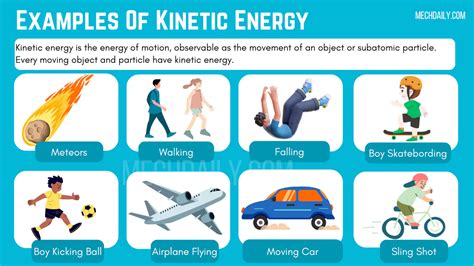
Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses when it is in motion. This fundamental concept in physics is crucial for understanding various phenomena in our daily lives, from the simplest movements to complex technological applications. The study of kinetic energy involves understanding its definition, how it is calculated, and its practical applications. Kinetic energy is calculated using the formula KE = 0.5 * m * v^2, where KE is the kinetic energy, m is the mass of the object, and v is its velocity. This formula shows that kinetic energy is directly proportional to the mass of the object and the square of its velocity, meaning that even small increases in velocity can result in significant increases in kinetic energy.
Understanding Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy is a form of energy that is associated with motion. Unlike potential energy, which is the energy of position or stored energy, kinetic energy is the energy of motion. An object moving at a constant velocity possesses kinetic energy, and the amount of kinetic energy it has depends on its mass and the speed at which it is moving. For example, a car moving at 60 km/h has kinetic energy due to its motion. The heavier the car and the faster it moves, the more kinetic energy it possesses.
Examples of Kinetic Energy
There are numerous examples of kinetic energy in everyday life and in various fields such as physics, engineering, and sports. Here are five kinetic energy examples that illustrate its presence and importance:
Rolling Ball: A ball rolling on the ground is a simple example of kinetic energy. As the ball moves, it possesses kinetic energy due to its motion. The energy is a result of the ball’s mass and its velocity. The faster the ball rolls, the more kinetic energy it has.
Running Athlete: An athlete running in a race is another example of kinetic energy. The athlete’s body, in motion, possesses kinetic energy. This energy is crucial for the athlete’s performance, as it directly relates to their speed and endurance. Factors such as the athlete’s mass (including their body weight and any equipment they might be wearing) and their running speed contribute to their kinetic energy.
Flowing Water: Water flowing through a river or a pipe also exhibits kinetic energy. The mass of the water and its flow rate determine the amount of kinetic energy present. Hydroelectric power plants harness this kinetic energy by using turbines to convert it into electrical energy, providing a practical application of kinetic energy conversion.
Moving Vehicle: A car or any other vehicle in motion is a significant example of kinetic energy. The vehicle’s mass, including its own weight plus the weight of the passengers and cargo, and its speed determine its kinetic energy. The kinetic energy of moving vehicles is what allows them to cover distances and perform work, such as transporting people and goods.
Wind Turbines: Wind turbines generate electricity by capturing the kinetic energy in wind. The blades of the turbine convert the kinetic energy of the moving air into mechanical energy, which is then converted into electrical energy. This process demonstrates how kinetic energy can be harnessed and converted into other forms of energy, highlighting its versatility and importance in renewable energy systems.
| Example | Description | Kinetic Energy |
|---|---|---|
| Rolling Ball | A ball moving on the ground | Depends on mass and velocity |
| Running Athlete | An athlete in motion | Depends on body mass and running speed |
| Flowing Water | Water moving through a river or pipe | Depends on water mass and flow rate |
| Moving Vehicle | A vehicle in motion | Depends on vehicle mass and speed |
| Wind Turbines | Blades moving due to wind | Depends on wind speed and turbine blade mass |
Key Points
- The formula for kinetic energy is KE = 0.5 * m * v^2, where m is the mass and v is the velocity of the object.
- Kinetic energy is directly proportional to the mass of the object and the square of its velocity.
- Examples of kinetic energy include rolling balls, running athletes, flowing water, moving vehicles, and wind turbines.
- Kinetic energy can be converted into other forms of energy, such as electrical energy in hydroelectric power plants and wind turbines.
- Understanding and efficiently harnessing kinetic energy can lead to significant advancements in various fields.
Applications and Implications of Kinetic Energy
The study and application of kinetic energy have numerous practical implications. In the field of renewable energy, kinetic energy is harnessed to generate electricity, offering a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. In transportation, understanding kinetic energy is crucial for designing more efficient vehicles and systems, which can lead to reduced fuel consumption and lower emissions. Moreover, in sports, athletes and coaches use the principles of kinetic energy to optimize performance, prevent injuries, and improve training methods.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the advancements in harnessing and utilizing kinetic energy, there are challenges and areas for further research. Improving the efficiency of energy conversion systems, developing more effective materials for kinetic energy applications, and exploring new sources of kinetic energy are some of the future directions. Additionally, integrating kinetic energy systems with other forms of renewable energy to create hybrid systems could offer even more efficient and sustainable solutions for energy production and consumption.
What is the difference between kinetic energy and potential energy?
+Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, while potential energy is the stored energy an object has due to its position or configuration. Kinetic energy is realized when an object moves, whereas potential energy is realized when the object's position changes, such as when an object falls from a height.
How is kinetic energy used in daily life?
+Kinetic energy is used in various aspects of daily life, from the movement of vehicles and machines to the functioning of wind turbines and hydroelectric power plants. It is also crucial in sports and physical activities, where understanding and optimizing kinetic energy can improve performance.
Can kinetic energy be converted into other forms of energy?
+Yes, kinetic energy can be converted into other forms of energy. For example, in a hydroelectric power plant, the kinetic energy of flowing water is converted into mechanical energy by turbines, which is then converted into electrical energy. Similarly, the kinetic energy of moving parts in a generator can be converted into electrical energy.
In conclusion, kinetic energy is a fundamental concept in physics that plays a crucial role in various aspects of our lives, from simple everyday movements to complex technological applications. Understanding kinetic energy and how it can be harnessed and converted offers significant potential for innovation and sustainability. As research and technology continue to evolve, the efficient use and conversion of kinetic energy will remain a key area of focus for achieving a more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly future.