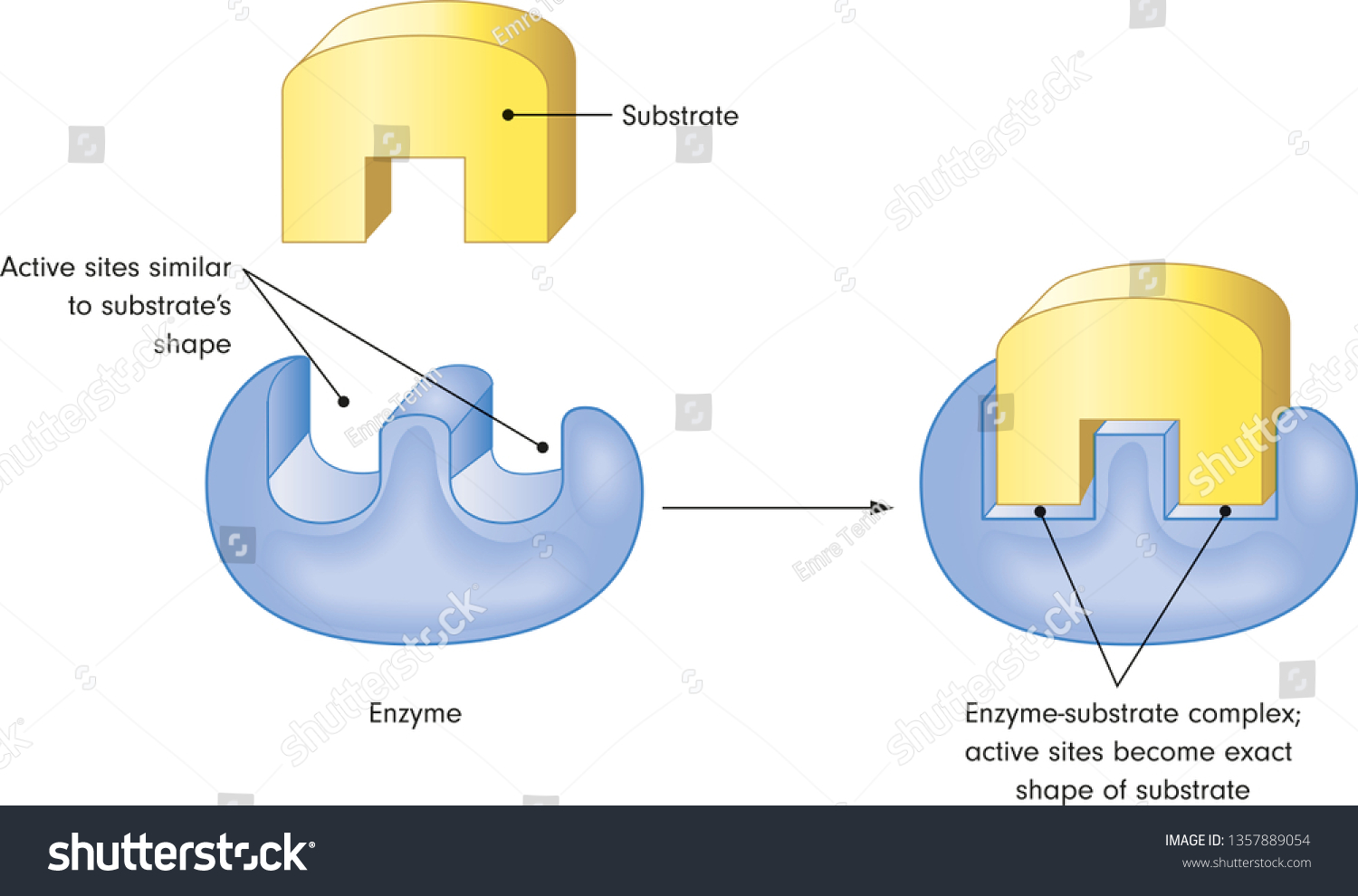
The enzyme substrate complex is a critical component in the field of biochemistry, playing a central role in the catalysis of biochemical reactions. Enzymes, biological molecules typically proteins, accelerate chemical reactions in living organisms, and their ability to form complexes with substrates is fundamental to their function. The interaction between an enzyme and its substrate is highly specific, much like a key fitting into a lock, and this specificity is what allows enzymes to catalyze particular reactions efficiently. In this context, understanding how the enzyme substrate complex works is essential for grasping the intricacies of biochemical processes.
Formation of the Enzyme Substrate Complex
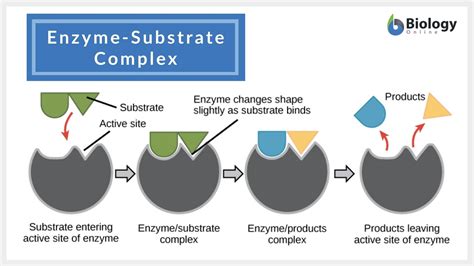
The formation of the enzyme substrate complex is the initial step in the catalytic process. This complex forms when a substrate binds to the active site of an enzyme. The active site is a region on the enzyme that is specifically designed to bind to a particular substrate, facilitating the chemical reaction that converts the substrate into a product. The specificity of the enzyme for its substrate is due to the unique shape and chemical properties of the active site, which allows it to recognize and bind to the substrate. This binding is crucial because it positions the substrate correctly for the enzyme to perform its catalytic function.
Lock and Key Model vs. Induced Fit Model
There are two main models that describe how enzymes recognize and bind to their substrates: the lock and key model and the induced fit model. The lock and key model suggests that the enzyme’s active site is a perfect fit for the substrate, much like a key fits into a lock. However, this model is too rigid and does not account for the dynamic nature of enzymes and substrates. The induced fit model, on the other hand, proposes that the binding of the substrate to the enzyme causes a conformational change in the enzyme’s active site, allowing it to fit more snugly around the substrate. This model better explains the specificity and efficiency of enzyme-substrate interactions.
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
| Lock and Key | Suggests a rigid, pre-existing fit between enzyme and substrate |
| Induced Fit | Proposes that substrate binding causes a conformational change in the enzyme |
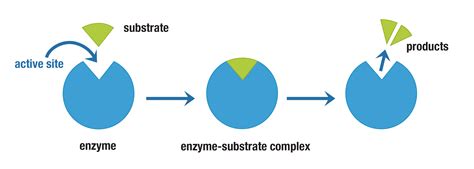
Catalytic Mechanism of Enzyme Substrate Complex
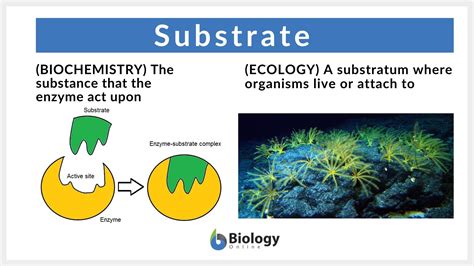
Once the enzyme substrate complex is formed, the enzyme can proceed to catalyze the conversion of the substrate into a product. Enzymes lower the activation energy required for the reaction to occur, allowing the reaction to proceed faster and more efficiently than it would without the enzyme. The catalytic mechanism can involve various steps, including the binding of the substrate, the formation of a transition state, and the release of the product. The specifics of the mechanism can vary depending on the enzyme and the reaction it catalyzes.
Types of Enzyme Catalysis
Enzymes can catalyze reactions through several mechanisms, including acid-base catalysis, covalent catalysis, and metal ion catalysis. Acid-base catalysis involves the enzyme acting as an acid or base to donate or accept a proton, facilitating the reaction. Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a covalent intermediate between the enzyme and the substrate, which helps to lower the activation energy of the reaction. Metal ion catalysis involves the use of a metal ion cofactor to facilitate the reaction, often by stabilizing the transition state or acting as an electron carrier.
Key Points
- The enzyme substrate complex is crucial for the catalysis of biochemical reactions.
- The lock and key model and induced fit model describe how enzymes recognize and bind to their substrates.
- Enzymes catalyze reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur.
- There are several mechanisms of enzyme catalysis, including acid-base, covalent, and metal ion catalysis.
- Understanding enzyme substrate complex formation and function is essential for drug development and biochemical research.
Biological Importance of Enzyme Substrate Complex
The biological importance of the enzyme substrate complex cannot be overstated. Enzymes are essential for life, and their ability to form complexes with substrates is what allows them to carry out their biological functions. Enzymes are involved in virtually every aspect of cellular metabolism, from the digestion of nutrients to the synthesis of DNA. Dysregulation of enzyme activity can lead to various diseases, highlighting the importance of understanding how enzymes work and how they interact with their substrates.
Enzyme Inhibition and Activation
Enzyme activity can be modulated through inhibition or activation. Enzyme inhibitors are molecules that bind to the enzyme and prevent it from forming a complex with its substrate, thereby reducing or eliminating enzyme activity. Enzyme activators, on the other hand, are molecules that increase enzyme activity, often by binding to a site other than the active site and inducing a conformational change that enhances substrate binding or catalysis. Understanding how to modulate enzyme activity is crucial for developing therapeutic strategies for diseases caused by enzyme dysregulation.
| Modulation | Description |
|---|---|
| Inhibition | Reduces or eliminates enzyme activity |
| Activation | Increases enzyme activity |
What is the role of the active site in enzyme substrate complex formation?
+The active site is the region on the enzyme where the substrate binds, and it is specifically designed to recognize and bind to a particular substrate, facilitating the chemical reaction that converts the substrate into a product.
How do enzymes lower the activation energy of reactions?
+Enzymes lower the activation energy of reactions by forming a complex with the substrate that positions the substrate correctly for the reaction to occur, and by stabilizing the transition state of the reaction, thereby making it easier for the reaction to proceed.
What are the implications of understanding enzyme substrate complex formation for drug development?
+Understanding enzyme substrate complex formation is crucial for drug development because it allows for the design of drugs that can specifically target and modulate enzyme activity, either by inhibiting or activating the enzyme, depending on the therapeutic goal.
In conclusion, the enzyme substrate complex plays a vital role in the catalysis of biochemical reactions, and understanding how it works is essential for appreciating the intricacies of biochemical processes. The specificity of enzyme substrate interactions, the mechanisms of catalysis, and the importance of enzyme regulation all contribute to the complex and fascinating world of biochemistry. As research continues to uncover the details of enzyme function and substrate interaction, new opportunities for therapeutic intervention and biochemical manipulation will emerge, further highlighting the significance of this fundamental biological process.