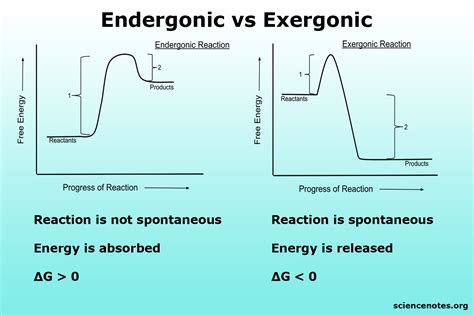
Endergonic reactions, a fundamental concept in biochemistry, refer to processes that require energy input to proceed. Understanding these reactions is crucial for grasping how living organisms function, from the simplest metabolic pathways to complex cellular processes. The term "endergonic" itself implies a need for energy, typically in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), to drive a reaction forward. This energy requirement is what sets endergonic reactions apart from their exergonic counterparts, which release energy. Here, we'll delve into five essential tips for comprehending and working with endergonic reactions, providing a solid foundation for further exploration into biochemical processes.
Key Points
- Understanding the basics of thermodynamics as it applies to biochemical reactions is essential for grasping endergonic processes.
- Endergonic reactions are critical in biosynthesis, allowing cells to build complex molecules from simpler ones.
- The energy for endergonic reactions often comes from the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and inorganic phosphate.
- Coupling endergonic reactions with exergonic reactions is a common strategy cells use to efficiently utilize energy.
- Regulation of endergonic reactions is key to maintaining cellular homeostasis and responding to environmental changes.
Understanding Endergonic Reactions: The Basics
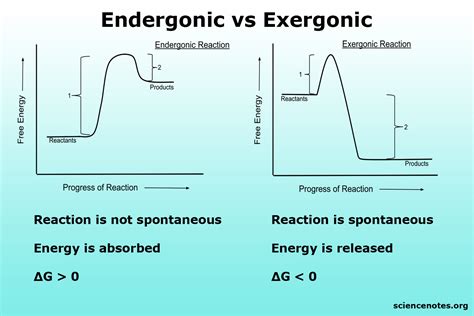
To approach endergonic reactions, it’s vital to first understand the principles of thermodynamics. The Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) of a reaction is a measure of its spontaneity, with negative ΔG values indicating exergonic (spontaneous) reactions and positive ΔG values indicating endergonic (non-spontaneous) reactions. Endergonic reactions have a positive ΔG, meaning they require an input of energy to proceed. This energy can come from various sources but is commonly provided by the cell in the form of ATP.
The Role of ATP in Endergonic Reactions
ATP serves as the primary energy currency of the cell. Its hydrolysis to ADP and inorganic phosphate releases energy that can be used to drive endergonic reactions. This process is fundamental to many biochemical pathways, including those involved in muscle contraction, biosynthesis, and transport of molecules against concentration gradients. Understanding how ATP is utilized and replenished is crucial for appreciating the dynamics of endergonic reactions within cellular metabolism.
| Energy Source | Reaction Type | ΔG |
|---|---|---|
| ATP Hydrolysis | Exergonic | Negative |
| Biosynthesis | Endergonic | Positive |
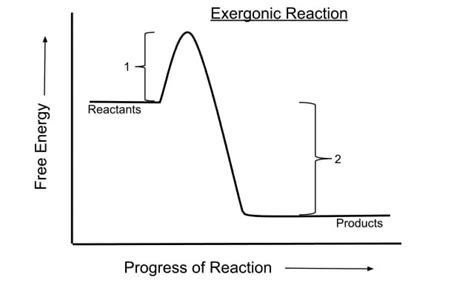
Regulation and Efficiency in Endergonic Reactions

The regulation of endergonic reactions is tightly controlled within the cell to ensure that energy is used efficiently and that the cell’s needs are met without unnecessary expenditure of resources. This regulation can involve allosteric control of enzymes, feedback inhibition, and the modulation of gene expression to alter the production of enzymes involved in endergonic pathways. Efficiency is also enhanced by the coupling of endergonic reactions with exergonic reactions, allowing the cell to harness energy released in one process to drive another that requires energy input.
Applications and Implications of Endergonic Reactions
Endergonic reactions have far-reaching implications in fields such as medicine, biotechnology, and environmental science. Understanding how to manipulate these reactions can lead to the development of new drugs, more efficient biofuels, and novel strategies for dealing with environmental pollutants. Moreover, research into the mechanisms and regulation of endergonic reactions continues to illuminate the intricate workings of cellular metabolism, offering insights into how living organisms adapt to their environments and respond to challenges.
What is the primary energy source for endergonic reactions in cells?
+The primary energy source for endergonic reactions in cells is the hydrolysis of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and inorganic phosphate. This reaction releases energy that can then be used to drive endergonic processes.
How are endergonic reactions regulated within the cell?
+Endergonic reactions are regulated through various mechanisms, including allosteric control of enzymes, feedback inhibition, and modulation of gene expression. These regulatory mechanisms ensure that endergonic reactions are tightly controlled, allowing the cell to efficiently use energy and respond to changing conditions.
What are some examples of endergonic reactions in cellular metabolism?
+Examples of endergonic reactions include the synthesis of glucose from carbon dioxide and water (gluconeogenesis), the production of amino acids from simpler molecules, and the synthesis of fatty acids. These reactions are crucial for the cell's growth, repair, and maintenance.
In conclusion, endergonic reactions are fundamental to the biochemical processes that sustain life. By understanding the principles that govern these reactions, including their energy requirements, regulation, and applications, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex and highly efficient metabolic networks that operate within living cells. Whether in the context of human health, environmental sustainability, or biotechnological innovation, knowledge of endergonic reactions offers a powerful tool for addressing some of the most pressing challenges of our time.