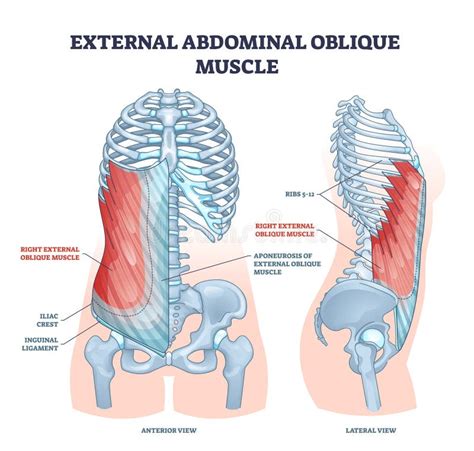
The external abdominal oblique muscle, one of the largest and most superficial muscles in the abdominal wall, plays a crucial role in movements such as rotation, lateral flexion, and compression of the abdominal contents. Its anatomy and functions are intricately linked to both the stability and mobility of the torso. Understanding the external abdominal oblique's functions and how to engage it effectively can be beneficial for athletic performance, posture, and overall core strength. Here, we'll explore five ways to target and strengthen the external abdominal oblique muscle.
Key Points
- Understanding the anatomy and primary functions of the external abdominal oblique muscle is essential for targeted strengthening exercises.
- Engaging in rotational movements, such as woodchoppers and Russian twists, can effectively target the external obliques.
- Lateral flexion exercises, like side plank and lateral bends, also engage the external abdominal obliques.
- Core stabilization exercises, including planks and bird dogs, can indirectly strengthen the external obliques by engaging the entire core musculature.
- Incorporating dynamic movements that involve twisting and bending, such as golf swings or tennis serves, can functionally strengthen the external abdominal obliques.
Anatomical and Functional Overview
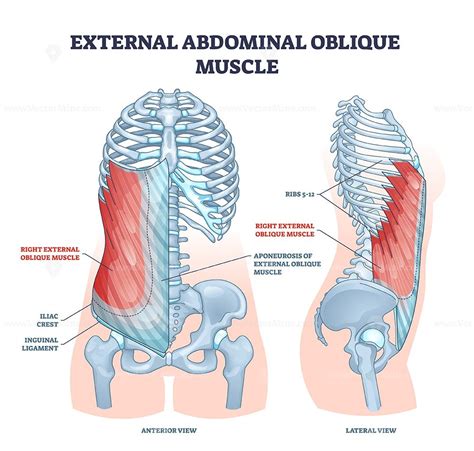
The external abdominal oblique muscle originates from the external surfaces of the lower eight ribs and inserts into the iliac crest, the linea alba (a tendinous structure that runs along the midline of the abdomen), and the pubic bone. Its primary actions include rotating the torso to the opposite side, laterally flexing the spine, and assisting in the compression of abdominal contents during actions like coughing or heavy lifting. Given its wide range of functions, strengthening the external abdominal oblique is crucial for both athletes and individuals seeking to improve their core stability and reduce the risk of lower back injuries.
1. Rotational Exercises: Woodchoppers and Russian Twists
Exercises that involve rotational movements are highly effective for targeting the external abdominal obliques. The woodchopper exercise, which can be performed with a cable machine or a medicine ball, involves rotating the torso from side to side while keeping the arms straight. This movement closely mimics the rotational action of the external obliques. Similarly, Russian twists, which can be done with or without weight, involve twisting the torso from side to side while seated on the floor with knees bent and feet flat. Both exercises require engagement of the external obliques to facilitate the rotational movement.
| Exercise | Description | Muscles Targeted |
|---|---|---|
| Woodchopper | Rotational movement with arms straight | External Abdominal Obliques, Intercostal Muscles |
| Russian Twist | Twisting movement while seated | External Abdominal Obliques, Internal Abdominal Obliques |
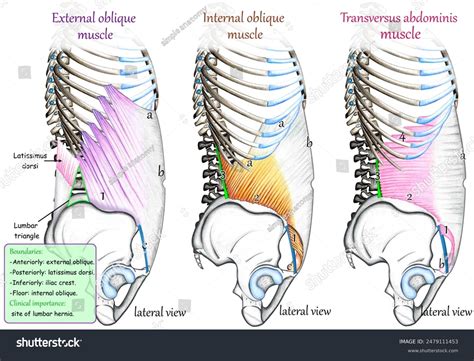
2. Lateral Flexion Exercises: Side Plank and Lateral Bends
Lateral flexion exercises, which involve bending to the side, are another effective way to engage the external abdominal obliques. The side plank, where one lies on their side with feet stacked and lifts their hips off the ground, requires the external obliques to stabilize the body and maintain proper alignment. Lateral bends, which can be performed standing or seated, involve bending to one side and then the other, targeting the external obliques as they contract to facilitate the movement.
Core Stabilization and Dynamic Movements
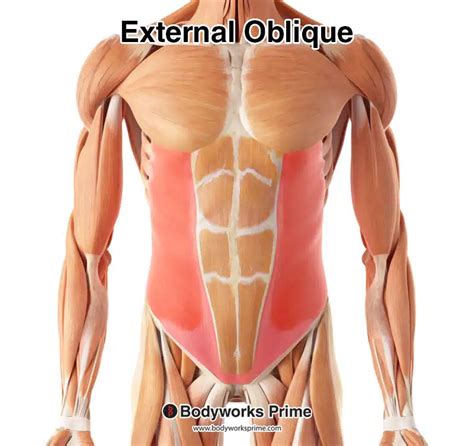
While the external abdominal obliques are directly engaged in rotational and lateral flexion movements, they also play a crucial role in core stabilization exercises. Planks, for example, require the engagement of the entire core, including the external obliques, to maintain a stable position. Dynamic movements that involve twisting, such as golf swings or tennis serves, functionally engage the external obliques as part of the overall core stabilization and movement pattern. Incorporating these exercises into a workout routine can provide a well-rounded strengthening program for the external abdominal obliques.
3. Core Stabilization Exercises: Planks and Bird Dogs
Core stabilization exercises are essential for building a strong foundation that includes the external abdominal obliques. Planks, which involve holding a position similar to a push-up but with the body straight and rigid, require the external obliques to engage and help stabilize the torso. Bird dogs, an exercise where one starts on hands and knees and lifts the right arm and left leg off the ground, holding for a moment before lowering and repeating with the opposite arm and leg, also engage the external obliques as part of the core stabilization mechanism.
4. Dynamic Movements: Golf Swings and Tennis Serves
Dynamic movements that involve rotation and twisting are excellent functional exercises for the external abdominal obliques. Golf swings and tennis serves, for example, require rapid rotational movements that engage the external obliques to generate power and speed. These movements not only strengthen the muscle but also improve coordination and overall athletic performance.
5. Incorporating Variety for Comprehensive Strengthening
To comprehensively strengthen the external abdominal obliques, it’s essential to incorporate a variety of exercises that target the muscle from different angles and through different movements. This includes a mix of rotational exercises, lateral flexion exercises, core stabilization exercises, and dynamic movements. By varying the exercises and intensity, individuals can ensure a well-rounded strengthening program that prepares the muscle for a wide range of activities and reduces the risk of injury.
What is the primary action of the external abdominal oblique muscle?
+The primary actions of the external abdominal oblique muscle include rotating the torso to the opposite side, laterally flexing the spine, and assisting in the compression of abdominal contents.
How can I effectively engage my external abdominal obliques during exercises?
+Engaging your external abdominal obliques during exercises involves focusing on rotational movements, lateral flexion, and core stabilization. Exercises like woodchoppers, Russian twists, side planks, and dynamic movements such as golf swings can effectively target these muscles.
What are the benefits of strengthening the external abdominal obliques?
+Strengthening the external abdominal obliques can improve core stability, enhance athletic performance, reduce the risk of lower back injuries, and improve overall posture and abdominal muscle definition.