The extensor digitorum muscle plays a crucial role in the movement and extension of the fingers, contributing significantly to hand function and dexterity. Understanding the anatomy and physiology of this muscle, as well as its implications in various conditions and activities, is essential for both medical professionals and individuals seeking to maintain or improve hand health. Here, we will explore five key aspects related to the extensor digitorum, ranging from its anatomical structure to its role in musical performance and potential for injury.
Key Points
- The extensor digitorum muscle is crucial for finger extension, facilitating a wide range of activities from fine motor tasks to athletic endeavors.
- Anatomically, the muscle originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and inserts into the middle and distal phalanges of the fingers.
- Its function is intertwined with the extensor digitorum communis, and together they enable the complex movements of the fingers and wrist.
- Injury to the extensor digitorum, such as extensor tendonitis, can significantly impair hand function and may require a combination of rest, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgical intervention.
- The muscle's role in activities such as playing musical instruments highlights the importance of proper technique and regular exercise to prevent overuse injuries.
Anatomical Structure and Function
The extensor digitorum muscle is one of the key components of the posterior forearm, contributing to the extension of the wrist and fingers. It originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, sharing this origin with other extensor muscles of the forearm. The muscle then divides into four tendons that insert into the middle and distal phalanges of the index, middle, ring, and little fingers. This anatomical arrangement allows for the synchronized extension of these fingers, a movement essential for grasping and releasing objects.
Physiological Role in Movement
Physiologically, the extensor digitorum works in concert with other muscles and tendons of the hand and forearm to facilitate a wide range of movements. Its role in finger extension is complemented by the flexor digitorum profundus and superficialis muscles, which are responsible for finger flexion. The balance between these extensor and flexor muscles is crucial for the fine motor control necessary in activities such as writing, typing, and playing musical instruments.
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extensor Digitorum | Lateral epicondyle of humerus | Middle and distal phalanges of fingers | Extension of fingers and wrist |
| Flexor Digitorum Profundus | Ulna and interosseous membrane | Distal phalanges of fingers | Flexion of fingers |
| Flexor Digitorum Superficialis | Medial epicondyle of humerus, radius, and ulna | Middle phalanges of fingers | Flexion of fingers |
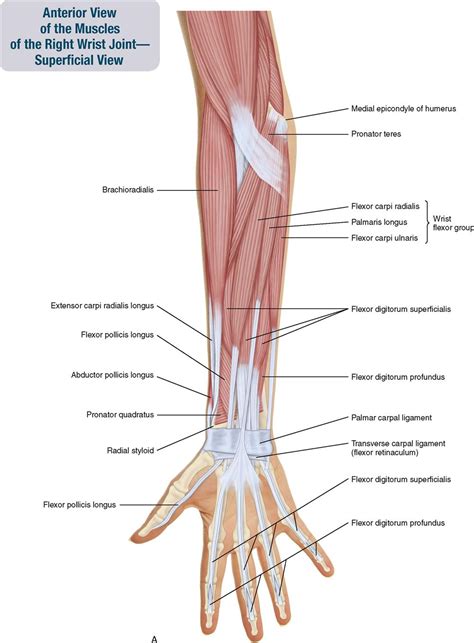
Clinical Implications and Injury Prevention
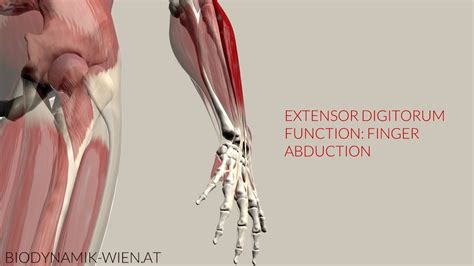
Clinically, the extensor digitorum muscle is susceptible to various injuries and conditions, including extensor tendonitis, which can result from overuse or direct trauma to the tendon. This condition is characterized by pain and swelling on the back of the hand or forearm, particularly during activities that involve gripping or extending the wrist and fingers. Prevention and treatment strategies include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), physical therapy to strengthen the muscle and improve flexibility, and in severe cases, surgical repair of the damaged tendon.
Role in Musical Performance
The extensor digitorum muscle plays a critical role in musical performance, particularly for musicians who play string or wind instruments. For violinists, for example, the extensor digitorum is essential for finger placement and movement on the fingerboard, allowing for the precise control needed to produce different notes and tones. Similarly, pianists rely on the extensor digitorum for finger extension and spreading, which is necessary for playing chords and complex melodies. The repetitive strain on this muscle can lead to overuse injuries, highlighting the importance of proper technique, regular practice, and preventive exercises to maintain hand health and prevent injury.
What are the primary functions of the extensor digitorum muscle?
+The primary functions of the extensor digitorum muscle include the extension of the fingers and wrist, facilitating actions such as grasping, releasing, and manipulating objects.
How does the extensor digitorum muscle contribute to musical performance?
+The extensor digitorum muscle is crucial for musicians, particularly those playing instruments that require precise finger movements, such as the violin or piano. It enables the extension and spreading of fingers necessary for playing complex melodies and chords.
What are the common injuries affecting the extensor digitorum muscle?
+Common injuries include extensor tendonitis, which can result from overuse or direct trauma to the tendon, leading to pain, swelling, and impaired function of the hand and fingers.
In conclusion, the extensor digitorum muscle is a vital component of the forearm and hand, contributing to the intricate movements and functions of these anatomical regions. Its role in finger extension, musical performance, and susceptibility to injury underscore the importance of understanding its anatomy, physiology, and clinical implications. By recognizing the significance of the extensor digitorum and adopting preventive strategies, individuals can maintain hand health, prevent injuries, and optimize performance in various activities.