The government is a complex entity that plays a crucial role in the lives of citizens. It is responsible for creating and enforcing laws, providing public services, and ensuring the overall well-being of its people. But have you ever wondered how the government actually works? In this article, we will explore the inner workings of the government and highlight five key ways it operates. From the legislative process to the role of the executive branch, we will delve into the intricacies of government functions and provide insights into the mechanisms that drive its decision-making processes.
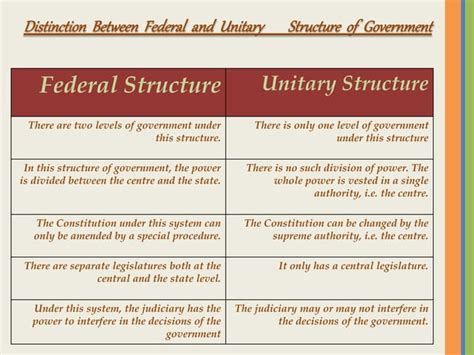
To understand how the government works, it's essential to grasp the concept of the separation of powers. This principle divides power among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, ensuring that no single entity has too much control. The legislative branch, composed of Congress, is responsible for creating laws. The executive branch, headed by the President, is tasked with enforcing laws. The judicial branch, comprising the Supreme Court and other federal courts, interprets laws and ensures they align with the Constitution. This separation of powers is a fundamental aspect of the US government, allowing for checks and balances that prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful.
Key Points
- The government operates through a system of separation of powers, dividing authority among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
- The legislative process involves the introduction, debate, and voting on bills, which can become laws if signed by the President or passed over a veto.
- The executive branch, led by the President, is responsible for enforcing laws and overseeing the administration of government programs.
- The judicial branch, comprising the Supreme Court and other federal courts, interprets laws and ensures they are consistent with the Constitution.
- The government also provides public services, such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure, which are essential for the well-being of citizens.
The Legislative Process
The legislative process is a critical component of the government’s functioning. It involves the introduction of bills, which are proposed laws, by members of Congress. These bills are then debated, amended, and voted on by both the House of Representatives and the Senate. If a bill passes both chambers, it is sent to the President, who can either sign it into law or veto it. If the President vetoes a bill, Congress can try to override the veto with a two-thirds majority vote in both the House and Senate. This process allows for the creation of new laws, which can have a significant impact on the lives of citizens.
How Bills Become Laws
The journey of a bill becoming a law is complex and involves several stages. First, a member of Congress introduces a bill, which is then referred to a committee for review. The committee may hold hearings, mark up the bill, and vote on it. If the committee approves the bill, it is sent to the full chamber for debate and voting. If the bill passes, it is sent to the other chamber, where the process is repeated. Once both chambers have passed the bill, it is sent to the President, who can sign it into law, veto it, or pocket veto it. The legislative process can be slow and contentious, but it is essential for ensuring that laws are carefully considered and reflect the will of the people.
| Stage of Legislative Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Introduction | A member of Congress introduces a bill, which is then referred to a committee. |
| Committee Review | The committee reviews the bill, holds hearings, and marks it up. |
| Chamber Vote | The full chamber debates and votes on the bill. |
| Presidential Action | The President signs the bill into law, vetoes it, or pocket vetoes it. |

The Executive Branch

The executive branch, led by the President, is responsible for enforcing laws and overseeing the administration of government programs. The President is both the head of state and the head of government, making them a powerful figure in the US political system. The President is also the commander-in-chief of the armed forces and has the power to negotiate treaties, appoint federal judges and other officials, and grant reprieves and pardons. The executive branch is composed of various departments and agencies, each responsible for a specific area of government, such as defense, education, and healthcare.
The Role of the President
The President plays a crucial role in the government, serving as both a symbol of national unity and a leader in policymaking. The President is responsible for setting the agenda for the government, working with Congress to pass laws, and overseeing the implementation of policies. The President also has significant diplomatic powers, representing the US in international relations and negotiations. The President’s role is multifaceted, requiring strong leadership, communication, and decision-making skills.
The Judicial Branch
The judicial branch, comprising the Supreme Court and other federal courts, is responsible for interpreting laws and ensuring they are consistent with the Constitution. The Supreme Court is the highest court in the land, with the final say on matters of federal law and the Constitution. The judicial branch plays a critical role in ensuring that the government does not overstep its authority and that the rights of citizens are protected. The judicial branch is also responsible for resolving disputes between states, hearing appeals from lower courts, and trying cases involving federal laws and the Constitution.
The Importance of Judicial Review
Judicial review is the process by which the Supreme Court and other federal courts review laws and government actions to ensure they are constitutional. This power allows the judicial branch to check the other branches of government, preventing them from abusing their authority. Judicial review is essential for protecting the rights of citizens and ensuring that the government operates within its constitutional limits. The judicial branch’s role in interpreting laws and the Constitution helps to maintain the rule of law and prevent tyranny.
What is the main function of the legislative branch?
+The main function of the legislative branch is to create laws. It does this by introducing, debating, and voting on bills, which can become laws if signed by the President or passed over a veto.
What is the role of the executive branch in the government?
+The executive branch, led by the President, is responsible for enforcing laws and overseeing the administration of government programs. It is also responsible for negotiating treaties, appointing federal judges and other officials, and granting reprieves and pardons.
What is the importance of judicial review in the US government?
+Judicial review is essential for protecting the rights of citizens and ensuring that the government operates within its constitutional limits. It allows the judicial branch to check the other branches of government, preventing them from abusing their authority.
In conclusion, the government works through a complex system of separation of powers, with each branch playing a critical role in the functioning of the state. The legislative process, the executive branch, and the judicial branch all work together to create, enforce, and interpret laws, ensuring that the government operates in the best interests of its citizens. By understanding how the government works, citizens can better participate in the democratic process and hold their elected officials accountable for their actions.