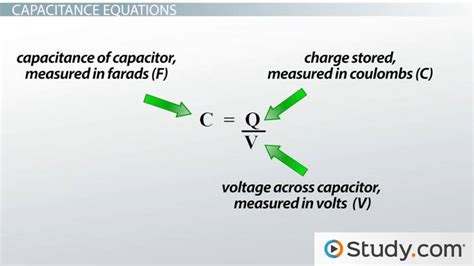
The capacitor equation is a fundamental concept in electrical engineering, describing the relationship between the voltage, current, and charge stored in a capacitor. A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in the form of an electric field, consisting of two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material. The capacitor equation is crucial for understanding the behavior of capacitors in various electrical circuits and systems.
Derivation of the Capacitor Equation
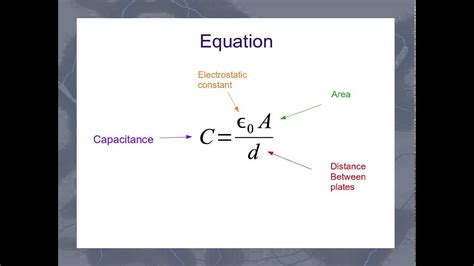
The capacitor equation can be derived from the definition of capacitance, which is the ratio of the charge stored in a capacitor to the voltage across it. The capacitance © of a capacitor is given by the formula: C = Q / V, where Q is the charge stored and V is the voltage across the capacitor. By rearranging this formula, we can express the charge stored in a capacitor as a function of the capacitance and voltage: Q = CV. This equation represents the fundamental relationship between the charge, capacitance, and voltage of a capacitor.
Current-Voltage Relationship
The current-voltage relationship in a capacitor is based on the concept that the current flowing through a capacitor is equal to the rate of change of the charge stored in it. Mathematically, this can be expressed as: i = dQ / dt, where i is the current and dQ / dt is the derivative of the charge with respect to time. Substituting the equation Q = CV into this expression, we get: i = d(CV) / dt. For a capacitor with constant capacitance, this simplifies to: i = C * dV / dt, which is the current-voltage equation for a capacitor.
| Parameter | Symbol | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Capacitance | C | Farad (F) |
| Charge | Q | Coulomb (C) |
| Voltage | V | Volt (V) |
| Current | i | Ampere (A) |
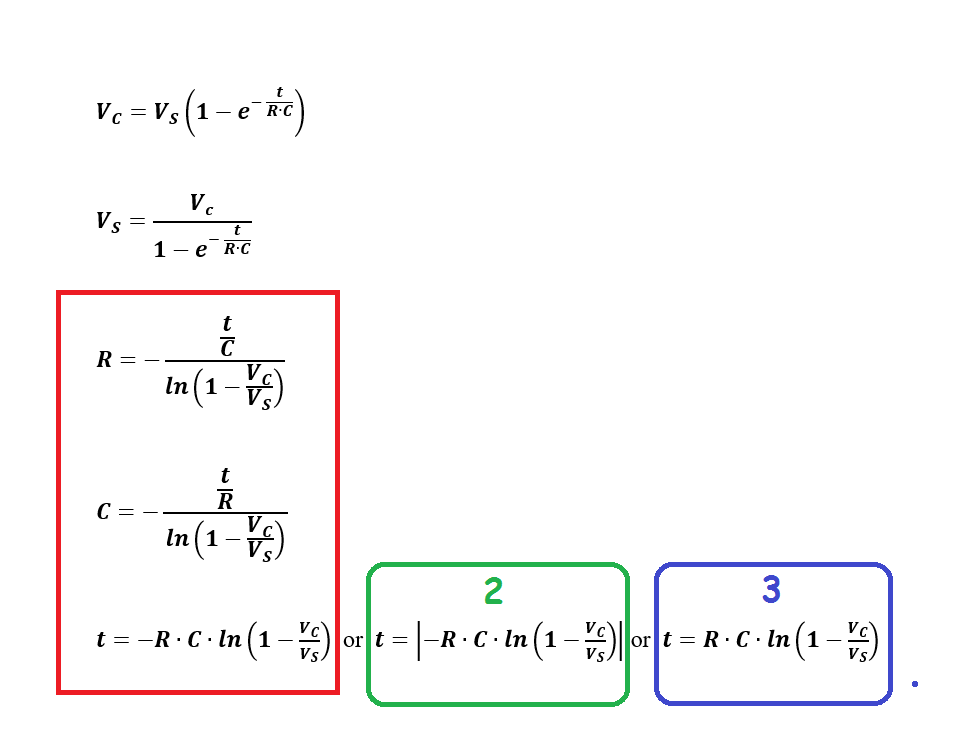
Applications of the Capacitor Equation
The capacitor equation has numerous applications in electrical engineering, including the design of filters, resonant circuits, and power systems. In filter design, the capacitor equation is used to determine the cutoff frequency and bandwidth of a filter. In resonant circuits, the capacitor equation is used to calculate the resonant frequency and quality factor of the circuit. In power systems, the capacitor equation is used to analyze the behavior of capacitors in power factor correction and voltage regulation applications.
Energy Storage and Release
Capacitors are also used for energy storage and release applications, such as in power supplies, audio equipment, and medical devices. The capacitor equation is essential for designing these applications, as it allows engineers to calculate the energy stored in a capacitor and the rate at which it is released. The energy stored in a capacitor is given by the equation: E = (1⁄2) * CV^2, where E is the energy, C is the capacitance, and V is the voltage across the capacitor.
Key Points
- The capacitor equation describes the relationship between the voltage, current, and charge stored in a capacitor.
- The capacitance of a capacitor is given by the formula: C = Q / V.
- The current-voltage equation for a capacitor is: i = C \* dV / dt.
- The energy stored in a capacitor is given by the equation: E = (1/2) \* CV^2.
- The capacitor equation is essential for designing and analyzing electrical circuits, including filters, resonant circuits, and power systems.
In conclusion, the capacitor equation is a fundamental concept in electrical engineering, describing the relationships between the voltage, current, and charge stored in a capacitor. By understanding and applying the capacitor equation, engineers can design and analyze a wide range of electrical circuits and systems, from simple filters to complex power systems.
What is the unit of capacitance?
+The unit of capacitance is the Farad (F).
What is the current-voltage equation for a capacitor?
+The current-voltage equation for a capacitor is: i = C * dV / dt.
What is the energy stored in a capacitor given by?
+The energy stored in a capacitor is given by the equation: E = (1⁄2) * CV^2.