Mechanical waves are a fundamental concept in physics, essential for understanding various phenomena in our daily lives. These waves require a physical medium to propagate and can be found in numerous forms, from water waves and sound waves to seismic waves. The study of mechanical waves is crucial for grasping the principles of energy transfer, interference, and superposition. In this article, we will delve into the world of mechanical waves, exploring their characteristics, types, and examples, as well as their significance in different fields.
Key Points
- Mechanical waves require a physical medium to propagate and can be classified into two main types: longitudinal and transverse waves.
- Sound waves, water waves, and seismic waves are examples of mechanical waves that play a vital role in our understanding of the physical world.
- The characteristics of mechanical waves, including frequency, wavelength, and amplitude, determine their behavior and interactions.
- Understanding mechanical waves is essential for various applications, such as sonar technology, medical imaging, and seismic exploration.
- Interference and superposition are critical concepts in the study of mechanical waves, as they describe how waves interact with each other and their surroundings.
Characteristics of Mechanical Waves
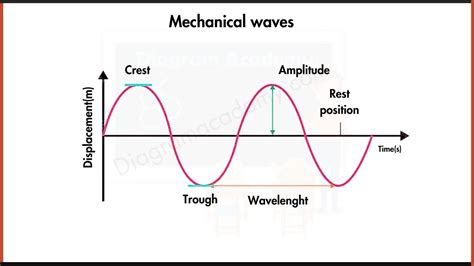
Mechanical waves exhibit distinct characteristics that define their behavior and interactions. These characteristics include frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed. The frequency of a wave is the number of oscillations or cycles per second, measured in Hertz (Hz). The wavelength is the distance between two consecutive points in phase, typically measured in meters. The amplitude of a wave is the maximum displacement of the medium from its equilibrium position, which determines the wave’s intensity. The speed of a mechanical wave depends on the properties of the medium, such as its density and elasticity.
Types of Mechanical Waves
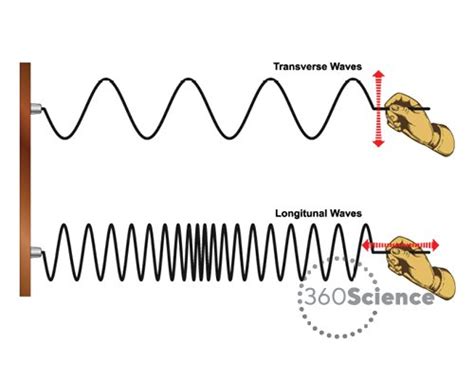
There are two primary types of mechanical waves: longitudinal and transverse waves. Longitudinal waves, also known as compressional waves, are characterized by the back-and-forth motion of the medium along the direction of propagation. Sound waves are a classic example of longitudinal waves, where the air molecules compress and expand in the direction of wave propagation. Transverse waves, on the other hand, involve the perpendicular motion of the medium relative to the direction of propagation. Water waves and light waves are examples of transverse waves, where the medium oscillates perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
| Wave Type | Characteristics | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Longitudinal Waves | Back-and-forth motion, compressional | Sound waves, seismic P-waves |
| Transverse Waves | Perpendicular motion, oscillatory | Water waves, light waves, seismic S-waves |
Examples of Mechanical Waves
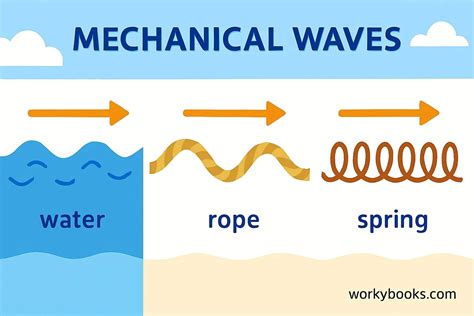
Mechanical waves are ubiquitous in our environment, and their examples can be found in various forms. Sound waves, for instance, are a type of mechanical wave that travels through the air, water, or solids. They are generated by the vibration of objects, such as guitar strings or vocal cords, and can be heard as sound. Water waves, on the other hand, are a type of transverse wave that propagates through the surface of oceans, lakes, or rivers. They are generated by wind, tides, or earthquakes and can cause significant damage to coastal areas.
Seismic Waves
Seismic waves are another example of mechanical waves that play a vital role in our understanding of the Earth’s interior. They are generated by earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or other seismic events and can travel through the Earth’s crust, mantle, or core. Seismic waves can be classified into two main types: P-waves (primary waves) and S-waves (shear waves). P-waves are longitudinal waves that travel through the Earth’s interior, while S-waves are transverse waves that travel through the Earth’s crust and mantle.
What is the difference between mechanical and electromagnetic waves?
+Mechanical waves require a physical medium to propagate, whereas electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum. Mechanical waves are also characterized by their frequency, wavelength, and amplitude, which determine their behavior and interactions.
What are some applications of mechanical waves in real-life scenarios?
+Mechanical waves have numerous applications in various fields, including sonar technology, medical imaging, seismic exploration, and non-destructive testing. Understanding mechanical waves is essential for analyzing and predicting the behavior of physical systems, from the propagation of sound waves in the atmosphere to the behavior of seismic waves during earthquakes.
How do mechanical waves interact with their surroundings?
+Mechanical waves interact with their surroundings through interference and superposition. When two or more waves overlap, they can either reinforce or cancel each other, resulting in a complex pattern of wave behavior. Understanding these interactions is crucial for analyzing and predicting the behavior of mechanical waves in various physical systems.
In conclusion, mechanical waves are a fundamental concept in physics that plays a vital role in our understanding of the physical world. From sound waves and water waves to seismic waves, mechanical waves are ubiquitous in our environment and have numerous applications in various fields. By understanding the characteristics, types, and examples of mechanical waves, we can gain insights into the behavior of physical systems and develop new technologies that exploit the properties of these waves.


