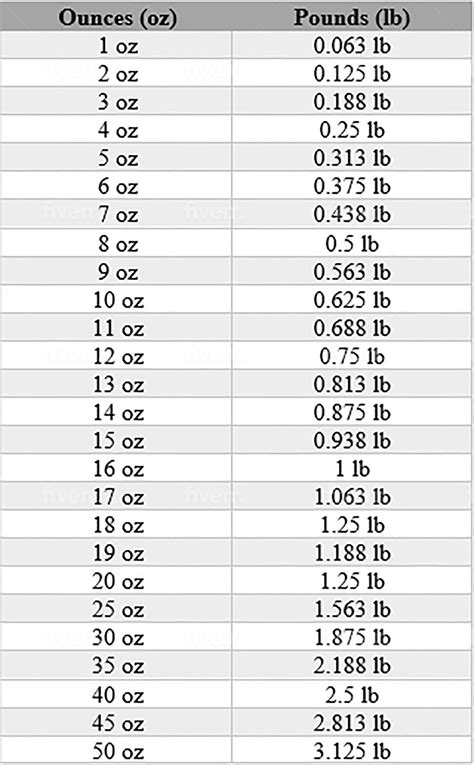
Converting fluid ounces (fl oz) to pounds (lbs) is a common task in various fields, including cooking, chemistry, and engineering. However, it's essential to understand that fluid ounces are a unit of volume, while pounds are a unit of weight or mass. To perform this conversion, we need to know the density of the substance being measured, as the same volume of different substances can have different weights.
Understanding Density and Conversion
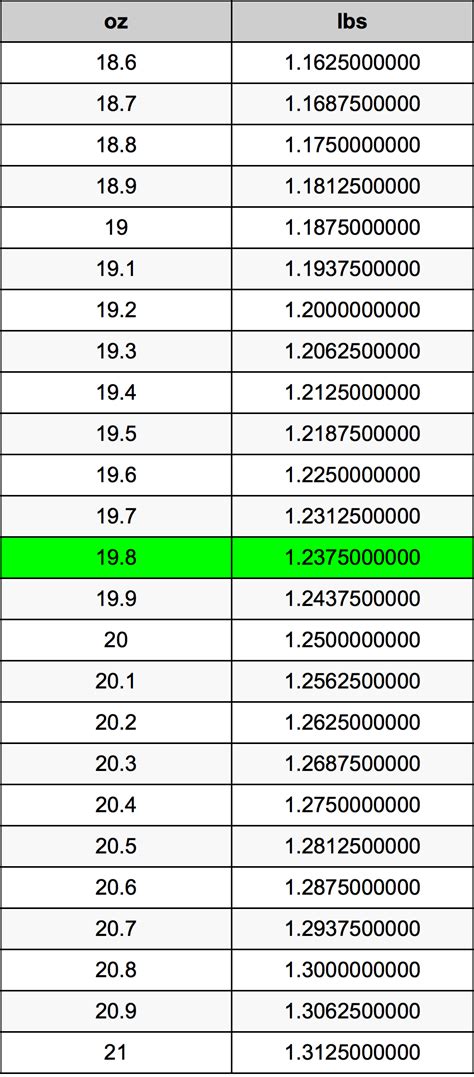
Density is defined as mass per unit volume. It’s expressed in units such as grams per milliliter (g/mL) or pounds per cubic foot (lb/ft³). The density of a substance can vary depending on its composition and the conditions it’s under, such as temperature and pressure. For example, the density of water is approximately 1 gram per milliliter (g/mL) at room temperature, which means that 1 fluid ounce of water weighs about 1 ounce (since 1 fluid ounce of water is approximately equal to 1 ounce by weight due to its density being close to 1 g/mL).
Density of Common Substances
The density of substances can vary widely. For instance, the density of alcohol is less than that of water, while the density of honey is greater. Knowing the exact density of a substance is crucial for accurate conversions from fluid ounces to pounds. The following are approximate densities for some common substances:
| Substance | Density (g/mL) |
|---|---|
| Water | 1.0 |
| Alcohol (Ethanol) | 0.79 |
| Honey | 1.36 |
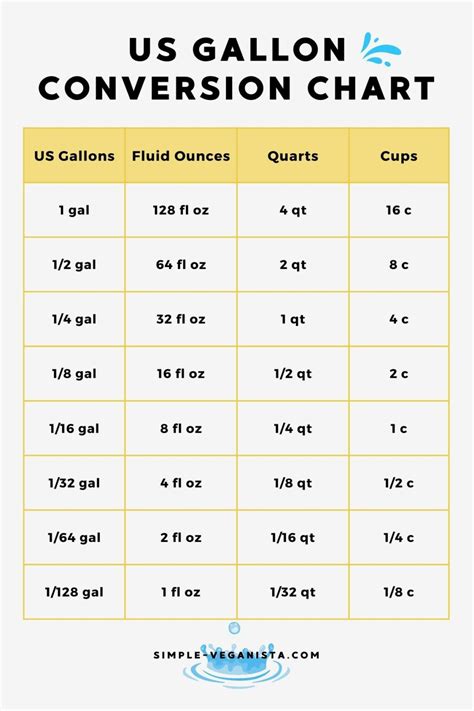
Conversion Process
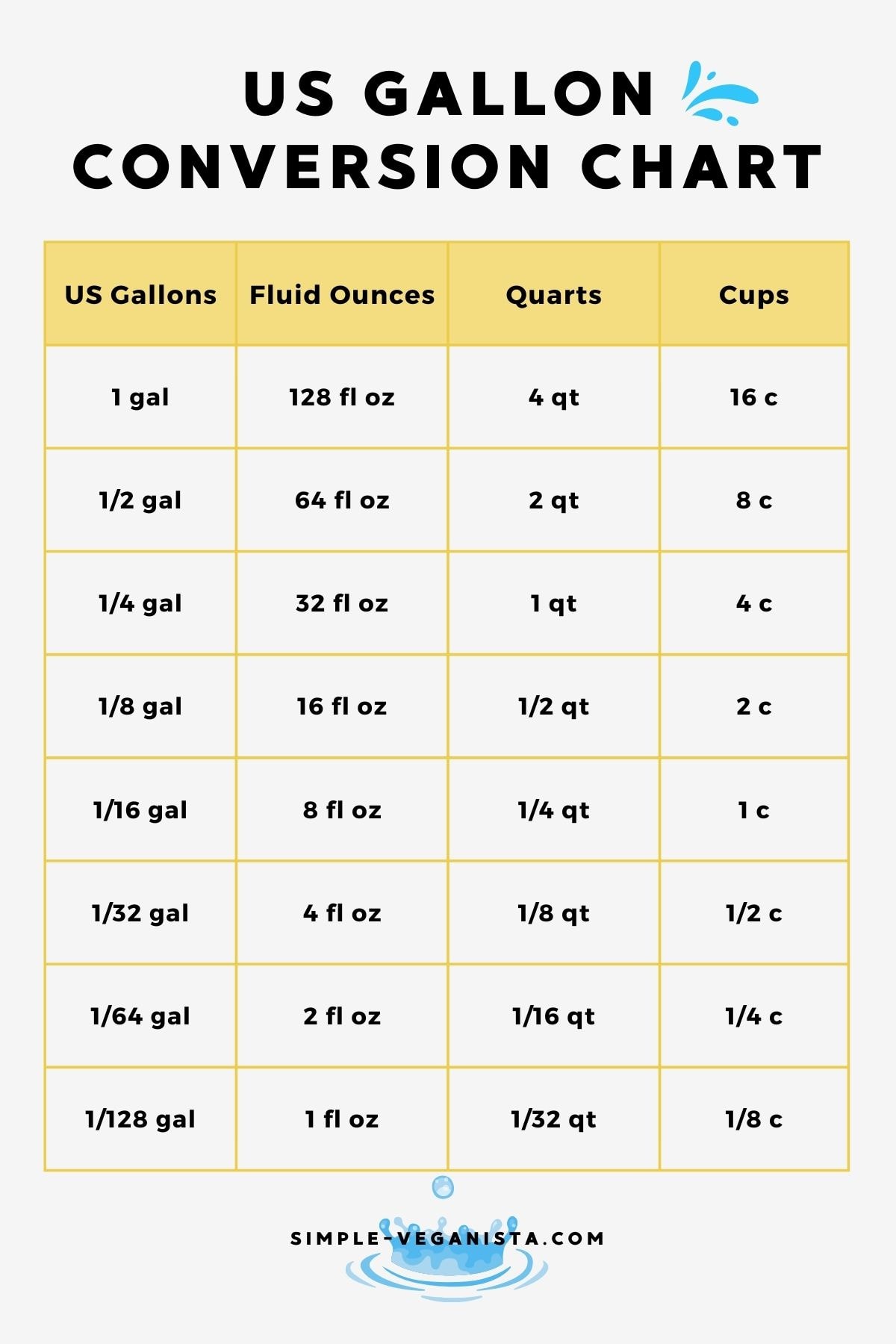
To convert fluid ounces to pounds, you can follow a simple formula once you know the density of the substance. First, convert the fluid ounces to milliliters (mL) if necessary, knowing that 1 fluid ounce is approximately equal to 29.5735 mL. Then, use the substance’s density to find the mass in grams, and finally convert grams to pounds, remembering that 1 pound is approximately equal to 453.592 grams.
Example Conversion
Let’s convert 16 fluid ounces of water to pounds, knowing the density of water is approximately 1 g/mL. First, convert fluid ounces to milliliters: 16 fl oz * 29.5735 mL/fl oz ≈ 473.18 mL. Then, calculate the mass in grams using the density: 473.18 mL * 1 g/mL ≈ 473.18 grams. Finally, convert grams to pounds: 473.18 grams / 453.592 grams/pound ≈ 1.043 pounds.
Key Points
- Fluid ounces are a unit of volume, while pounds are a unit of weight or mass.
- The conversion from fluid ounces to pounds requires knowledge of the substance's density.
- Density varies among substances and conditions, such as temperature and pressure.
- Common substances have known densities that can be used for conversions, such as water (approximately 1 g/mL) and alcohol (approximately 0.79 g/mL).
- The conversion process involves calculating the volume in milliliters, then using density to find mass in grams, and finally converting grams to pounds.
In conclusion, converting fluid ounces to pounds involves understanding the relationship between volume and mass, which is mediated by density. By knowing the density of the substance in question and following a straightforward conversion process, one can accurately determine the weight of a given volume of a substance.
What is the primary factor in converting fluid ounces to pounds?
+The primary factor is the density of the substance, as it determines how much a given volume weighs.
How do you convert fluid ounces of water to pounds?
+First, convert fluid ounces to milliliters, then use the density of water (approximately 1 g/mL) to find the mass in grams, and finally convert grams to pounds.
Why is density important in conversions between volume and weight?
+Density is crucial because it allows us to relate the volume of a substance to its mass or weight, enabling accurate conversions between different units of measurement.