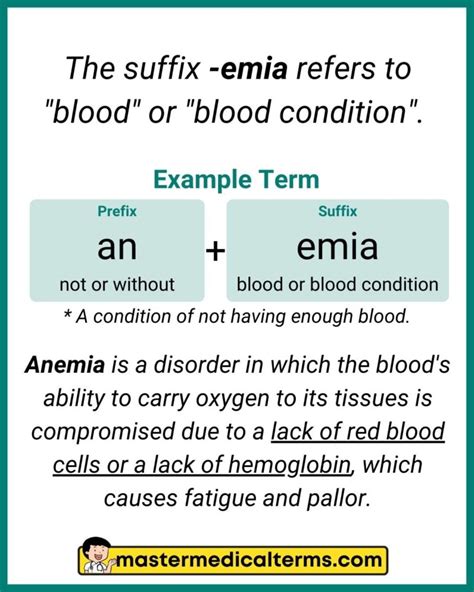
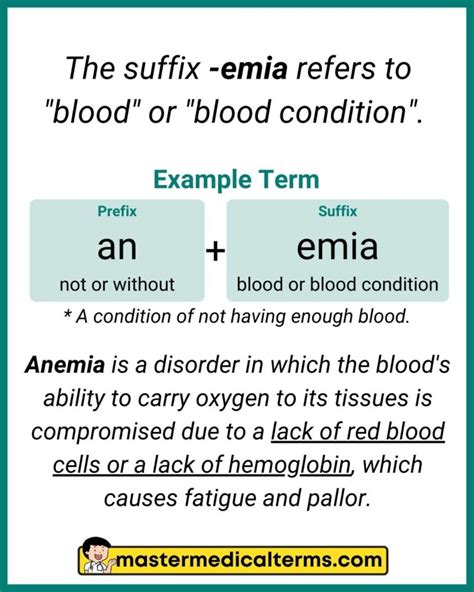
Medical terminology is a vast and complex field, with numerous terms that are used to describe various conditions, procedures, and concepts. Emia is a prefix that refers to a condition or state related to the blood. Here are 5 medical terms that start with the prefix Emia:
Emia-Related Medical Terms

The following terms are related to conditions or states that affect the blood or blood cells. Understanding these terms is essential for medical professionals and individuals who want to learn more about blood-related disorders.
1. Anemia
Anemia is a medical condition characterized by a decrease in the number of red blood cells or the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. Hemoglobin is a protein that carries oxygen to different parts of the body. Anemia can be caused by various factors, including iron deficiency, vitamin deficiency, or chronic diseases such as kidney disease or cancer.
2. Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. It is characterized by an abnormal increase in the number of white blood cells, which can lead to a decrease in the production of healthy blood cells. Leukemia can be acute or chronic, and it requires prompt medical attention and treatment.
3. Thrombemia
Thrombemia is a condition characterized by the presence of blood clots in the bloodstream. These clots can form in the veins or arteries and can lead to serious complications, such as pulmonary embolism or stroke. Thrombemia can be caused by various factors, including injury, surgery, or genetic disorders.
4. Hyperemia
Hyperemia is a condition characterized by an increase in blood flow to a particular area of the body. This can be caused by various factors, including inflammation, infection, or injury. Hyperemia can lead to swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected area.
5. Hypovolemia
Hypovolemia is a condition characterized by a decrease in blood volume, which can lead to a decrease in blood pressure. This can be caused by various factors, including dehydration, bleeding, or burns. Hypovolemia requires prompt medical attention and treatment to prevent serious complications.
Key Points
- Anemia is a condition characterized by a decrease in red blood cells or hemoglobin.
- Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow.
- Thrombemia is a condition characterized by the presence of blood clots in the bloodstream.
- Hyperemia is a condition characterized by an increase in blood flow to a particular area of the body.
- Hypovolemia is a condition characterized by a decrease in blood volume, which can lead to a decrease in blood pressure.
| Medical Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Anemia | A decrease in red blood cells or hemoglobin. |
| Leukemia | A type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. |
| Thrombemia | A condition characterized by the presence of blood clots in the bloodstream. |
| Hyperemia | A condition characterized by an increase in blood flow to a particular area of the body. |
| Hypovolemia | A condition characterized by a decrease in blood volume, which can lead to a decrease in blood pressure. |
What is the difference between Anemia and Leukemia?
+Anemia is a condition characterized by a decrease in red blood cells or hemoglobin, while Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. While both conditions affect the blood, they have distinct causes and symptoms.
What are the symptoms of Thrombemia?
+The symptoms of Thrombemia can vary depending on the location and severity of the blood clot. Common symptoms include pain, swelling, and warmth in the affected area, as well as shortness of breath or chest pain if the clot is in the lungs.
How is Hyperemia treated?
+Hyperemia is typically treated by addressing the underlying cause of the condition, such as inflammation or infection. Treatment may include medications to reduce inflammation, antibiotics to treat infection, or other therapies to reduce blood flow to the affected area.