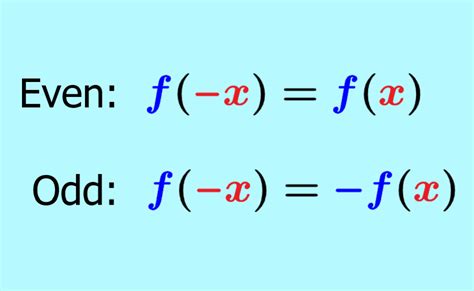Functions, in mathematics, are relations between a set of inputs, called the domain, and a set of possible outputs, known as the range. Among these functions, two special categories are of particular interest: even functions and odd functions. These classifications are based on the function's symmetry properties. Understanding even and odd functions is crucial in various mathematical disciplines, including algebra, calculus, and trigonometry, as they simplify the analysis of functions and their graphs.
The symmetry of a function can provide insights into its behavior and properties. For instance, the graph of an even function is symmetric with respect to the y-axis, meaning if we were to fold the graph along the y-axis, the two halves would perfectly match. On the other hand, the graph of an odd function is symmetric with respect to the origin, meaning if we rotate the graph 180 degrees about the origin, it looks the same. This fundamental difference in symmetry is the basis for distinguishing between even and odd functions.
Key Points
- Even functions satisfy the condition f(x) = f(-x) for all x in the domain, meaning they are symmetric with respect to the y-axis.
- Odd functions satisfy the condition f(-x) = -f(x) for all x in the domain, meaning they are symmetric with respect to the origin.
- The sum of two even functions is even, the sum of two odd functions is odd, and the sum of an even and an odd function is neither purely even nor odd.
- The product of two even functions is even, the product of two odd functions is even, and the product of an even and an odd function is odd.
- Identifying whether a function is even, odd, or neither can simplify its integration, differentiation, and graphing.
Even Functions
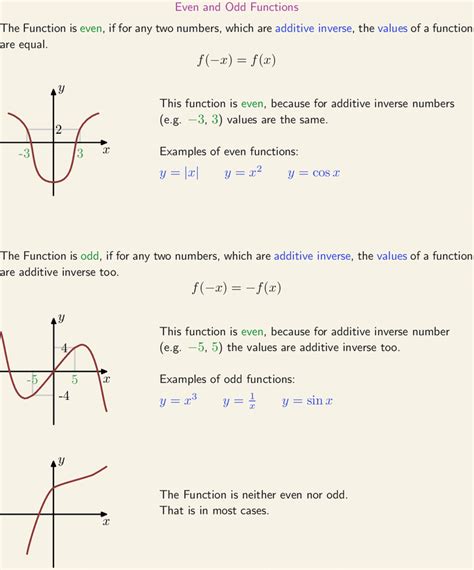
An even function is one where f(x) = f(-x) for all x in the domain of the function. This condition implies that the function’s graph is symmetric with respect to the y-axis. Examples of even functions include y = x^2, y = cos(x), and y = |x|. For instance, the function y = x^2 is even because (-x)^2 = x^2 for all real numbers x. This symmetry property can be useful in evaluating definite integrals and understanding the behavior of the function.
Properties of Even Functions
Even functions have several key properties that make them useful in mathematical analysis. Firstly, the sum of two even functions is even. This can be seen by considering f(x) and g(x) as two even functions; their sum, h(x) = f(x) + g(x), will also satisfy the condition h(x) = h(-x), because f(x) = f(-x) and g(x) = g(-x). Additionally, the product of two even functions is even, as the product of two functions symmetric about the y-axis will also be symmetric about the y-axis.
| Function Type | Example | Symmetry Property |
|---|---|---|
| Even Function | y = x^2 | f(x) = f(-x) |
| Odd Function | y = x^3 | f(-x) = -f(x) |
| Neither Even nor Odd | y = x^2 + x | Does not satisfy either condition |
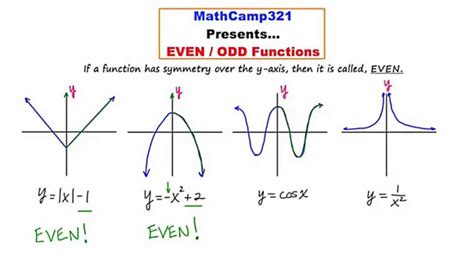
Odd Functions

An odd function satisfies the condition f(-x) = -f(x) for all x in the domain. This condition means that the graph of the function is symmetric with respect to the origin. Examples of odd functions include y = x^3, y = sin(x), and y = x. The function y = x^3 is odd because (-x)^3 = -x^3 for all real numbers x. This type of symmetry is essential in various applications, including signal processing and physics, where the distinction between even and odd functions can significantly affect the analysis and interpretation of data.
Properties of Odd Functions
Odd functions also exhibit specific properties. The sum of two odd functions is odd, following the logic that if f(x) and g(x) are odd, then h(x) = f(x) + g(x) will satisfy h(-x) = -h(x), combining the properties of f and g. Interestingly, the product of two odd functions is even, as the product of two functions symmetric about the origin results in a function symmetric about the y-axis.
Applications and Implications
The distinction between even and odd functions has profound implications in various fields of study. In physics, for example, the symmetry properties of functions can describe the behavior of particles and forces. In electrical engineering, the analysis of signals often involves decomposing them into even and odd components, which can simplify the design and analysis of circuits and systems. Furthermore, in data analysis, understanding the symmetry of a function can provide insights into the underlying patterns and structures of the data.
What is the primary difference between even and odd functions?
+The primary difference lies in their symmetry properties. Even functions are symmetric with respect to the y-axis, while odd functions are symmetric with respect to the origin.
How can you determine if a function is even, odd, or neither?
+You can determine this by checking the function's symmetry properties. If f(x) = f(-x) for all x, the function is even. If f(-x) = -f(x) for all x, the function is odd. If neither condition is satisfied, the function is neither even nor odd.
What are some common examples of even and odd functions?
+Common examples of even functions include y = x^2 and y = cos(x). Examples of odd functions include y = x^3 and y = sin(x).
In conclusion, understanding the properties and behaviors of even and odd functions is fundamental in mathematics and its applications. The symmetry properties of these functions not only provide a framework for simplifying mathematical operations but also underpin many principles in physics, engineering, and data analysis. By recognizing and applying the concepts of even and odd functions, professionals and students alike can deepen their understanding of mathematical and scientific phenomena, leading to more accurate analyses and innovative solutions.