Chemical energy is a form of potential energy that is stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules. It is released when these bonds are broken or formed, often through chemical reactions. This type of energy is fundamental to various processes in nature and human-made systems. Understanding chemical energy is crucial for appreciating how various systems, from living organisms to industrial processes, function. Let's explore five examples of chemical energy in action, highlighting its role and significance.
Chemical Energy in Batteries
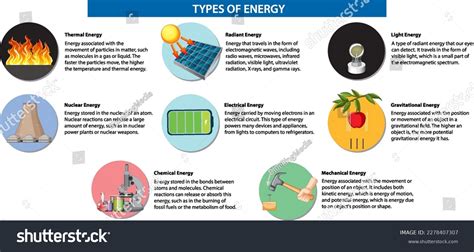
Batteries are one of the most common examples of chemical energy storage and release. Inside a battery, chemical energy is stored in the form of chemical bonds between the battery’s internal components, such as zinc and copper in a traditional alkaline battery, or lithium and cobalt in lithium-ion batteries. When a battery is connected to a device, a chemical reaction occurs that breaks these bonds, releasing energy in the form of electricity. This process is reversible in rechargeable batteries, where the chemical bonds are reformed during charging. For instance, in a lithium-ion battery, lithium ions move between the anode and cathode, releasing or absorbing electrons and thus storing or releasing electrical energy.
Chemical Reactions in Cooking
Cooking involves numerous chemical reactions that convert raw ingredients into a meal. For example, the Maillard reaction, a chemical reaction between amino acids and reducing sugars that gives browned food its distinctive flavor, is a form of chemical energy transformation. When food is heated, the energy breaks the chemical bonds in the ingredients, leading to new compounds that have different flavors, textures, and aromas. This transformation of chemical energy into sensory experiences is fundamental to the art of cooking and the enjoyment of food.
| Type of Reaction | Chemical Energy Transformation |
|---|---|
| Maillard Reaction | Breakdown of amino acids and sugars into new compounds |
| Caramelization | Breakdown of sugar molecules into new compounds with distinct flavors and colors |

Chemical Energy in Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, are another significant example of stored chemical energy. These fuels are formed over millions of years from the remains of ancient plants and animals. When burned, the chemical bonds in these fuels are broken, releasing energy in the form of heat and light. This process is utilized in power plants to generate electricity, in vehicles for transportation, and in heating systems for warming buildings. However, the burning of fossil fuels also releases carbon dioxide and other pollutants into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change and environmental degradation.
Chemical Energy in Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in glucose, a sugar. This process is vital for life on Earth as it provides the primary source of energy for nearly all food chains. During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide and water are converted into glucose and oxygen, using sunlight as the energy source. The chemical bonds in glucose store energy that can be released when glucose is broken down during cellular respiration, providing energy for the organism’s metabolic processes.
Key Points
- Chemical energy is stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules.
- Batteries store chemical energy that is released as electrical energy.
- Cooking involves chemical reactions that transform ingredients into a meal.
- Fossil fuels store chemical energy that is released when burned.
- Photosynthesis converts light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose.
Chemical Energy in the Human Body
The human body also utilizes chemical energy, primarily stored in the food we eat. Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are broken down during digestion into simpler molecules like glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids. These molecules are then further processed within cells through cellular respiration, where their chemical bonds are broken down, releasing energy that is used to power the body’s functions, from movement and growth to maintaining body temperature and facilitating thought processes.
What is the primary source of chemical energy for the human body?
+The primary source of chemical energy for the human body is the food we eat, specifically carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, which are broken down and processed to release energy.
How is chemical energy stored in batteries?
+Chemical energy is stored in batteries in the form of chemical bonds between the battery's internal components. When a battery is connected to a device, these bonds are broken, releasing energy in the form of electricity.
What role does photosynthesis play in storing chemical energy?
+Photosynthesis plays a crucial role in storing chemical energy by converting light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in glucose. This process is vital for life on Earth as it provides the primary source of energy for nearly all food chains.
In conclusion, chemical energy is a vital component of various natural and human-made systems, from the food we eat and the batteries that power our devices to the fossil fuels that drive our vehicles and the photosynthesis that sustains life on Earth. Understanding chemical energy and its transformations is essential for appreciating the intricate balance of our ecosystem and the technological advancements that shape our world.