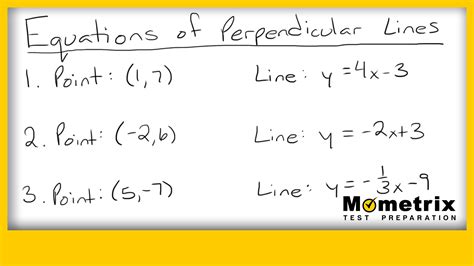
The concept of perpendicularity is a fundamental principle in geometry and various fields of science and engineering. It refers to the relationship between two lines or planes that intersect at a right angle, forming a 90-degree angle. This concept has numerous applications in architecture, design, physics, and mathematics. In this article, we will explore five ways perpendicularity is utilized in different contexts, highlighting its significance and versatility.
Key Points
- Perpendicularity in architecture ensures stability and aesthetic appeal in building designs.
- In physics, perpendicular forces and motions are crucial for understanding and calculating energy transfer and work done.
- Perpendicular lines and planes are essential in geometry for defining angles, shapes, and spatial relationships.
- In engineering, perpendicularity is vital for designing and constructing stable and efficient systems, such as bridges and mechanical components.
- Perpendicularity also plays a role in data analysis and statistics, particularly in regression analysis and dimensionality reduction techniques.
Perpendicularity in Architecture and Design
Architects and designers often utilize perpendicular lines and shapes to create structures that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also stable and functional. The use of perpendicular elements, such as walls, columns, and beams, helps in distributing weight evenly and providing support to the building. Moreover, the incorporation of right angles in design can enhance the sense of space and create a more organized and balanced environment. For instance, the ancient Egyptians used perpendicular lines in the construction of pyramids, demonstrating the early recognition of the importance of this geometric principle in large-scale architectural projects.
Applications in Physics and Engineering
In the realm of physics, perpendicular forces and motions are critical for understanding various phenomena, such as energy transfer, work done, and the behavior of objects under different conditions. For example, when a force is applied perpendicularly to the direction of motion of an object, it results in a change in the object’s direction without altering its speed, illustrating the concept of centrifugal force. In engineering, the principle of perpendicularity is applied in the design of mechanical systems, including gears, levers, and pulleys, where the perpendicular arrangement of components is essential for efficient energy transmission and mechanical advantage.
| Field of Application | Importance of Perpendicularity |
|---|---|
| Architecture | Stability, aesthetic appeal, and functional efficiency |
| Physics | Understanding energy transfer, work done, and motion |
| Engineering | Designing efficient and stable mechanical systems |
| Geometry | Defining shapes, angles, and spatial relationships |
| Data Analysis | Regression analysis and dimensionality reduction techniques |
Perpendicularity in Geometry and Spatial Reasoning
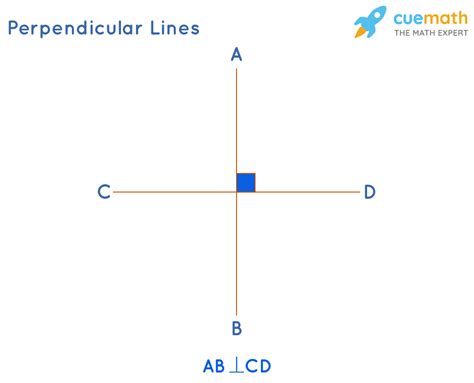
Geometry, the branch of mathematics concerned with the properties and relationships of points, lines, and solids, relies heavily on the concept of perpendicularity. The definition of angles, the classification of shapes (such as rectangles and squares), and the calculation of distances and areas all depend on the relationship between perpendicular lines and planes. Moreover, understanding perpendicularity is essential for spatial reasoning, as it helps individuals visualize and navigate through three-dimensional spaces, whether in real-life situations or in abstract mathematical contexts.
Role in Data Analysis and Statistics
In the realm of data analysis and statistics, perpendicularity plays a significant role, particularly in techniques such as principal component analysis (PCA) and linear regression. PCA, a method used for dimensionality reduction, involves finding new axes (principal components) that are perpendicular to each other, allowing for the representation of data in a lower-dimensional space while retaining most of the information. Similarly, in linear regression, the concept of perpendicularity is used to minimize the sum of the squared errors between observed responses and predicted responses, ensuring that the regression line is the best fit for the data.
As we delve into the various applications of perpendicularity, it becomes clear that this geometric principle is not just a mathematical concept but a fundamental aspect of how we understand, describe, and interact with our environment. Whether in the design of buildings, the calculation of physical forces, the analysis of data, or the definition of geometric shapes, perpendicularity serves as a cornerstone, enabling us to create, predict, and explain the world around us with precision and clarity.
What is the significance of perpendicularity in architecture?
+Perpendicularity in architecture ensures the stability and aesthetic appeal of buildings by allowing for the even distribution of weight and the creation of balanced and organized spaces.
How is perpendicularity applied in physics and engineering?
+In physics, perpendicular forces and motions are crucial for understanding energy transfer and work done. In engineering, perpendicularity is vital for designing efficient and stable mechanical systems, such as gears and levers.
What role does perpendicularity play in geometry and spatial reasoning?
+Perpendicularity is essential in geometry for defining angles, shapes, and spatial relationships. It also aids in spatial reasoning by helping individuals visualize and navigate through three-dimensional spaces.
Meta Description: Discover the significance and applications of perpendicularity across various fields, including architecture, physics, engineering, geometry, and data analysis, highlighting its importance in understanding and describing the world.