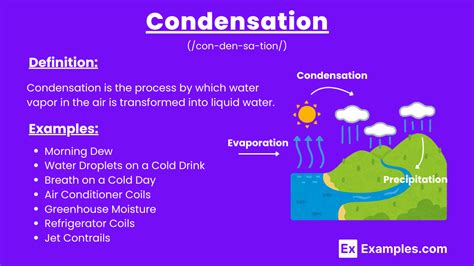
The concept of condensation is a fundamental principle in physics, where a substance changes state from gas to liquid. This phenomenon occurs when the temperature of the gas decreases, causing the molecules to slow down and come together, forming droplets of liquid. In this article, we will explore five examples of condensation, highlighting the diverse range of applications and occurrences of this principle in our daily lives.
Key Points
- Condensation is the process by which a substance changes state from gas to liquid.
- Examples of condensation include dew formation, fog, cloud formation, breathing on cold surfaces, and condenser coils in refrigeration systems.
- Condensation plays a crucial role in various industries, such as water harvesting, climate regulation, and refrigeration.
- The process of condensation is influenced by factors such as temperature, humidity, and surface area.
- Understanding condensation is essential for developing efficient technologies and mitigating the effects of climate change.
Examples of Condensation
One of the most common examples of condensation is the formation of dew on grass and other surfaces. As the air temperature cools overnight, the water vapor in the air condenses onto the cooler surfaces, forming droplets of water. This process is an essential part of the water cycle, as it helps to redistribute water from the atmosphere to the earth. Another example of condensation is the formation of fog, which occurs when the air is cooled to its dew point, causing the water vapor to condense into tiny droplets.
Cloud Formation and Condensation
Clouds are another example of condensation, where water vapor in the air condenses onto tiny particles in the atmosphere, such as dust and salt. This process is facilitated by the presence of nucleation sites, which provide a surface for the water vapor to condense onto. The formation of clouds is a critical aspect of the earth’s climate system, as it helps to regulate the amount of solar radiation that reaches the earth’s surface. Furthermore, the process of condensation is also essential for the formation of precipitation, such as rain and snow.
| Example | Description |
|---|---|
| Dew Formation | Condensation of water vapor onto cool surfaces, such as grass and leaves. |
| Fog | Condensation of water vapor into tiny droplets, reducing visibility. |
| Cloud Formation | Condensation of water vapor onto particles in the atmosphere, regulating climate and precipitation. |
| Breathing on Cold Surfaces | Condensation of water vapor from breath onto cool surfaces, such as mirrors and glass. |
| Condenser Coils | Condensation of refrigerant vapor onto cool coils, facilitating heat transfer and cooling. |

Applications of Condensation
Condensation has numerous applications in various industries, including refrigeration, air conditioning, and water harvesting. In refrigeration systems, condenser coils are used to condense the refrigerant vapor, facilitating heat transfer and cooling. Similarly, in air conditioning systems, condensation is used to remove heat from the air, providing a cooling effect. Additionally, condensation is used in water harvesting systems, where the water vapor in the air is condensed and collected, providing a source of clean water.
Importance of Condensation in Climate Regulation
Condensation plays a crucial role in regulating the earth’s climate, as it helps to control the amount of solar radiation that reaches the earth’s surface. Clouds, which are formed through condensation, reflect a significant portion of the sun’s radiation, cooling the planet. Furthermore, condensation is also essential for the formation of precipitation, which helps to distribute water around the globe, supporting life and agriculture.
What is the difference between condensation and evaporation?
+Condensation is the process by which a substance changes state from gas to liquid, while evaporation is the process by which a substance changes state from liquid to gas.
What are some common examples of condensation in everyday life?
+Common examples of condensation include dew formation, fog, breathing on cold surfaces, and condensation on windows and mirrors.
How does condensation affect the climate?
+Condensation plays a crucial role in regulating the earth's climate, as it helps to control the amount of solar radiation that reaches the earth's surface, and is essential for the formation of precipitation.
In conclusion, condensation is a fundamental principle in physics, with diverse applications and occurrences in our daily lives. By understanding the process of condensation, we can develop more efficient technologies, mitigate the effects of climate change, and appreciate the beauty of the natural world. As we continue to explore and learn about condensation, we may uncover new and innovative ways to harness its power and improve our lives.