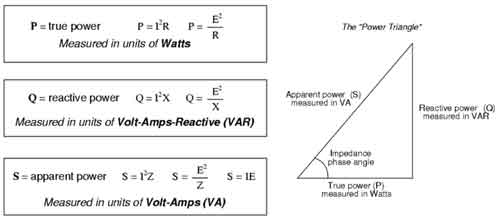
Electricity is a fundamental part of our daily lives, powering everything from the lights in our homes to the devices we use to stay connected with the world. But have you ever stopped to think about how electricity actually works? From the generation of power at a plant to the transmission lines that carry it to our homes, the process of getting electricity from one place to another is complex and fascinating. In this article, we'll explore five ways electricity works, highlighting the key concepts and technologies that make it all possible.
Key Points
- Electricity generation through various methods, including thermal, nuclear, and renewable sources
- Transmission and distribution systems that carry electricity from power plants to homes and businesses
- Transformers that step up or step down voltage to ensure efficient transmission and safe use
- Circuit breakers and fuses that protect against electrical overloads and short circuits
- Smart grid technologies that optimize energy distribution and consumption for greater efficiency and sustainability
Generation: Where Electricity Begins

The journey of electricity begins at a power plant, where energy is generated through various methods. Thermal power plants, for example, burn fossil fuels like coal or natural gas to produce steam, which drives a turbine to generate electricity. Nuclear power plants, on the other hand, use nuclear reactions to produce steam and drive turbines. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind power are also becoming increasingly important, as they offer a cleaner and more sustainable way to generate electricity. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewable energy sources accounted for 26% of global electricity generation in 2020, up from 21% in 2015.
Transmission: Getting Electricity from Point A to Point B
Once electricity is generated, it needs to be transmitted to homes and businesses through a network of high-voltage transmission lines. These lines are designed to carry large amounts of electricity over long distances with minimal loss of energy. The transmission system is typically operated at high voltages, ranging from 115 kV to 500 kV, to reduce energy losses and increase efficiency. For instance, the high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission system is used to transmit electricity over long distances with minimal energy loss.
| Transmission Voltage | Energy Loss |
|---|---|
| 115 kV | 2-3% |
| 230 kV | 1-2% |
| 500 kV | 0.5-1% |
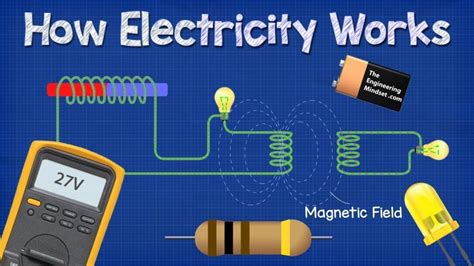
Distribution: Delivering Electricity to the End User

After transmission, electricity is distributed to homes and businesses through a network of medium-voltage distribution lines. These lines are designed to carry electricity at lower voltages, typically ranging from 12 kV to 35 kV, to reduce energy losses and increase safety. The distribution system includes transformers, circuit breakers, and fuses that work together to ensure reliable and efficient delivery of electricity. For example, circuit breakers are designed to interrupt the flow of electricity in case of an overload or short circuit, protecting the consumer from potential electrical hazards.
Transformers: Stepping Up or Stepping Down Voltage
Transformers play a critical role in the transmission and distribution of electricity. They are designed to step up or step down voltage to ensure efficient transmission and safe use. Step-up transformers are used to increase voltage for long-distance transmission, while step-down transformers are used to decrease voltage for safe distribution to homes and businesses. By understanding the principles of transformers, we can optimize the grid for greater efficiency and reliability. For instance, the transformer efficiency can be improved by using advanced materials and designs, such as the amorphous core transformer.
Smart Grid Technologies: Optimizing Energy Distribution and Consumption
The smart grid is a modernized grid system that uses advanced technologies to optimize energy distribution and consumption. It includes smart meters, smart appliances, and renewable energy sources that work together to create a more efficient and sustainable grid. Smart grid technologies enable real-time monitoring and control of energy distribution, allowing utilities to respond quickly to changes in energy demand and reduce energy waste. According to the United States Department of Energy, the smart grid can help reduce energy consumption by up to 10% and greenhouse gas emissions by up to 20%.
What is the difference between a circuit breaker and a fuse?
+A circuit breaker is a device that automatically interrupts the flow of electricity in case of an overload or short circuit, while a fuse is a device that melts and breaks the circuit in case of an overload or short circuit. Circuit breakers can be reset, while fuses need to be replaced.
How does a transformer work?
+A transformer works by using electromagnetic induction to transfer energy from one coil to another. The primary coil is connected to a power source, and the secondary coil is connected to a load. The transformer steps up or steps down the voltage, depending on the number of turns in the primary and secondary coils.
What is the benefit of using smart grid technologies?
+The benefit of using smart grid technologies is that they enable real-time monitoring and control of energy distribution, allowing utilities to respond quickly to changes in energy demand and reduce energy waste. Smart grid technologies can also help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve the overall efficiency and reliability of the grid.
In conclusion, electricity works through a complex process of generation, transmission, distribution, and consumption. By understanding the principles of electricity and the technologies that support it, we can optimize the grid for greater efficiency and reliability. As we continue to evolve and modernize the grid, it’s essential to consider the role of smart grid technologies and renewable energy sources in creating a more sustainable and efficient energy system.