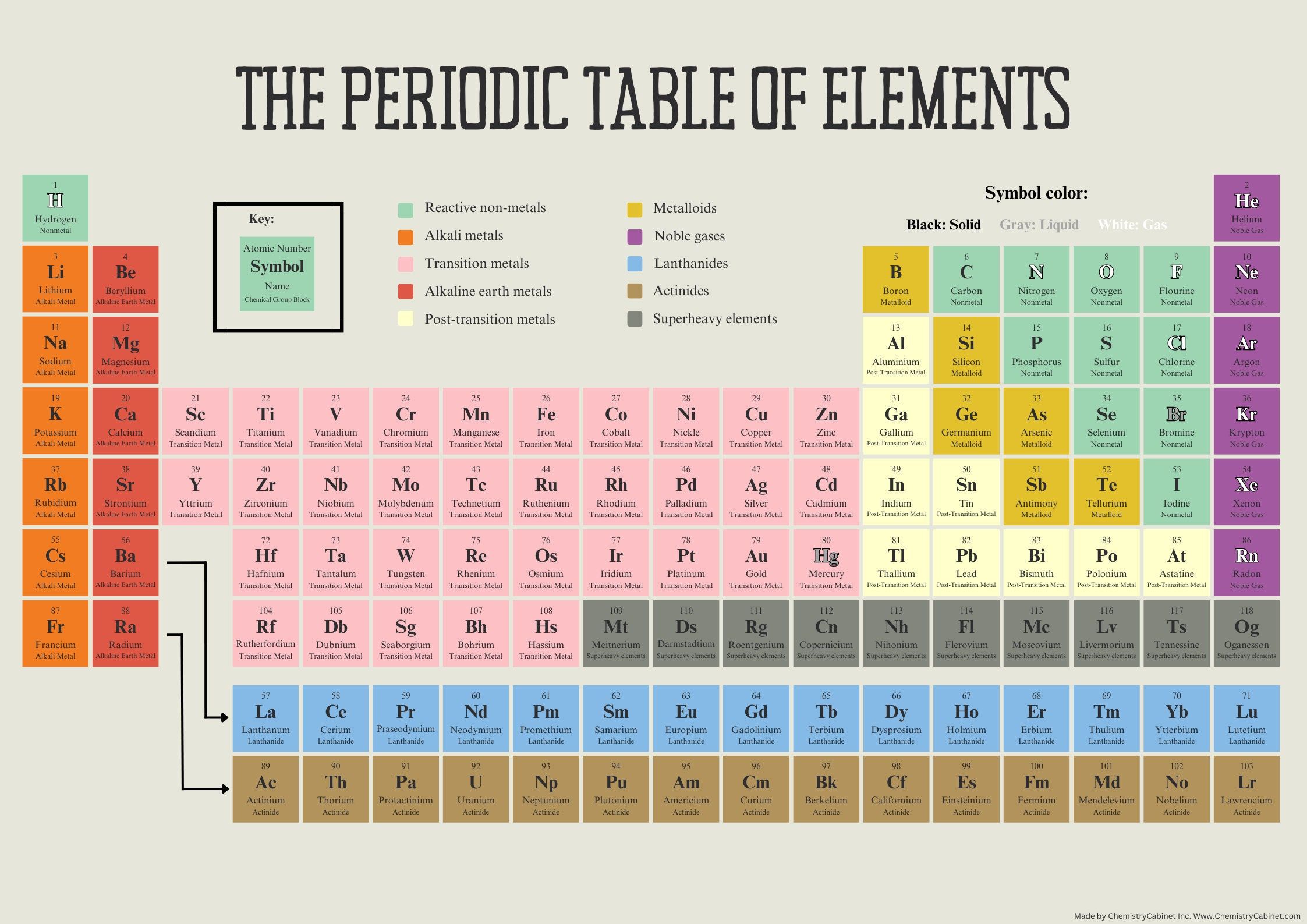
The Element Table, also known as the Periodic Table of Elements, is a tabular display of the known chemical elements, organized by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus) and are grouped into rows called periods and columns called groups or families. The periodic table is a powerful tool for understanding the properties and behavior of elements, and it has played a crucial role in the development of modern chemistry.
History of the Periodic Table
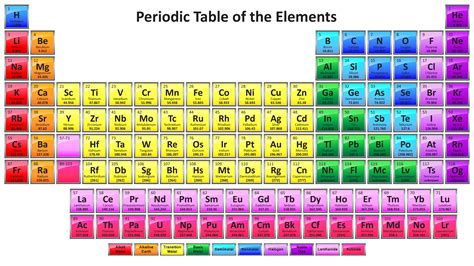
The concept of a periodic table of elements dates back to the early 19th century, when chemists such as John Newlands and Dmitri Mendeleev began to recognize patterns in the properties of elements. Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, is credited with developing the first comprehensive periodic table in 1869. He arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic weight and grouped them into rows and columns based on their chemical properties. Mendeleev’s table was groundbreaking because it predicted the existence of undiscovered elements and provided a framework for understanding the relationships between elements.
Development of the Modern Periodic Table
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the discovery of subatomic particles such as electrons, protons, and neutrons led to a deeper understanding of the structure of atoms and the development of the modern periodic table. The modern periodic table is based on the atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus) rather than atomic weight, and it includes additional groups and periods to accommodate newly discovered elements. The table has undergone numerous revisions and updates, with the most recent version being published by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) in 2016.
| Element | Atomic Number | Atomic Mass |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 | 1.00794 |
| Helium | 2 | 4.002602 |
| Lithium | 3 | 6.941 |
| Beryllium | 4 | 9.012182 |
| Boron | 5 | 10.811 |
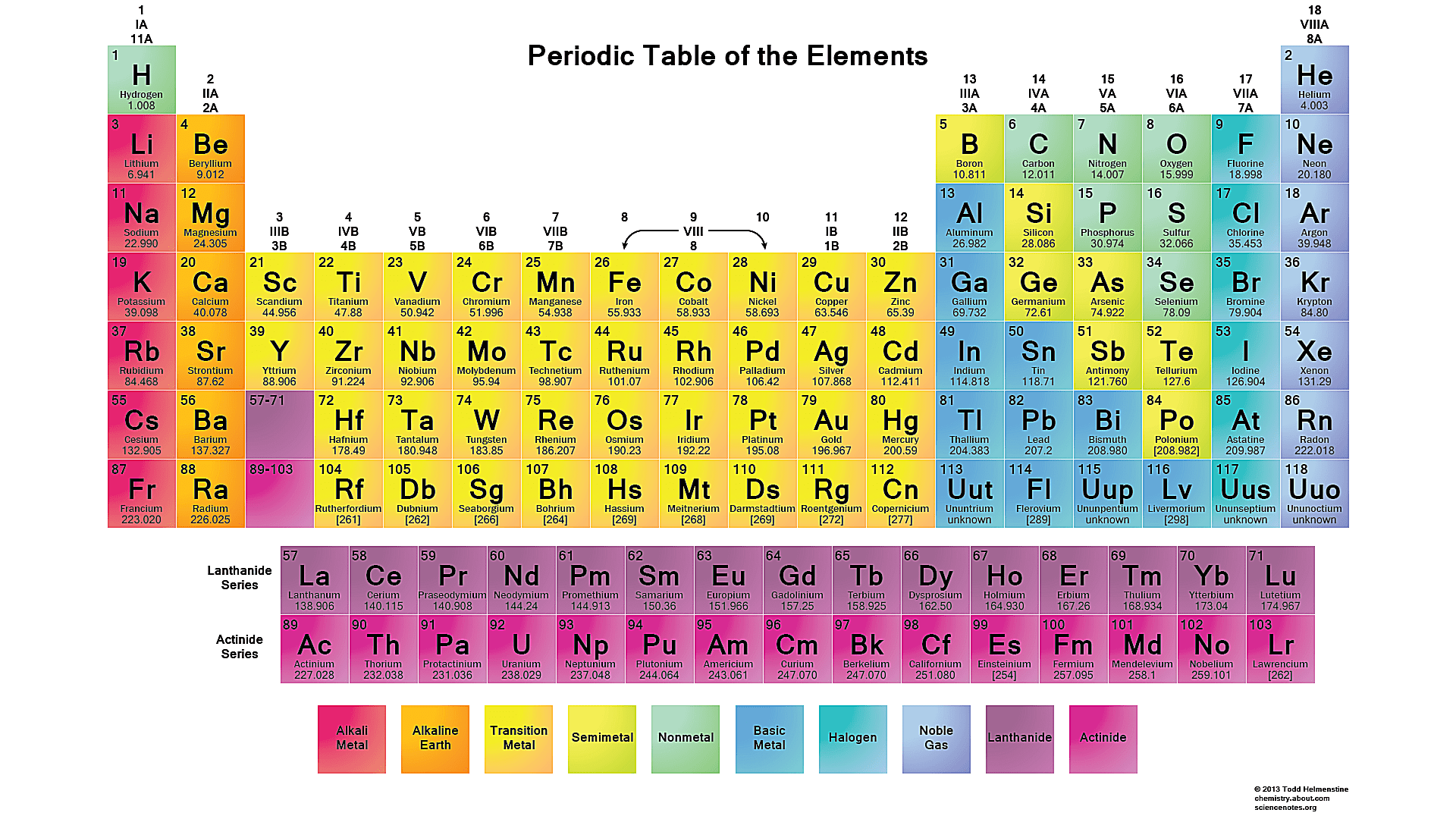
Structure of the Periodic Table
The periodic table is composed of rows called periods and columns called groups or families. The elements in each group have similar chemical properties, while the elements in each period have the same number of electron shells. The table is divided into several blocks, including the s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block, which are based on the electron configuration of the elements. The s-block elements are in the first two groups of the periodic table and are characterized by a single electron in the outermost energy level. The p-block elements are in the remaining groups of the periodic table and are characterized by multiple electrons in the outermost energy level.
Blocks of the Periodic Table
The s-block elements are typically highly reactive and include the alkali metals (Group 1) and the alkaline earth metals (Group 2). The p-block elements are also highly reactive and include the halogens (Group 17) and the noble gases (Group 18). The d-block elements are in the middle of the periodic table and are characterized by multiple electrons in the outermost energy level. The f-block elements are at the bottom of the periodic table and are characterized by multiple electrons in the inner energy levels.
Key Points
- The periodic table is a tabular display of the known chemical elements, organized by their atomic number and electron configuration.
- The elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number and are grouped into rows called periods and columns called groups or families.
- The periodic table is a powerful tool for understanding the properties and behavior of elements, and it has played a crucial role in the development of modern chemistry.
- The table is divided into several blocks, including the s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block, which are based on the electron configuration of the elements.
- The elements in each group have similar chemical properties, while the elements in each period have the same number of electron shells.
Applications of the Periodic Table
The periodic table has numerous applications in chemistry, physics, and engineering. It is used to predict the properties of newly discovered elements, to understand the relationships between elements, and to identify patterns in the properties of elements. The table is also used to develop new materials and technologies, such as semiconductors, catalysts, and pharmaceuticals. Additionally, the periodic table is used in various fields, including environmental science, geology, and biology, to understand the behavior of elements in different environments.
Environmental Applications
The periodic table is used to understand the behavior of elements in the environment and to develop strategies for mitigating the impact of human activities on the environment. For example, the table is used to predict the fate and transport of pollutants in the environment, to develop methods for removing pollutants from contaminated sites, and to understand the effects of climate change on the environment.
What is the periodic table of elements?
+The periodic table of elements is a tabular display of the known chemical elements, organized by their atomic number and electron configuration.
What are the blocks of the periodic table?
+The periodic table is divided into several blocks, including the s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block, which are based on the electron configuration of the elements.
What are the applications of the periodic table?
+The periodic table has numerous applications in chemistry, physics, and engineering, including predicting the properties of newly discovered elements, understanding the relationships between elements, and developing new materials and technologies.
In conclusion, the periodic table of elements is a powerful tool for understanding the properties and behavior of elements, and it has played a crucial role in the development of modern chemistry. The table is composed of rows called periods and columns called groups or families, and it is divided into several blocks based on the electron configuration of the elements. The periodic table has numerous applications in chemistry, physics, and engineering, and it continues to be an essential tool for scientists and researchers today.