Covalent compounds are a class of chemical substances that are formed when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to achieve a more stable electronic configuration. This type of chemical bonding is characteristic of molecules, where the atoms involved in the bond are typically nonmetals. The sharing of electrons leads to the formation of a strong and stable bond, which is essential for the existence of the molecule. In this article, we will delve into the world of 5 covalent compounds, exploring their properties, structures, and applications.
Key Points
- Covalent compounds are formed through the sharing of electrons between atoms
- The properties of covalent compounds depend on the type of atoms involved and the molecular structure
- Covalent compounds can exhibit a wide range of physical and chemical properties
- The applications of covalent compounds are diverse, ranging from pharmaceuticals to materials science
- Understanding the properties and behavior of covalent compounds is essential for advancing various fields of science and technology
Properties of Covalent Compounds
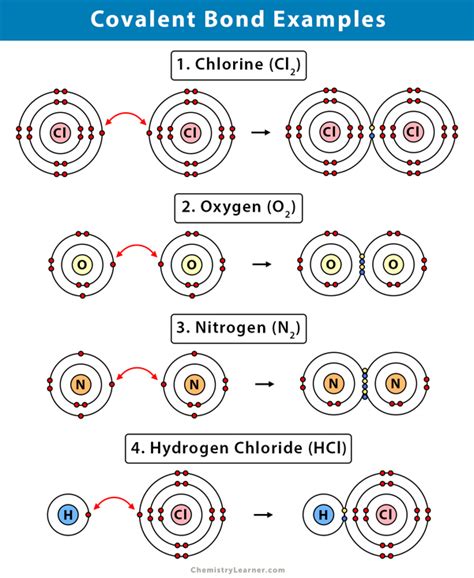
Covalent compounds exhibit a wide range of physical and chemical properties, which are determined by the type of atoms involved in the molecule and the molecular structure. For example, the polarity of a covalent bond can affect the solubility and reactivity of the compound. The molecular shape and size can also influence the physical properties, such as melting and boiling points. Additionally, the presence of functional groups can impart specific chemical properties, such as acidity or basicity.
Molecular Structure and Bonding
The molecular structure of a covalent compound is crucial in determining its properties and behavior. The arrangement of atoms in space can be described using various models, such as the valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory. This theory predicts the shape of a molecule based on the number of electron pairs around the central atom. For instance, a molecule with four electron pairs around the central atom will have a tetrahedral shape. Understanding the molecular structure is essential for predicting the physical and chemical properties of a covalent compound.
| Compound | Molecular Formula | Molecular Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Methane | CH4 | Tetrahedral |
| Ammonia | NH3 | Trigonal pyramidal |
| Carbon dioxide | CO2 | Linear |
| Water | H2O | Bent |
| Ozone | O3 | Bent |

Applications of Covalent Compounds

Covalent compounds have a wide range of applications in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and energy. For example, covalent compounds are used as active ingredients in many medications, such as antibiotics and anticancer drugs. In materials science, covalent compounds are used to develop new materials with unique properties, such as strength, conductivity, and optical properties. Additionally, covalent compounds are used in energy storage and conversion, such as in batteries and solar cells.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Covalent compounds are used extensively in the pharmaceutical industry as active ingredients in medications. The properties of covalent compounds, such as solubility, reactivity, and stability, can affect their efficacy and safety as drugs. For instance, the covalent compound aspirin is used to treat pain and inflammation, while the covalent compound penicillin is used to treat bacterial infections. Understanding the properties and behavior of covalent compounds is essential for developing new and effective medications.
What is the difference between a covalent compound and an ionic compound?
+A covalent compound is formed through the sharing of electrons between atoms, while an ionic compound is formed through the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions.
What are some common properties of covalent compounds?
+Covalent compounds can exhibit a wide range of physical and chemical properties, including solubility, reactivity, and stability, which are determined by the type of atoms involved and the molecular structure.
What are some applications of covalent compounds?
+Covalent compounds have a wide range of applications in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and energy, due to their unique properties and behavior.
In conclusion, covalent compounds are an essential class of chemical substances that are formed through the sharing of electrons between atoms. Understanding the properties, structures, and applications of covalent compounds is crucial for advancing various fields of science and technology. By exploring the world of covalent compounds, we can gain insights into the behavior of molecules and develop new materials, medications, and technologies that can improve our daily lives.


