Cellular respiration is a complex process by which cells generate energy from the food they consume. It is a critical function that occurs in the cells of most living organisms, including humans, animals, plants, and microorganisms. The cellular respiration equation provides a comprehensive overview of this process, highlighting the reactants, products, and energy yield. In this article, we will delve into the cellular respiration equation, breaking it down into its components and exploring the significance of this process in living organisms.
Cellular Respiration Overview
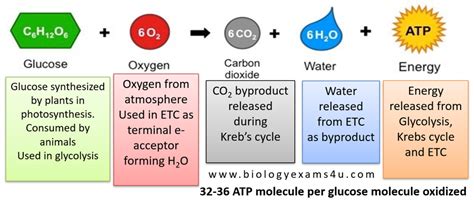
Cellular respiration is a metabolic process that converts glucose and oxygen into carbon dioxide, water, and energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). This process is essential for the survival of cells, as it provides the energy necessary for various cellular functions, such as growth, repair, and maintenance. The cellular respiration equation can be simplified as follows: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP (energy). This equation illustrates the conversion of glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2) into carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and energy in the form of ATP.
Stages of Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration consists of three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Glycolysis is the first stage, where glucose is converted into pyruvate, generating a small amount of ATP and NADH. The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, is the second stage, where pyruvate is converted into acetyl-CoA, producing more ATP, NADH, and FADH2. The final stage, oxidative phosphorylation, occurs in the mitochondria, where the electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed through a series of electron transport chains, generating a proton gradient that drives the production of ATP.
| Stage | Reactants | Products | Energy Yield |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycolysis | Glucose | Pyruvate, ATP, NADH | 2 ATP, 2 NADH |
| Citric Acid Cycle | Pyruvate | Acetyl-CoA, ATP, NADH, FADH2 | 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2 |
| Oxidative Phosphorylation | NADH, FADH2 | ATP | 32-34 ATP |

Key Points
- The cellular respiration equation is a simplified representation of the complex process of energy production in cells.
- Glucose and oxygen are the primary reactants, while carbon dioxide, water, and ATP are the products.
- The three stages of cellular respiration are glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
- The complete breakdown of glucose yields 36-38 ATP molecules, highlighting the importance of the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
- Cellular respiration is essential for the survival of cells, providing energy for various cellular functions.
Significance of Cellular Respiration
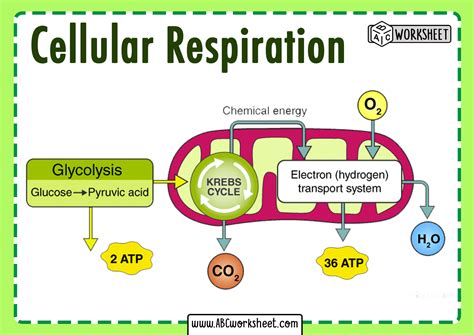
Cellular respiration is a vital process that occurs in the cells of most living organisms. It provides the energy necessary for various cellular functions, such as growth, repair, and maintenance. The energy produced in cellular respiration is used to power the cell’s various activities, including muscle contraction, nerve impulses, and biosynthesis. In addition, cellular respiration plays a critical role in maintaining the body’s overall energy balance, regulating blood sugar levels, and responding to changes in energy demand.
Implications of Cellular Respiration
The implications of cellular respiration are far-reaching, with significant effects on our daily lives. For example, understanding the cellular respiration equation can help us appreciate the importance of a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep in maintaining optimal energy levels. Additionally, research into cellular respiration has led to the development of new treatments for various diseases, such as diabetes, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders. By continuing to explore the complexities of cellular respiration, we can gain a deeper understanding of the intricate processes that govern life and develop innovative solutions to improve human health and well-being.
What is the primary function of cellular respiration?
+The primary function of cellular respiration is to generate energy for the cell through the breakdown of glucose and oxygen.
What are the three stages of cellular respiration?
+The three stages of cellular respiration are glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
What is the energy yield of cellular respiration?
+The complete breakdown of glucose yields 36-38 ATP molecules.
In conclusion, the cellular respiration equation provides a simplified representation of the complex process of energy production in cells. By understanding the reactants, products, and energy yield of cellular respiration, we can appreciate the critical role of glucose and oxygen in generating energy for the cell. The significance of cellular respiration extends beyond the cellular level, with implications for our daily lives and overall health and well-being. As we continue to explore the intricacies of cellular respiration, we may uncover new insights into the intricate processes that govern life and develop innovative solutions to improve human health and well-being.



