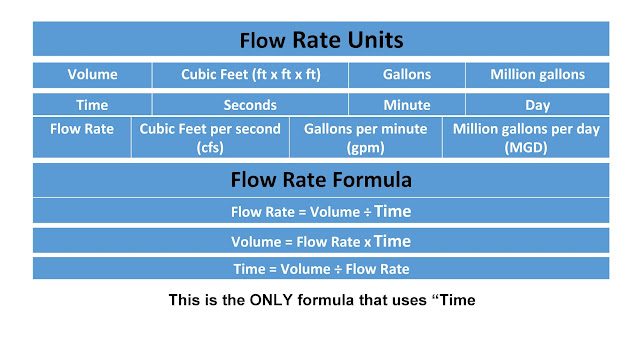
The concept of flow rate is a fundamental aspect of fluid dynamics, which is the study of the behavior of fluids in motion. In the International System of Units (SI), flow rate is typically measured in cubic meters per second (m³/s). This unit represents the volume of fluid that flows through a given cross-sectional area per unit time. Understanding flow rate in SI units is crucial in various fields, including engineering, physics, and chemistry, as it helps in designing and optimizing systems that involve fluid flow, such as pipelines, pumps, and turbines.
Flow rate can be calculated using the formula Q = A * v, where Q is the flow rate, A is the cross-sectional area of the flow, and v is the velocity of the fluid. The unit of flow rate, m³/s, is derived from the units of area (m²) and velocity (m/s). This formula highlights the direct relationship between the flow rate and both the area through which the fluid flows and its velocity. For instance, if the cross-sectional area of a pipe increases while the velocity of the fluid remains constant, the flow rate will increase proportionally.
Key Points
- The flow rate is a critical parameter in fluid dynamics, measured in cubic meters per second (m³/s) in the SI system.
- It can be calculated using the formula Q = A * v, where Q is the flow rate, A is the cross-sectional area, and v is the velocity of the fluid.
- Understanding flow rate is essential in designing and optimizing systems that involve fluid flow, such as pipelines and pumps.
- Changes in cross-sectional area or fluid velocity directly impact the flow rate, with potential applications in engineering and physics.
- Accurate measurement and calculation of flow rate are vital for ensuring the efficiency and safety of fluid-based systems.
Measurement and Calculation of Flow Rate

The measurement and calculation of flow rate are pivotal in various applications, including the design of pipelines, the operation of water supply systems, and the optimization of industrial processes. There are several methods to measure flow rate, including the use of flow meters, which can be based on different principles such as differential pressure, velocity, or positive displacement. The choice of method depends on the specific application, the properties of the fluid, and the desired accuracy of the measurement.
For example, in the oil and gas industry, accurate flow rate measurement is critical for determining the volume of fluids being transported or processed. This information is used for billing purposes, as well as for monitoring and controlling the process to ensure safety and efficiency. Similarly, in chemical engineering, flow rates are crucial in designing reactors and separations units, where the rates of chemical reactions and mass transfer processes depend on the flow rates of reactants and products.
Flow Rate Applications and Considerations
Beyond its fundamental importance in fluid dynamics, flow rate has significant implications in various practical applications. In hydraulic systems, for instance, the flow rate of fluid (often oil or water) determines the power that can be transmitted to perform work, such as lifting loads or driving machinery. In environmental engineering, flow rates are essential in designing wastewater treatment plants and in assessing the capacity of natural water bodies to absorb and process pollutants without significant degradation.
| Application | Importance of Flow Rate |
|---|---|
| Pipeline Design | Determines the required pipe diameter and material to ensure safe and efficient transport of fluids. |
| Chemical Reactors | Influences the rate of chemical reactions and the yield of products. |
| Water Supply Systems | Essential for meeting the demand for water and ensuring adequate pressure throughout the distribution network. |
| Industrial Processes | Impacts the efficiency, productivity, and safety of various industrial operations. |
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the importance of flow rate in various applications, there are challenges associated with its measurement and calculation, particularly in complex systems or under extreme conditions. Advances in technology, such as the development of more accurate and robust flow meters, are addressing some of these challenges. Additionally, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and other simulation tools are increasingly being used to model and predict flow rates in complex geometries and under various operating conditions, allowing for more precise design and optimization of fluid-based systems.
Looking forward, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning with flow rate measurement and prediction is expected to further enhance the accuracy and efficiency of fluid-based systems. This could involve real-time monitoring and adjustment of flow rates to optimize performance, minimize energy consumption, and reduce environmental impact. Furthermore, the development of new materials and technologies, such as nanofluids and microfluidics, is opening up new avenues for the application of flow rate principles in innovative and potentially groundbreaking ways.
What is the unit of flow rate in the SI system?
+The unit of flow rate in the SI system is cubic meters per second (m³/s).
How is flow rate calculated?
+Flow rate can be calculated using the formula Q = A * v, where Q is the flow rate, A is the cross-sectional area, and v is the velocity of the fluid.
Why is accurate measurement of flow rate important?
+Accurate measurement of flow rate is vital for ensuring the efficiency, safety, and environmental sustainability of fluid-based systems across various industries.